U
U chemical symbol, uranium; unit; uracil.
U-suture interrupted horizontal mattress suture.
UAA ochre codon, one of the three stop codons.
UAG amber codon, one of the three stop codons.
uakari (Cacajao spp.) small, bald-faced New World monkey with a short, stumpy tail.
Uberreiter’s syndrome see chronic superficial keratitis.
ubiquinol [u″b –kw
–kw –nol’] the form of ubiquinone when reduced by two electrons.
–nol’] the form of ubiquinone when reduced by two electrons.
UD Utility Dog; the third level title, after CD and CDX, awarded in obedience trial competition.
u. abscesses these form at the base of the teat and are usually associated with summer mastitis.
u. acne see udder impetigo (below).
u. amputation done in cows with severe mastitis or rupture of the suspensory apparatus (below).
u. dermatitis see intertrigo; flexural seborrhea, ulcerative mammary dermatitis.
u. development failure congenital defect of no mammary development in a female
u. infusion tube see teat tube.
u.-thigh dermatitis see flexural seborrhea, ulcerative mammary dermatitis.
u. washing see teat sanitization.
UDP-G-pyrophosphorylase an enzyme that synthesizes uridine diphosphoglucose as part of glycogenesis.
UDX Utility Dog Excellent; the highest level title earned in obedience trial competition.
UFAW Universities Federation for Animal Welfare.
UGA opal codon, one of the three stop codons.
Uhl’s anomaly [yōōl] congenital hypoplasia of the myocardium of the right ventricle.
Boxer u. see refractory ulcer (below).
decubitus u. see decubital ulcer.
eosinophilic u. see eosinophilic ulcer.
geographic u. a superficial, irregularly shaped corneal ulcer.
indolent u. see eosinophilic ulcer, refractory ulcer (below).
lip u. see eosinophilic ulcer.
lip and leg u. see ulcerative dermatosis.
melting u. see collagenase ulcer (above).
necrotic u. of swine see ulcerative granuloma of swine.
u. of pars esophagea of swine see gastric ulcer of swine.
phagedenic u. a necrotizing lesion in which tissue destruction is prominent.
rodent u. see eosinophilic ulcer
stromal u. a corneal ulcer involving the stroma.
ulcerate [ul’s r-āt] to undergo ulceration.
r-āt] to undergo ulceration.
ulceration [ul″s r-a’sh
r-a’sh n] 1. formation or development of an ulcer. 2. an ulcer.
n] 1. formation or development of an ulcer. 2. an ulcer.
ulcerative [ul’s –ra″tiv, ul’s
–ra″tiv, ul’s r–
r–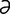 –tiv] pertaining to or characterized by ulceration.
–tiv] pertaining to or characterized by ulceration.
u. balanitis see enzootic balanoposthitis.
u. cellulitis see ulcerative lymphangitis.
u. colitis see eosinophilic ulcerative colitis, histiocytic ulcerative colitis.
u. enteritis see ulcerative enteritis.
u. gingivitis see necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis.
u. keratitis see corneal ulcer.
u. lymphangitis see ulcerative lymphangitis.
u. mammillitis see bovine herpes mammillitis.
u. pododermatosis see ulcerative pododermatitis.
u. posthitis occurs sporadically in rams and bulls and as part of ulcerative dermatosis in rams.
u. shell disease see shell rot.
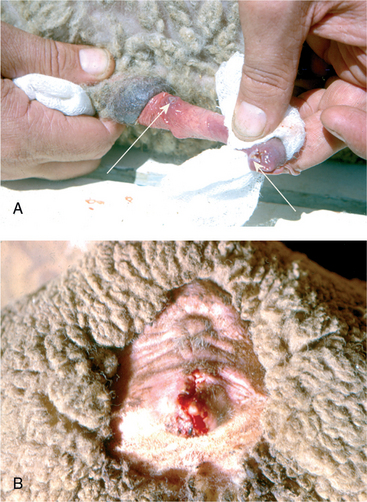
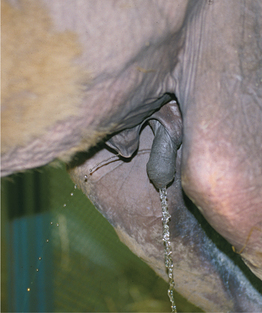
U-2: (A) Ulcerative dermatosis of the penis in a ram. (B) Ulcerative dermatosis on the vulva of a ewe
u. vulvitis of ewes, see ulcerative dermatosis (above).
ulcerogangrenous [ul″s r-o-gang’r
r-o-gang’r –n
–n s] characterized by both ulceration and gangrene.
s] characterized by both ulceration and gangrene.
ulcerogenic [ul″s r-o-jen’ik] causing ulceration; leading to the production of ulcers.
r-o-jen’ik] causing ulceration; leading to the production of ulcers.
ulcerous [ul’s r–
r– s] 1. of the nature of an ulcer. 2. affected with ulceration.
s] 1. of the nature of an ulcer. 2. affected with ulceration.
ulcus [ul’k s] pl. ulcera [L.] ulcer.
s] pl. ulcera [L.] ulcer.
ulectomy [u-lek’t –me] 1. excision of scar tissue. 2. excision of the gingiva; gingivectomy.
–me] 1. excision of scar tissue. 2. excision of the gingiva; gingivectomy.
ulitis inflammation of the gums.
ulna [ul’n ] together with the radius, forms the skeleton of the forearm. See Table 10.
] together with the radius, forms the skeleton of the forearm. See Table 10.
ulnad [ul’nad] toward the ulna.
cutaneous u. vein in birds, a venipuncture site.
u. nerve block see ulnar block.
u. nerve injury results in extension of the carpus, a ‘dropped’ carpus.
ulnaris [ l-na’ris] [L.] ulnar.
l-na’ris] [L.] ulnar.
ulnocarpal [ul″no-kahr’p l] pertaining to the ulna and carpus.
l] pertaining to the ulna and carpus.
ulnoradial [ul″no-ra’de– l] pertaining to the ulna and radius.
l] pertaining to the ulna and radius.
ulocace ulceration of the gums.
uloglossitis inflammation of the gums and tongue; gingivoglossitis.
ulorrhagia a sudden discharge of blood from the gums.
ulotomy [u-lot’ –me] 1. incision of scar tissue. 2. incision of the gums.
–me] 1. incision of scar tissue. 2. incision of the gums.
u. duct cysts derived from remnants of the ultimobranchial body and found in the thyroid gland.
u. tumor a neoplasm containing thyroid C cells.
ultra- word element. [L.] beyond, excess.
ultracentrifuge [ul″tr –sen’tr
–sen’tr –fūj] the centrifuge used in ultracentrifugation.
–fūj] the centrifuge used in ultracentrifugation.
ultrafilter [ul″tr –fil’t
–fil’t r] the filter used in ultrafiltration.
r] the filter used in ultrafiltration.
ultraheat heating to a very high temperature for a very brief period.
u. treated milk milk heated at 175–200°F (79–93°C) for a few seconds.
ultramicroscopic [ul″tr –mi″kro-skop’ik] too small to be seen with the ordinary light microscope.
–mi″kro-skop’ik] too small to be seen with the ordinary light microscope.
u. heating the use of ultrasound for producing localized hyperthermia.
u. pregnancy diagnosis see ultrasonography.
u. tooth scaling the use of vibrations to remove supragingival calculus. See also ultrasonic scaler.
ultrasonogram [ul″tr –son’o-gram] the record obtained by ultrasonography.
–son’o-gram] the record obtained by ultrasonography.
Doppler u. see Doppler ultrasound.
ultrastructure [ul’tr –struk″ch
–struk″ch r] the structure visible under the electron microscope.
r] the structure visible under the electron microscope.
umbilical [ m-bil’
m-bil’ –k
–k l] pertaining to the umbilicus.
l] pertaining to the umbilicus.
u. abscess see urachal abscess.
u. cord inflammation see omphalitis, funisitis.
u. gas gangrene umbilicus infected with Clostridium septicum, C. oedematiens.
u. inflammation see omphalitis.
u. vein infection see omphalophlebitis.
u. vein abscess residual after subsidence of acute omphalophlebitis.
umbilicated [ m-bil’
m-bil’ –kāt″
–kāt″ d] marked by depressed spots resembling the umbilicus.
d] marked by depressed spots resembling the umbilicus.
Umbilicus rupestris Cotyledon umbilicus.
umbo [um’bo] pl. umbones [L.] a round projection.
umbrella tree Jatropha multifida, Schefflera actinophylla.
UMP uridine 5’-monophosphate, a pyrimidine nucleotide.
UMP synthase deficiency see DUMPS.
unciform [un’s –form] hooked or shaped like a hook.
–form] hooked or shaped like a hook.
Uncinaria a genus of canine hookworms in the order Strongylida, suborder Ancylostomatoidea.
U. criniformis occurs in the badger and fox.
U. hamiltoni, U. lucasi found in the fur seal.
U. stenocephala the common species in the dog, cat and fox.
U. yukonensis found in all ursids.
uncinate [un’s –nāt] 1. unciform. 2. relating to or affecting the uncinate gyrus.
–nāt] 1. unciform. 2. relating to or affecting the uncinate gyrus.
uncipressure [un’s –presh″
–presh″ r] pressure with a hook to stop hemorrhage.
r] pressure with a hook to stop hemorrhage.
unclassified viruses a diminishingly small number of viruses remain unclassified.
uncovertebral [ung″ko-ver’t –br
–br l] pertaining to the uncinate processes of a vertebra.
l] pertaining to the uncinate processes of a vertebra.
unction [ungk’sh n] 1. an ointment. 2. application of an ointment or salve; inunction.
n] 1. an ointment. 2. application of an ointment or salve; inunction.
unctuous [ungk’choo– s] greasy or oily.
s] greasy or oily.
uncus [ung’k s] the medially curved anterior part of the hippocampal gyrus.
s] the medially curved anterior part of the hippocampal gyrus.
undecylenate see undecylenic acid.
underfeeding see malnutrition, starvation.
underflue the soft, fluffy part of a feather, next to the skin. Called also flue.
undernutrition [un″d r-noo-trish’
r-noo-trish’ n] see malnutrition, starvation.
n] see malnutrition, starvation.
undersized see dwarfism, runt.
undescended testis see cryptorchidism.
u. chronic pneumonia see enzootic pneumonia.
undulant fever [un’dy –l
–l nt] brucellosis of humans.
nt] brucellosis of humans.
undulation [un″dy –la’sh
–la’sh n] a wavelike motion in any medium; a vibration.
n] a wavelike motion in any medium; a vibration.
unethical said of conduct not conforming with professional ethics.
unfavorable therapeutic response see adverse response.
ung. [L.] unguentum (ointment).
unguent [ung’gw nt] an ointment.
nt] an ointment.
unguentum [ ng-gwen’t
ng-gwen’t m] pl. unguenta [L.] ointment.
m] pl. unguenta [L.] ointment.
unguiculate [ ng-gwik’u-lāt] having claws; clawlike.
ng-gwik’u-lāt] having claws; clawlike.
unguilysis necrosis and dissolution of the claw or hoof as in equine canker.
unguinal pertaining to a nail.
unguis [ung’gwis] pl. ungues [L.] a nail. See also claw, nail.
uniaxial [u″ne-ak’se– l] 1. having only one axis. 2. developed in an axial direction only.
l] 1. having only one axis. 2. developed in an axial direction only.
unicameral [u″n –kam’
–kam’ r–
r– l] having only one cavity or compartment, e.g. unicameral cyst.
l] having only one cavity or compartment, e.g. unicameral cyst.
unicellular [u″n –sel’u-l
–sel’u-l r] made up of a single cell, as the bacteria or protozoa.
r] made up of a single cell, as the bacteria or protozoa.
uniform basic data set see minimum data set.
uniglandular [u″n –glan’du-l
–glan’du-l r] affecting only one gland.
r] affecting only one gland.
unigravida [u″n –grav’
–grav’ –d
–d ] a female pregnant for the first time; primigravida; gravida I.
] a female pregnant for the first time; primigravida; gravida I.
unilocular [u″n –lok’u-l
–lok’u-l r] having only one loculus or compartment; monolocular.
r] having only one loculus or compartment; monolocular.
uninucleated [u″n –noo’kle-āt″
–noo’kle-āt″ d] mononuclear.
d] mononuclear.
uniocular [u″ne-ok’u-l r] monocular.
r] monocular.
uniovular [u″ne-ov’u-l r] monovular, monozygotic.
r] monovular, monozygotic.
uniparous [u-nip’ –r
–r s] 1. producing only one ovum or offspring at a time. 2. primiparous.
s] 1. producing only one ovum or offspring at a time. 2. primiparous.
unipolar [u″n –po’l
–po’l r] having a single pole or process, as a nerve cell.
r] having a single pole or process, as a nerve cell.
SI u. any unit of the International System of units (the metric system). See SI units.
unitary [u’n –tar″e] pertaining to a single object or individual.
–tar″e] pertaining to a single object or individual.
unitocous giving birth to a single young at one time.
univalent [u″n –va’l
–va’l nt] having a valence of one.
nt] having a valence of one.
unmyelinated [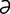 n-mi’
n-mi’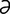 –l
–l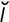 –nāt″
–nāt″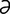 d] not having a myelin sheath.
d] not having a myelin sheath.
unpacking lay term for parturition in camelids
unphysiological not in harmony with the laws of physiology.
u. fatty acids see fatty acid.
unsex to deprive of the gonads.
unsharpness [ n-shahrp’nis] lack of detail in an X-ray picture.
n-shahrp’nis] lack of detail in an X-ray picture.
unstriated [ n-stri’āt–
n-stri’āt– d] having no striations, as smooth muscle.
d] having no striations, as smooth muscle.
unthrifty weaner sheep see weaner illthrift.
ununbium (Uub) a temporary name for a chemical element, atomic number 112, atomic weight 285. See Table 4.
ununhexium (Uuh) a temporary name for a chemical element, atomic number 116, atomic weight 293. See Table 4.
u. medial coronoid process see fragmented coronoid process.
ununoctium (Uuo) a temporary name for a chemical element, atomic number 118, atomic weight 294. See Table 4.
ununpentium (Uup) a temporary name for a synthetic chemical element, atomic number 115, atomic weight 288. See Table 4.
ununquadium (Uuq) a temporary name of a radioactive chemical element, atomic number 114, atomic weight 289. See Table 4.
ununseptium (Uus) a temporary name of an undiscovered chemical element, atomic number 117, atomic weight is 294. See Table 4.
ununtrium (Uut) a temporary name for a synthetic chemical element, atomic number 113, atomic weight 284. See Table 4.
UPC urine protein:creatinine ratio.
upper burner in traditional Chinese medicine, the thoracic cavity; associated with respiration.
upsilon [up’si-lon] twentieth letter in the Greek alphabet, ϒ or υ.
urachal [u’r –k
–k l] pertaining to urachus.
l] pertaining to urachus.
u. cyst symptomless fluid-filled cavities in the urachal remnant.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
 –kw
–kw –nō n’] coenzyme Q; component of the electron transport chain of oxidative phosphorylation.
–nō n’] coenzyme Q; component of the electron transport chain of oxidative phosphorylation. r] mammary gland of farm animals. The cow has four quarters and four teats. The rest of the ruminants and the mare have two. The sow may have as many as 18. See also mammary gland, mastitis, teat.
r] mammary gland of farm animals. The cow has four quarters and four teats. The rest of the ruminants and the mare have two. The sow may have as many as 18. See also mammary gland, mastitis, teat.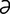 r] a full-thickness defect of cutaneous, mucosal or corneal epithelium. The exposed supporting tissue is inevitably damaged and inflamed, often infected, and may produce a covering layer of fibrinous inflammatory exudate (diphtheritic membrane). Occurs in many organs and can found under those headings, e.g. abomasal, corneal, gastric.
r] a full-thickness defect of cutaneous, mucosal or corneal epithelium. The exposed supporting tissue is inevitably damaged and inflamed, often infected, and may produce a covering layer of fibrinous inflammatory exudate (diphtheritic membrane). Occurs in many organs and can found under those headings, e.g. abomasal, corneal, gastric.
 r] pertaining to the ulna; the medial aspect of the upper forelimb, as opposed to the radial or lateral aspect.
r] pertaining to the ulna; the medial aspect of the upper forelimb, as opposed to the radial or lateral aspect. –mo-brang’ke–
–mo-brang’ke– l] pertaining to the tissue originating from the fifth pharyngeal pouch of the embryo.
l] pertaining to the tissue originating from the fifth pharyngeal pouch of the embryo. –s
–s n-trif″u-ga’sh
n-trif″u-ga’sh n] subjection of material to a very high centrifugal force (up to 200 000 times the force of gravity), which will separate and sediment the molecules of a substance or subcellular components.
n] subjection of material to a very high centrifugal force (up to 200 000 times the force of gravity), which will separate and sediment the molecules of a substance or subcellular components. –de’
–de’ n] pertaining to a period of less than 24 hours; applied to the rhythmic repetition of certain phenomena in living organisms occurring in cycles of less than a day (ultradian rhythm).
n] pertaining to a period of less than 24 hours; applied to the rhythmic repetition of certain phenomena in living organisms occurring in cycles of less than a day (ultradian rhythm). –fil’trāt] substances which pass through an ultrafilter, i.e. a semipermeable membrane through which the filtrate passes under pressure.
–fil’trāt] substances which pass through an ultrafilter, i.e. a semipermeable membrane through which the filtrate passes under pressure. –fil-tra’sh
–fil-tra’sh n] filtration through a filter capable of removing colloidal particles from a dispersion medium, as in the filtration of plasma at the capillary membrane.
n] filtration through a filter capable of removing colloidal particles from a dispersion medium, as in the filtration of plasma at the capillary membrane. –son’ik] beyond the audible range; relating to sound waves having a frequency of more than 20 000 cycles per second
–son’ik] beyond the audible range; relating to sound waves having a frequency of more than 20 000 cycles per second –s
–s –nog’r
–nog’r –fe] an imaging technique in which deep structures of the body are visualized by recording the reflections (echoes) of ultrasonic waves directed into the tissues. Frequencies in the range of 1 000 000–10 000 000 hz are used in diagnostic ultrasonography. The lower frequencies provide a greater depth of penetration and are used to examine abdominal organs; those in the upper range provide less penetration and are used predominantly to examine more superficial structures such as the eye. The basic principle of ultrasonography is the same as that of depth-sounding in oceanographic studies of the ocean floor. The ultrasonic waves are confined to a narrow beam that may be transmitted through, refracted, absorbed, or reflected by the medium toward which they are directed, depending on the nature of the surface they strike. In diagnostic ultrasonography the ultrasonic waves are produced by electrically stimulating a piezoelectric crystal called a transducer. As the beam strikes an interface or boundary between tissues of varying acoustic impedance (e.g. muscle and blood) some of the sound waves are reflected back to the transducer as echoes. The echoes are then converted into electrical impulses that are displayed on an oscilloscope, presenting a ‘picture’ of the tissues under examination. Ultrasonography can be utilized in examination of the heart (echocardiography) and in identifying size and structural changes in organs in the abdominopelvic cavity. It is, therefore, of value in identifying and distinguishing cancers and benign cysts. The technique also may be used to evaluate tumors and foreign bodies of the eye, and to demonstrate retinal detachment. Ultrasonography is not, however, of much value in examination of the lungs because ultrasound waves do not pass through structures that contain air. A particularly important use of ultrasonography is in the field of obstetrics and gynecology. It is a fast, relatively safe, and reliable technique for diagnosing pregnancy, and for detecting some typical fetal anomalies.
–fe] an imaging technique in which deep structures of the body are visualized by recording the reflections (echoes) of ultrasonic waves directed into the tissues. Frequencies in the range of 1 000 000–10 000 000 hz are used in diagnostic ultrasonography. The lower frequencies provide a greater depth of penetration and are used to examine abdominal organs; those in the upper range provide less penetration and are used predominantly to examine more superficial structures such as the eye. The basic principle of ultrasonography is the same as that of depth-sounding in oceanographic studies of the ocean floor. The ultrasonic waves are confined to a narrow beam that may be transmitted through, refracted, absorbed, or reflected by the medium toward which they are directed, depending on the nature of the surface they strike. In diagnostic ultrasonography the ultrasonic waves are produced by electrically stimulating a piezoelectric crystal called a transducer. As the beam strikes an interface or boundary between tissues of varying acoustic impedance (e.g. muscle and blood) some of the sound waves are reflected back to the transducer as echoes. The echoes are then converted into electrical impulses that are displayed on an oscilloscope, presenting a ‘picture’ of the tissues under examination. Ultrasonography can be utilized in examination of the heart (echocardiography) and in identifying size and structural changes in organs in the abdominopelvic cavity. It is, therefore, of value in identifying and distinguishing cancers and benign cysts. The technique also may be used to evaluate tumors and foreign bodies of the eye, and to demonstrate retinal detachment. Ultrasonography is not, however, of much value in examination of the lungs because ultrasound waves do not pass through structures that contain air. A particularly important use of ultrasonography is in the field of obstetrics and gynecology. It is a fast, relatively safe, and reliable technique for diagnosing pregnancy, and for detecting some typical fetal anomalies.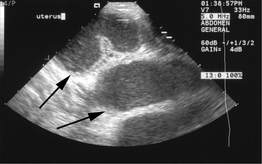
 –sound] mechanical radiant energy of a frequency greater than 20 000 cycles per second; used in veterinary medicine in the technique of ultrasonography. See also Doppler ultrasound.
–sound] mechanical radiant energy of a frequency greater than 20 000 cycles per second; used in veterinary medicine in the technique of ultrasonography. See also Doppler ultrasound. –vi’
–vi’ –l
–l t] denoting electromagnetic radiation of wavelength shorter than that of the violet end of the spectrum, having wavelengths of 4–400 nm.
t] denoting electromagnetic radiation of wavelength shorter than that of the violet end of the spectrum, having wavelengths of 4–400 nm.
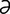 m-bil″
m-bil″ –ka’sh
–ka’sh n] a depression, usually central. In nodular neoplasms is an indication of malignancy, since these tend to undergo central necrosis.
n] a depression, usually central. In nodular neoplasms is an indication of malignancy, since these tend to undergo central necrosis. m-bil’
m-bil’ –k
–k s] the scar marking the site of entry of the umbilical cord in the fetus; called also navel. It is usually only depressed in the human abdomen and is inconspicuous in most domestic species. In dogs it is a palpable knot advertised by a convergent whorl of hair.
s] the scar marking the site of entry of the umbilical cord in the fetus; called also navel. It is usually only depressed in the human abdomen and is inconspicuous in most domestic species. In dogs it is a palpable knot advertised by a convergent whorl of hair.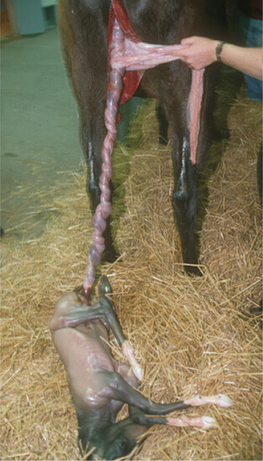
 –ri’
–ri’ –sis] the disease caused by Uncinaria in cats and dogs. Similar to, but less severe than ancylostomiasis, with only mild blood loss and enteritis. Larval migration causes pedal dermatitis.
–sis] the disease caused by Uncinaria in cats and dogs. Similar to, but less severe than ancylostomiasis, with only mild blood loss and enteritis. Larval migration causes pedal dermatitis. n-kon’sh
n-kon’sh s] insensible; incapable of responding to sensory stimuli and of having subjective experiences.
s] insensible; incapable of responding to sensory stimuli and of having subjective experiences. l-en’ik] an unsaturated fatty acid, used topically, in ointment or powder form, as an antifungal agent; toxic reactions are rare.
l-en’ik] an unsaturated fatty acid, used topically, in ointment or powder form, as an antifungal agent; toxic reactions are rare. r-k
r-k t] in the preparation of a tooth cavity for restoration, a cavity under the edges of the opening which is intended to aid in retention of a filling.
t] in the preparation of a tooth cavity for restoration, a cavity under the edges of the opening which is intended to aid in retention of a filling. r-de-vel’
r-de-vel’ p-m
p-m nt] an error in X-ray film developing procedure. Causes the production of a flat film with poor contrast; the unexposed background is gray instead of black.
nt] an error in X-ray film developing procedure. Causes the production of a flat film with poor contrast; the unexposed background is gray instead of black. n-dif″
n-dif″ r-en’she-āt–
r-en’she-āt– d] not differentiated; primitive. 1. in neoplasia refers to a primitive cell type and likely to be malignant. 2. In clinical medicine refers to a group diagnosis in which there is no differentiation from the pathoanatomical diagnosis, e.g. failure to take the additional step of differentiating between a diagnosis of diarrhea and the etiologically specific diagnosis, e.g. Escherichia coli. See also undifferentiated diarrhea of the newborn.
d] not differentiated; primitive. 1. in neoplasia refers to a primitive cell type and likely to be malignant. 2. In clinical medicine refers to a group diagnosis in which there is no differentiation from the pathoanatomical diagnosis, e.g. failure to take the additional step of differentiating between a diagnosis of diarrhea and the etiologically specific diagnosis, e.g. Escherichia coli. See also undifferentiated diarrhea of the newborn.
 l] pertaining to the nails, claws or hooves. u. crest a crescent-shaped process on the distal phalanx, encircling the corium of the nail or claw, best developed in cats, especially the big cats where it protects the growing matrix.
l] pertaining to the nails, claws or hooves. u. crest a crescent-shaped process on the distal phalanx, encircling the corium of the nail or claw, best developed in cats, especially the big cats where it protects the growing matrix. ] hoof.
] hoof. –grād″] the stance of an ungulate; the disposition of standing on hooves. The ultimate running gait. See also digitigrade.
–grād″] the stance of an ungulate; the disposition of standing on hooves. The ultimate running gait. See also digitigrade. n] the growing together of tissues separated by injury, as of the ends of a fractured bone, or of the edges of a wound.
n] the growing together of tissues separated by injury, as of the ends of a fractured bone, or of the edges of a wound. –r
–r ] a female which has had one pregnancy that resulted in a viable infant; primipara; para I.
] a female which has had one pregnancy that resulted in a viable infant; primipara; para I. –t
–t nt, u″n
nt, u″n –po-ten’sh
–po-ten’sh l] having only one power, as giving rise to cells of one order only.
l] having only one power, as giving rise to cells of one order only. n-sach’
n-sach’ –rāt″
–rāt″ d] 1. not having all affinities of its elements satisfied (unsaturated compound). 2. not holding all of a solute which can be held in solution by the solvent (unsaturated solution). 3. denoting compounds in which two or more atoms are united by double or triple bonds.
d] 1. not having all affinities of its elements satisfied (unsaturated compound). 2. not holding all of a solute which can be held in solution by the solvent (unsaturated solution). 3. denoting compounds in which two or more atoms are united by double or triple bonds.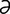 n-thrif’te-nis] failure to grow or to put on weight as well as expected in the presence of adequate quantity and quality of feed, and in the absence of overt clinical signs of illness. Called also illthrift. See also weaner illthrift.
n-thrif’te-nis] failure to grow or to put on weight as well as expected in the presence of adequate quantity and quality of feed, and in the absence of overt clinical signs of illness. Called also illthrift. See also weaner illthrift.