Chapter 8 Upper Motor Neuron
The upper motor neuron (UMN) is the motor system that is confined to the central nervous system (CNS) and is responsible for the initiation of voluntary movement, the maintenance of muscle tone for support of the body against gravity, and the regulation of posture to provide a stable background upon which to initiate voluntary activity. Traditionally, it has been divided into pyramidal and extrapyramidal components. This separation is more significant in primates, in which the pyramidal system is more highly developed and has more important functions than have been observed in domestic animals.
PYRAMIDAL SYSTEM
The development of the pyramidal system is directly related to the capacity of an animal to perform skilled movements. In primates, its termination in the spinal cord is most dense in the areas of the lateral portion of the ventral gray column in which the cell bodies of the general somatic efferent (GSE) lower motor neuron (LMN) to muscles of the digits are located. Here, it may synapse directly on the dendritic zone of the alpha motor neuron (GSE). This anatomic arrangement occurs in primates and in the raccoon, two unrelated species that possess considerable manipulative ability in their thoracic limb digits.1 The pyramidal system is poorly developed in domestic animals, especially in the horse, ox, and sheep. In the horse, this system makes a sizable contribution to the facial nuclei, the location of the GSE-LMNs that innervate muscles for lip movement, suggesting that these muscles of prehension perform the most highly skilled activity in this species. This system also terminates in the spinal cord dorsal gray column, where it influences the activity of ascending sensory systems.
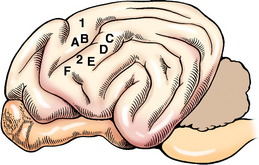
The cell body of the pyramidal system neuron is located in the cerebral cortex. The majority are located in the motor area in the frontal lobe or the adjacent parietal lobe (Fig. 8-1). In primates, this involves primarily the precruciate gyrus. In carnivores, it overlaps on the sensory area, where it is limited to the postcruciate and rostral suprasylvian gyri.12,19,39 In ungulates, the motor area is located medially along the frontal lobe in the region of the precruciate gyrus. Electrophysiologic stimulation studies have shown that these motor areas can be subdivided into the regions of the body that are innervated by LMNs receiving impulses from the pyramidal system neurons that originate in these specific parts of the motor cortex. This is referred to as a somatotopic organization, in which the various portions of the body are represented topographically on specific regions of the cerebral gyri. The homunculus drawn on the surface of the human cerebrum depicts this phenomenon. Regions involved with more highly skilled functions have a larger representation in this motor area. Muscles with small motor units also have a larger area of representation. The primary motor area of one cerebrum serves the musculature on the contralateral side of the body. In the carnivore, the postcruciate gyrus is related to the innervation of the appendicular musculature.12,17 The suprasylvian gyrus is related to the motor function of the cervical muscles and the muscles of specific areas of the head. In addition to these motor areas, there are components of the pyramidal system that have cell bodies in the premotor area, the somesthetic area, and related association areas.
Many of these pyramidal system cell bodies are large and are referred to as giant pyramidal cells or Betz cells.39 They are located in lamina V of the cerebral cortex of the gyri that comprise the motor area of the cerebral cortex. The axons of these cell bodies descend through the white matter of the brain in the following order: the corona radiata of the gyrus in the motor area, the cerebral centrum semiovale, the internal capsule of the telencephalon and diencephalon, the central portion of the crus cerebri of the mesencephalon, the longitudinal fibers of the pons, and the pyramid of the medulla. At the caudal end of the pyramid, 75% or more of these axons cross in the pyramidal decussation and pass through the gray matter to the dorsal portion of the lateral funiculus (see Figs. 2-14 and 2-15). The decussation is not visible on the ventral surface of the medulla because it occurs as the crossing fibers course dorsally into the parenchyma of the junction between the medulla and the first cervical spinal cord segment. These crossed pyramidal system axons form the lateral corticospinal tract medial to the cranial projecting spinocerebellar tracts in the dorsolateral funiculus.90 In the dog, as the lateral corticospinal tract courses caudally, about 50% of these axons terminate in the cervical spinal cord gray matter, 20% in the thoracic spinal cord gray matter, and 30% in the lumbosacral spinal cord gray matter. Most synapse on interneurons in the ventral gray column that influence the GSE-LMNs located here.53,63,68 Pyramidal system neurons that have their cell bodies in the somesthetic cerebral cortex synapse on neurons in the dorsal gray column to influence the activity of projection sensory systems. The remaining 25% or less of the pyramidal axons in the medulla continue caudally without crossing and enter the ventral funiculus adjacent to the ventral median fissure where they comprise the ventral corticospinal tract. The axons in this tract course caudally to about the level of the midthoracic spinal cord segments. Prior to terminating in the gray matter along this course, these axons cross to the opposite side. Their synapses are similar to those described for the axons of the lateral corticospinal tract. In cats, this pyramidal system serves the entire spinal cord gray matter. In ungulates, the entire pyramidal system is confined primarily to the cervical spinal cord segments.10,11
The pyramidal system axons are organized regionally in the various portions of the central white matter where they are located. In the crus cerebri, the pyramidal system comprises the projection axons in the center of this crus. The axons to the lumbosacral intumescence (pelvic limb) are lateral. Those projecting to the cervical intumescence (the thoracic limb) are in the middle, and those projecting to the brainstem nuclei (the head muscles) are medial. In the cat, the pyramid in the medulla has been mapped according to the muscle groups affected by its axons.39.94
Disturbances in the pyramidal system demonstrate the differences in the roles this system plays in primates compared with its roles in domestic animals. Lesions in the cerebral components of this system in humans cause paralysis of the contralateral voluntary muscle activity that is especially evident in the hands and feet and involves the muscles used in highly skilled functions. In dogs and cats examined a few days after experimental surgical removal of the frontoparietal lobes (motor area), no defect is seen in the gait when the animal walks on a level surface. However, these animals do have a deficiency in their responses to testing of postural reactions in the contralateral limbs. This is most readily appreciated when the hopping responses are tested. Similarly, experimental surgical sectioning of the canine pyramidal system axons in the crus cerebri does not affect the gait.47 A variety of naturally occurring cerebral lesions in this same area in all species of domestic animals present with a similar clinical syndrome of gait preservation and deficiency of contralateral postural reactions. Because these lesions usually also involve the conscious projections of the general proprioceptive and visual systems, such lesions are discussed in Chapters 9 and 14, with examples in the latter chapter.
HISTOLOGY OF THE CEREBRAL CORTEX
The cerebral cortex is made up of an elaborate organization of neural structures with innumerable connections that form the basis for the numerous functions allotted to it. They include consciousness, intellect, emotion, behavior, perception, and control of somatic and visceral motor functions. They are performed by the reciprocal relationship between the cerebral cortex and the rest of the central and peripheral nervous systems.
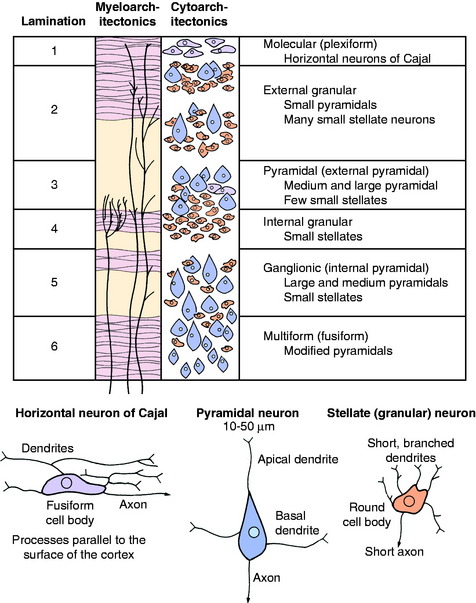
The cerebral cortex is the layer of gray matter that covers the white matter of each cerebral gyrus. This cortex varies from 1.5 to 4 mm in thickness and is situated between the pia mater on the surface and the underlying white matter, which it covers. This white matter is the corona radiata of the neocortex. The cortex contains neuronal cell bodies of many different sizes and shapes, axons, telodendria, dendritic zone processes, neuroglial cells, and an abundance of blood vessels, especially capillaries (Fig. 8-2 and 8-3). The neurons in the cortex constitute a system of chains of interrelated neurons. The cortex is a laminated structure based on the organization of the processes (myeloarchitectonics) or based on the arrangement of the cell bodies (cytoarchitectonics). When viewed according to the organization of the cell bodies, as many as six layers can be recognized (see Fig. 8-2). The extent to which each of these six laminae is developed varies throughout the cerebrum. In general, the neopallium has six layers and the archipallium (hippocampus) and paleopallium (olfactory cortex) have fewer layers. Some functional significance has been attached to the variation in the neocortical laminations in the different regions of the cerebrum. Maps have been prepared that show the laminar variations that occur throughout the cerebrum. Some include more than 100 different areas based on cytoarchitectonic studies. The cortical lamination of the archipallium and the paleopallium is different from the lamination of the neocortex, and it is different in each one. Specific characteristics of each permit their identification.
In general, the neocortical neuronal cell bodies are of two types. The stellate or granule neuron has a round cell body and short processes that are usually confined to the cortex. The pyramidal neuron has a pyramid-shaped cell body that varies in size and has long processes. The axon of the pyramidal neuron projects from the cortex into the underlying white matter of the corona radiata as an associative axon coursing to another cortical area in the same cerebrum, or as a commissural axon that crosses to a cortical area in the opposite cerebrum, or as a projection axon that projects to nuclear areas in the brainstem or spinal cord. The corticospinal neuron is an example of the last type. Each area of cerebral cortex receives axons from other cortical areas in the same cerebrum (association), from the opposite cerebrum (commissural), and from the brainstem, especially the thalamus (projection). The study of the arrangement of these processes within the cortex, including the processes of the granule neurons, is referred to as myeloarchitectonics.
In the neocortex, the six layers, from superficial to deep, consist of the molecular layer, external granule layer, pyramidal layer, internal granule layer, ganglion layer, and multiformic layer (see Fig. 8-2). The processes of the molecular and external and internal granule layers are confined to the cortex. Axons from the pyramidal, ganglionic, and multiformic layers compose the cortical efferents that form the association, commissural, and projection pathways.
EXTRAPYRAMIDAL SYSTEM
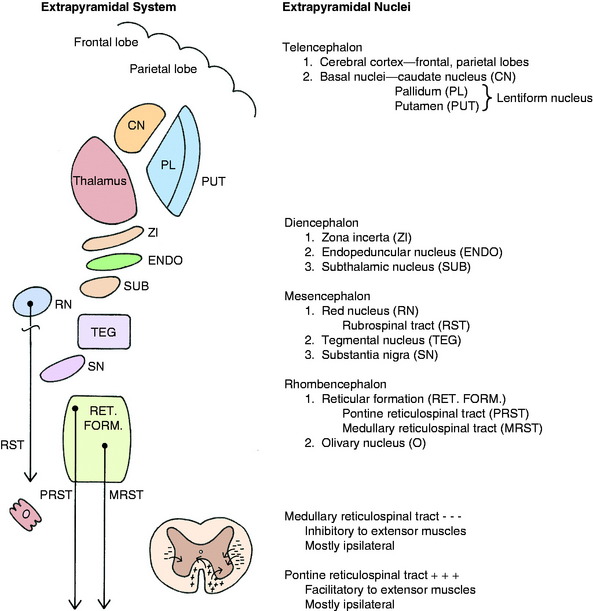
The extrapyramidal system embraces diverse, scattered groups of interconnected and functionally related structures that form a series of neurons in a multisynaptic pathway from the cerebrum to the LMN of the brainstem and spinal cord (Fig. 8-4). These pathways do not traverse the pyramids of the medulla but function with the pyramidal system by providing tonic mechanisms for the support of the body against gravity and by recruiting spinal reflexes for the initiation of voluntary movement. These functions are performed ultimately by the influence of this UMN system on the alpha and gamma motor neurons (LMN) in motor nuclei in the brainstem and in the ventral gray columns of the spinal cord.
Telencephalon
Basal Nuclei
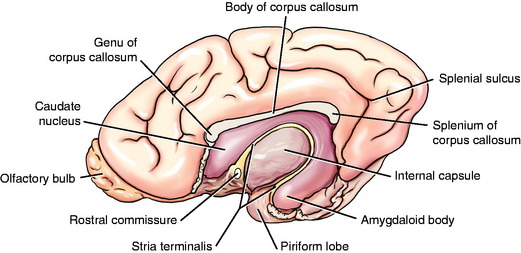
The basal nuclei are subcortical collections of neuronal cell bodies in the cerebrum. They include the septal nuclei and amygdala, which function in the limbic system. The caudate nucleus, nucleus accumbens, putamen, pallidum, and claustrum are extrapyramidal basal nuclei (Figs. 8-5 through 8-7; see also Fig. 8-4) that are generally considered to be involved with motor activity. The putamen and pallidum are referred to as the lentiform nucleus because of their collective overall shape on transverse or dorsal plane sections. The term corpus striatum includes the caudate nucleus, nucleus accumbens, pallidum, putamen, and claustrum along with the portions of the internal and external capsules of white matter that are related to these basal nuclei.
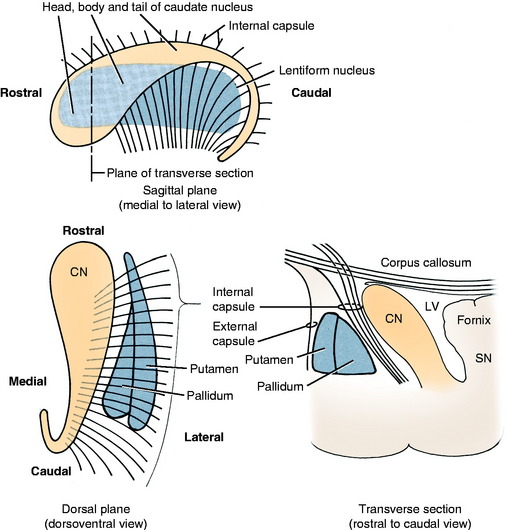
Figure 8-5 Extrapyramidal nuclei of the telencephalon. CN, Caudate nucleus; LV, lateral ventricle; PI, pallidum; SN, septal nuclei.
The caudate nucleus is located primarily in the floor of the rostral part of the lateral ventricle, medial to the internal capsule (see Fig. 2-2). The large head and most of the body are rostral to the diencephalon. The body narrows as it extends caudally, dorsolateral to the diencephalon and medial to the internal capsule (see Fig. 2-3). It is continued by a small tail that curves ventrally into the temporal lobe of the cerebrum. The tail is C-shaped as it curves around the internal capsule. Dorsally, it is medial to the internal capsule, and ventrally, it is lateral to it. The ventral portion ends just caudal to the amygdala. The caudate nucleus receives axons from extrapyramidal neurons in the cerebral cortex, and many of its axons project to the adjacent pallidum.94 Nigrostriatal projections are axons of cell bodies in the mesencephalic substantia nigra that project primarily to the caudate nucleus.88
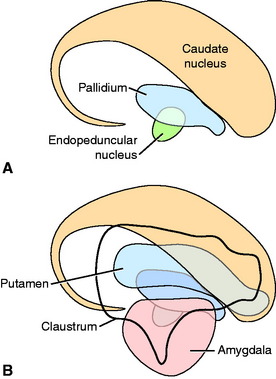
The lentiform nucleus comprises the pallidum (globus pallidus) medially and the putamen laterally. The two nuclei are separated by an irregular layer of white matter. The nucleus is bounded medially by the internal capsule and laterally by the thin external capsule (see Figs. 2-2 and 2-3). The nucleus begins rostrally in the frontal lobe, where it is separated from the head and body of the caudate nucleus by the internal capsule. It extends caudally through the parietal lobe and into the temporal lobe to a level caudal to the amygdala in the pyriform lobe, where the ventral portions of the lateral ventricle and hippocampus are located. The pallidum is medial to the putamen and is interspersed in the lateroventral portion of the rostral horn of the internal capsule, which gives it a reticulated pattern. The endopeduncular nucleus is a medioventral extension of the pallidum that is most obvious where it is positioned between the internal capsule and the optic tract (see Fig. 2-3). The putamen is the largest portion of the lentiform nucleus and is lateral to the pallidum. It blends with the internal capsule and caudate nucleus rostral to the pallidum and is separated laterally from the claustrum by the external capsule.
The claustrum forms a long thin plate lateral to the external capsule (see Fig. 2-3). It extends from the level of the head of the caudate nucleus rostrally to the level of the ventral extent of the lateral ventricle in the temporal lobe caudally. A very thin layer of white matter, the extreme capsule, separates part of this plate from the neocortex of the lateral aspect of the cerebrum. The ventral portion of the claustrum blends with the adjacent neocortex.
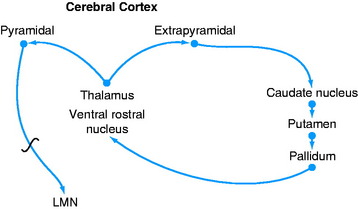
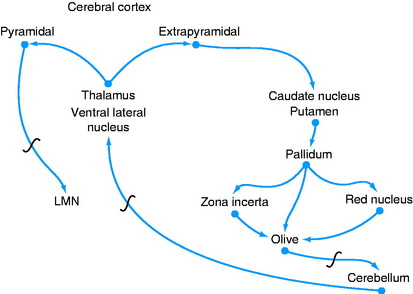
A feedback circuit is provided by a multisynaptic pathway from the neocortical extrapyramidal neurons to the caudate nucleus, to the pallidum, to the ventral rostral nucleus of the thalamus, to the neocortex (Fig. 8-8). At the time of cortical initiation of voluntary movement, such a circuit provides a modifying control mechanism. Certain specific thalamic nuclei serve to project information from the brainstem to the cerebrum. The ventral rostral thalamic nucleus is an example of such a projection nucleus for the extrapyramidal system.
Diencephalon
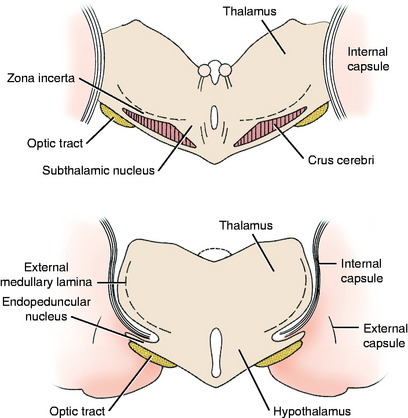
The extrapyramidal nuclei are located in the ventrolateral section of the thalamus, which is referred to as the subthalamus (Fig. 8-9). The endopeduncular nucleus was described with the pallidum, from which it is a medial extension between the optic tract and the internal capsule. It extends caudally, lateral to the hypothalamus (see Fig. 2-3). The zona incerta is a narrow nucleus located dorsomedial to the ventral thalamic portion of the internal capsule and lateral to the external medullary lamina of the thalamus. It extends through most of the subthalamic section (see Fig. 2-4). The subthalamic nucleus is in the caudal thalamus, caudal to the endopeduncular nucleus on the dorsomedial surface of the crus cerebri (see Fig. 2-4). All three of these nuclei are connected to the extrapyramidal nuclei in the telencephalon and caudal brainstem by afferent and efferent axons, but no axons project directly to the spinal cord.
Mesencephalon
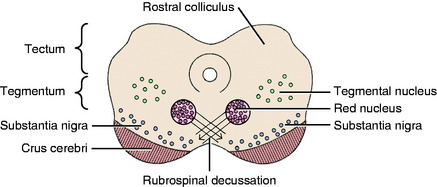
There are two well-defined extrapyramidal nuclear areas in the midbrain: the substantia nigra and the red nucleus (Fig. 8-10). The substantia nigra is so named because its cell bodies contain a melanin pigment that increases with age and is macroscopic in some species.55 This nucleus can be found throughout the length of the mesencephalon dorsal to the crus cerebri and ventral to the tegmentum (see Fig 2-5 through 2-7). It is bounded rostrally by the subthalamic nucleus. Many of the substantia nigra neurons project rostrally to the caudate nucleus. Dopamine, which is synthesized by the substantia nigra neurons, is secreted as the neurotransmitter at this level. This is referred to as the nigrostriatal system.86
The red nucleus is a well-defined round nucleus in the tegmentum at the level of the rostral colliculi and ventrolateral to the oculomotor nucleus (see Figs. 2-6 and 2-7). It receives a group of afferent axons from the ipsilateral motor area of the neocortex by way of the internal capsule and crus cerebri. Axons of the cell bodies in the red nucleus immediately decussate at the level of this nucleus in the tegmentum and course caudally as the rubrospinal tract. This tract courses from the ventrolateral mesencephalon through the pons and medulla into the lateral funiculus of the spinal cord (see Fig. 2-17). Here the tract is closely associated with the lateral corticospinal tract deep to the superficially positioned cranially projecting spinocerebellar tracts in the dorsal portion of the lateral funiculus. The rubrospinal tract extends through the entire spinal cord. Its axons terminate on interneurons in the ventral gray column of the spinal cord. These interneurons, in turn, influence the activity of the GSE alpha and gamma LMNs. This corticorubrospinal tract is organized somatotopically.72,74 The neurons in the thoracic limb area of the motor cortex project to the dorsal part of the red nucleus. The neurons in this dorsal part of the red nucleus project to the ventral gray column of the spinal cord segments that innervate the contralateral thoracic limb muscles. Corticorubral neurons from the pelvic limb region of the motor cortex synapse in the ventral part of the red nucleus, whose neurons project to the ventral gray column of the spinal cord segments that innervate the contralateral pelvic limb muscles.46 The red nucleus neurons are predominantly facilitory to motor neurons of flexor muscles and therefore function in the initiation of protraction of the limbs in gait generation.48
The red nucleus also participates in a feedback circuit between the neocortex and the cerebellum (see Fig. 13-20). A significant number of neurons in the neocortex project their axons to the ipsilateral pontine nucleus. The axons of these pontine cell bodies cross in the transverse fibers of the pons to enter the cerebellum via the contralateral middle cerebellar peduncle. Synapses occur in the cerebellar cortex; they are described in Chapter 13, which discusses the cerebellum. Ultimately, the neural impulses from the cerebellar cortex activate a cerebellar nucleus whose axons emerge from the cerebellum in the rostral cerebellar peduncle. These axons cross in the tegmentum of the midbrain, and some of them terminate on neuronal cell bodies in the contralateral red nucleus. The axons of these neurons course to the thalamus and synapse in the ventral rostral nucleus, whose axons project to the neocortex. This is a cerebropontocerebellar-cerebellorubrothalamocortical circuit that begins and ends in the same area of neocortex. There are also connections from the red nucleus to telencephalic basal nuclei.
Reticular Formation
Before describing the components of the extrapyramidal system in the rhombencephalon, it is necessary to define the reticular formation. The reticular formation is a collection of neuronal cell bodies of various sizes and a plethora of processes that form an ill-defined meshwork in the central core of the brainstem. It extends from the medulla to the caudal diencephalon. Many functions are attributed to the reticular formation. One major function is the role it plays in activating the cerebral cortex to establish the awake state and the level of consciousness. This is referred to as the ascending reticular activating system and is described in Chapter 19, which concerns the diencephalon. The reticular formation is also involved in the various neural connections that induce sleep. Several groups of reticular formation neurons make up the brainstem centers that are involved in the caudally projecting UMN control of respiration, cardiovascular function, voluntary excretions, swallowing, vomiting, and muscle tone and voluntary movement. The extrapyramidal system is involved in this caudally projecting pathway that influences the GSE- and GVE-LMNs involved in voluntary and involuntary motor activity.62
Rhombencephalon
A pontine and a medullary nucleus are components of the reticular formation that have a major role in the UMN extrapyramidal control of weight support and the generation of gait. Studies in the cat have defined an area of the reticular formation in the pons that exerts a facilitory influence on spinal cord GSE neurons that innervate extensor muscles by way of a reticulospinal tract (see Figs. 2-9 and 2-10).68,69 This pontine reticulospinal tract courses mostly in the ipsilateral ventral funiculus. Similarly, an area of the medullary reticular formation has an inhibitory influence on spinal cord GSE neurons that innervate extensor muscles by way of a medullary reticulospinal tract that courses primarily in the central portion of the ipsilateral lateral funiculus (see fig 2-11 through 2-15). These pontine and medullary reticular formation nuclei are activated predominantly by corticoreticular pathways from the contralateral cerebral hemisphere. These corticoreticular axons cross the midline of the brainstem at the level of the reticular formation nuclei. Most of the axons of the cell bodies in these pontine and medullary reticular formation nuclei make up the pontine reticulospinal tract and the medullary reticulospinal tract that course caudally in the ipsilateral ventral and lateral funiculi, respectively. Thus, this pathway permits one cerebral hemisphere to control predominantly the motor activity in the opposite side of the body. This contralateral influence is observed in both the motor and the sensory systems.
The olivary nucleus is considered an extrapyramidal nucleus in the medulla. It is located ventrally in the medulla from a level caudal to the facial nucleus to a level caudal to the obex and rostral to the pyramidal decussation. It is dorsolateral to the pyramids and medial lemniscus and medial to the hypoglossal axons that are coursing ventrolaterally (see Figs. 2-14 and 2-15). It is composed of three nuclear groups that at some levels have the appearance of fingers directed ventrolaterally. This extrapyramidal nucleus receives afferent axons from many of the extrapyramidal nuclei in the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon. Its efferent axons project primarily to the contralateral portion of the cerebellum. These axons leave the olivary nucleus and immediately cross the midline dorsal to the pyramids, intermingle with the axons in the medial lemniscus, and continue rostrally in a dorsolateral position to enter the caudal cerebellar peduncle, where they are distributed to the cerebellum. This is a major source of extrapyramidal system projection to the cerebellum. An extrapyramidal system feedback circuit also exists between the cerebrum and the cerebellum via this olivary nucleus (Fig. 8-11; see also Fig. 13-20).
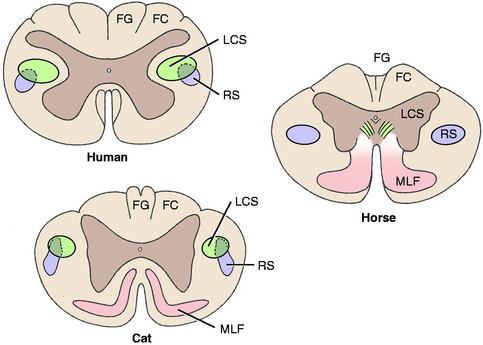
A comparison of the development of the UMN tracts in the human, cat, and horse craniocervical spinal cords reveals the decrease in importance of the pyramidal system (corticospinal tract) and the increase in the contribution of the extrapyramidal system (rubrospinal tract) in the domestic animal (Fig. 8-12).
UPPER MOTOR NEURON FUNCTION
Neuromuscular Spindles
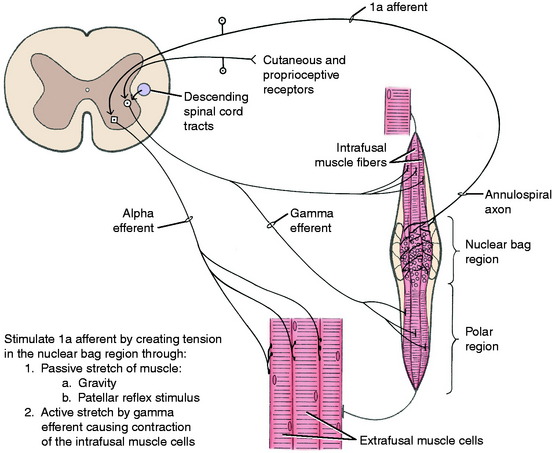
Neuromuscular spindles have a significant role in the function of the UMN. This system carries out its function by influencing the activity of the alpha and gamma motor neurons in the ventral gray columns of the spinal cord. The activity of the neuromuscular spindles in modulating muscle tone involves their control over the stretch reflexes in which the neuromuscular spindles play a major role as a sensory organ. These spindle organs are located in the belly of skeletal muscle (Fig. 8-13). They are spindle-shaped structures composed of intrafusal fibers that are very small, modified striated muscle cells. They are positioned in parallel with the large extrafusal muscle cells in which the spindles are located. A connective tissue capsule encloses the small group of intrafusal fibers and is attached to the endomysium of the adjacent extrafusal fibers. Within the spindle, there are two types of intrafusal fibers. The nuclear bag fiber is interrupted near its middle by a nonstriated dilation containing most of the cell’s nuclei. The nuclear chain fiber has no central dilation, although most of its nuclei are accumulated near the middle of the fiber. These features create for the spindle a central distended nuclear region augmented by a lymph space that envelops the middle portion of the intrafusal fibers. The poles of the spindle are tapered and contain the contractile striated portion of the intrafusal fibers.
The intrafusal fibers are innervated in the polar regions by small myelinated neurons whose cell bodies are in the ventral gray column of the spinal cord intermingled with the larger GSE neurons. These small neurons are called gamma efferent neurons; the larger GSE neurons are referred to as alpha efferent neurons. The gamma efferent neurons are further divided into plate and trail gamma efferent neurons.
Gait Generation
The extrapyramidal system brainstem nuclei caudal to the diencephalon are considered to be the most important UMN systems necessary for gait generation (Fig. 8-14). The postural phase of the gait is dependent on the activation of antigravity extensor muscles and the inhibition of the flexor muscles. This is the responsibility of the pontine reticular formation nuclei and pontine reticulospinal tracts. The vestibulospinal tract also contributes to this function. The initiation of protraction requires the activation of flexor muscles and the inhibition of extensor muscles to elevate the limb from the ground. This is a function of the medullary reticular formation nuclei and their medullary reticulospinal tracts and of the red nuclei and the rubrospinal tracts. As the protraction phase is completed, the activation of these systems shifts back to the activation of extensors muscles and inhibition of flexor muscles. Further support for the role of the UMN system in locomotion is provided by observation of the results of experimental or natural lesions.
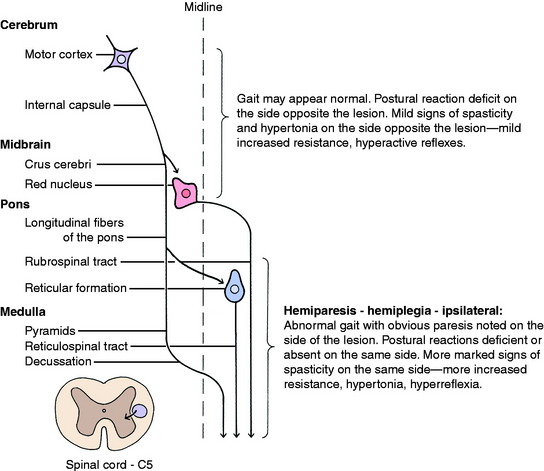
Experimental lesions that selectively destroy the motor cortex, the lentiform nucleus, or the caudate nucleus do not affect gait generation. Experimental or natural lesions that destroy the frontoparietal cortex or the adjacent portion of the internal capsule do not interfere with gait generation, but the postural reactions are deficient in the contralateral (opposite-side) limbs. However, the components of the UMN system affected here are mixed with components of the conscious portion of the general proprioceptive (GP) system, which are also necessary for postural reactions to be normal. We consider that cerebral lesions do not interfere with gait generation but do result in delayed hopping responses in the contralateral limbs as a result of the loss of function of both the UMN and the conscious GP systems located there. This should not be referred to solely as a hemiparesis because the GP system is also involved in the lesion. Case examples are described after the discussion of the GP sensory system in Chapter 9. The only exception to this is that with acute, especially traumatic, cerebral lesions, mild contralateral hemiparesis and loss of general proprioception may be observed in the gait for 2 to 3 days following the onset of the lesion. After that, the gait will be normal, but the contralateral postural reactions will be deficient.
Inquisitive students always ask: Where do unilateral lesions shift from affecting primarily the contralateral limbs to affecting the ipsilateral limbs? We do not know the exact level but believe that it is close to the caudal midbrain. Unilateral prosencephalic UMN lesions cause no loss of gait generation but do cause deficient postural reactions in the contralateral limbs. UMN lesions in the brainstem caudal to the midbrain cause gait deficit, ipsilateral hemiparesis, and postural reaction deficits in those limbs. A severe unilateral caudal medullary UMN lesion may cause ipsilateral hemiplegia. An infarct in one side of the cervical spinal cord cranial to the C5 segment caused by fibrocartilaginous emboli will cause complete UMN paralysis—spastic hemiplegia of the ipsilateral limbs. Case examples are presented in Chapter 10, Small Animal Spinal Cord Disease.