41 UMN
Intervertebral disc disease
INTRODUCTION
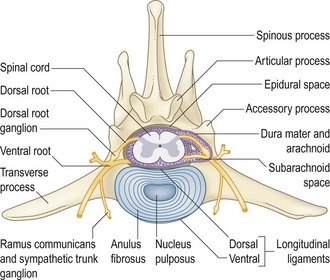
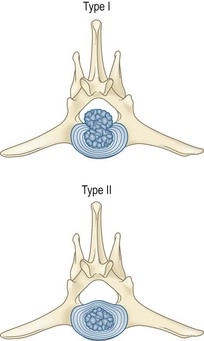
The anulus fibrosis of the intervertebral disc may rupture or bulge, and compress the adjacent spinal cord, nerve root, or both. Normal activity is sufficient to precipitate IVDD in a degenerate disc (Figs 41.1 and 41.2 and see Table 41.1).
Table 41.1 The nature of the anulus pathology has been categorized as type I or type II
| Type I | Type II | |
|---|---|---|
| Pathology | Tear, rupture | Bulge, prolapse |
| Breed |
Signs may occur suddenly or gradually. They can resolve with time and rest, or progressively worsen. Pain is a common sign, occurring in 60–70% of affected dogs (Table 41.2).
Table 41.2 Signs of disc disease
| Cervical | Thoracolumbar | |
|---|---|---|
| Location | All, except C1–2 | Caudal to T9–10 |
| Common presentation | ||
| Pain perception | Intact | May be absent |
| Respiration | ± Hypoventilation | Unaffected |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree