T
T symbol, tesla; tera-; (absolute) temperature; thymine.
T1 in magnetic resonance imaging, a time constant; called also spin-lattice relaxation time.
t in genetics, symbol for translocation.
t1/2 context context-sensitive half-time.
θ theta, small letter; eighth letter in the Greek alphabet.
T conformational state deoxy (‘tense’) conformational form of hemoglobin.
T helper cell see helper lymphocyte.
T lymphocyte see T lymphocyte.
T tubule see transverse tubules.
t-PA tissue plasminogen activator.
t-distribution see t statistic.
t-strain mycoplasma see Ureaplasma.
TAB a vaccine prepared from killed typhoid, paratyphoid A and paratyphoid B bacilli.
tabes [ta’bēz] any wasting of the body; progressive atrophy of the body or a part of it.
tabescent [t -bes’
-bes’ nt] growing emaciated; wasting away.
nt] growing emaciated; wasting away.
tabetiform [t -bet’
-bet’ -form] resembling tabes.
-form] resembling tabes.
inner t. the inner compact layer of the bones covering the brain.
outer t. the outer compact layer of the bones covering the brain.
statistical t. tables of values used in statistics, e.g. t-tables.
tabula vitrea [tă’bu-l ] inner layer of very dense bone in the bones of the cranium.
] inner layer of very dense bone in the bones of the cranium.
tabular [tab’u-l r] resembling a table.
r] resembling a table.
tachogram [tak’o-gram] the graphic record produced by tachography.
tachography [t -kog’r
-kog’r -fe] the recording of the movement and speed of the blood current.
-fe] the recording of the movement and speed of the blood current.
tachy- word element. [Gr.] rapid, swift.
tachycardia [tak″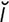 -kahr’de-
-kahr’de-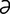 ] abnormally rapid heart rate.
] abnormally rapid heart rate.
ectopic t. rapid heart action in response to impulses arising outside the sinoatrial node.
idioventricular t. one occurring as a compensation for a sinus bradycardia and A-V block.
supraventricular t. a combination of junctional tachycardia and atrial tachycardia.
ventricular t. see ventricular tachycardia.
tachymeter [t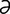 -kim’
-kim’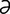 -t
-t r] an instrument for measuring rapidity of motion.
r] an instrument for measuring rapidity of motion.
tachyphagia [tak″ -fa’je-
-fa’je- ] rapid eating.
] rapid eating.
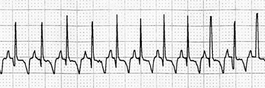
T-1 Sinus tachycardia in a dog.
From Ettinger SJ, Feldman E, Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 6th Edition. Saunders, 2004.
tachypneic respiratory failure see respiratory failure.
tack abbreviation for tackle; a horseman’s word for saddlery and gear generally.
tactile [tak’til] pertaining to touch.
t. hair hairs particularly sensitive to touch. See also hair (1).
t. placing reaction, t. reflex see placing reflex.
t. receptors located in the skin most are connected to very fast, myelinated nerve fibers.
tadpole edema virus see Ranavirus.
T. crassiceps adult tapeworms in foxes and coyotes, the larval stage (cysticercus) in rodents.
T. hyenae tapeworms are in hyenas and the cysticerci in antelopes.
T. martis the adult tapeworms in the marten and the cysticercus in the vole.
T. omissa adult tapeworms in the cougar and larvae in deer.
T. parva adult tapeworms in genets, larval stage in rodents.
T. polyacantha adults are in the intestine of foxes and the metacestodes in microtine rodents.
T. rileyi adult tapeworms found in lynx, larvae in rodents.
T. serrata see T. pisiformis (above).
T. twitchelli adult tapeworms found in wolverines, larvae in lungs and pleural cavity of porcupines.
taeniacide [te’ne- -sīd″] teniacide.
-sīd″] teniacide.
taeniafuge [te’ne- -fūj″] teniafuge.
-fūj″] teniafuge.
Taeniorhyncus the genus of mosquitoes.
tafes see Perralderia coronopifolia.
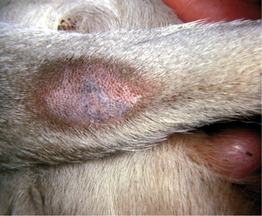
cutaneous t. see fibrovascular papilloma.
radioactive t. a radioisotope that has been incorporated in a chemical compound.
bob t., bobbed t. see bobtail.
caudal t. fold see caudal tailfold.
t. fold dermatitis see fold dermatitis.
t. and mane dystrophy see mane and tail dystrophy.
t. pyoderma equine staphylococcal folliculitis.
t. root where the tail joins the body.
t. sore the early or mild lesions in a tail-biting problem of pigs.
t. stock first part of the tail, of a whale or dolphin, before it divides into the flukes.
t. worm equine staphylococcal dermatitis.
tailhead dorsal aspect of the root of the tail.
taillessness see tail absence.
talampicillin [tal-amp″ -sil’in] an antibiotic derived from ampicillin.
-sil’in] an antibiotic derived from ampicillin.
talapoin (Miopithecus spp.) the smallest of the Old World monkeys.
talcosis [tal-ko’sis] a condition due to inhalation or implantation in the body of talc.
talcum [tal’k m] talc, talcum powder.
m] talc, talcum powder.
Talfan disease see porcine viral encephalomyelitis.
talipes [tal’ -pēz] see dactylomegaly.
-pēz] see dactylomegaly.
t. Cape honeyflower Melianthus major.
t. chloris Chloris ventricosa.
t. delphinium Delphinium trolliifolium.
t. yellowtop Senecio magnificus.
Tallebudgera horse disease see Ageratina adenophora.
tallow tree Chinese tallow tree; see Sapium sebiferum. Called also Chinese tallow wood.
talocalcaneal joint [ta″lo-kal-ka’ne- l] see tarsal joints, Table 11.
l] see tarsal joints, Table 11.
talocalcanean [ta″lo-kal-ka’ne- n] pertaining to the talus and calcaneus.
n] pertaining to the talus and calcaneus.
talocalcaneocentral joint the joint between the talus and central tarsal bone; see also tarsal joints, Table 11.
talocrural [ta″lo-kroo’r l] tarsocrural.
l] tarsocrural.
talofibular [ta″lo-fib’u-l r] pertaining to the talus and fibula.
r] pertaining to the talus and fibula.
talonavicular [ta″lo-n -vik’u-l
-vik’u-l r] pertaining to the talus and navicular bone.
r] pertaining to the talus and navicular bone.
talus [ta’l s] the most proximal of the tarsal bones. Called also the tibial tarsal bone. See also Table 10.
s] the most proximal of the tarsal bones. Called also the tibial tarsal bone. See also Table 10.
tamboril da campo see Enterolobium.
tameridone a purine alkyl piperidine derivative used to sedate cattle and wild ruminants.
Tamias striatus the genus of chipmunks.
tampan [tam’pan] a tick; see Ornithodorus.
tamponade [tam″pon-ād’ ] 1. surgical use of a tampon. 2. pathological compression of a part.
Tamus communis [ta’m s] see Dioscorea communis.
s] see Dioscorea communis.
Tamworth a golden-red, long faced, prick-eared bacon pig produced in the UK.
Tanaisia a genus of flukes in the family Eucotylidae.
T. zarudnyi found in ruffed grouse.
tangled hypericum Hypericum triquetrifolium.
tank [tank] an artificial receptacle for liquids.
tannate [tan’āt] any of the salts of tannic acid, all of which are astringent.
tanner grass [tan’ r] Brachiaria radicans.
r] Brachiaria radicans.
tansy Tanacetum vulgare. See also tansy ragwort and tansy mustard.
tantalum (Ta) [tan’t -l
-l m] a chemical element, atomic number 73, atomic weight 180.948. See Table 4. It is a noncorrosive and malleable metal used for plates or disks to repair cranial defects, for wire sutures, and for making prosthetic appliances.
m] a chemical element, atomic number 73, atomic weight 180.948. See Table 4. It is a noncorrosive and malleable metal used for plates or disks to repair cranial defects, for wire sutures, and for making prosthetic appliances.
TAP trypsinogen activation peptide.
tap [tap] 1. a quick, light blow. 2. to drain off fluid by paracentesis.
tape [tāp] a long, narrow strip of fabric or other flexible material.
tapeinocephaly [tap″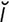 -no-sef’
-no-sef’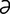 -le] flattening or depression of the skull.
-le] flattening or depression of the skull.
tapetal [t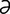 -pe’t
-pe’t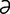 l] emanating from or pertaining to the tapetum.
l] emanating from or pertaining to the tapetum.
t. aplasia failure of the tapetum to develop. A variation of normal.
t. degeneration occurs as an inherited defect in beagles and in cats with Chediak–Higashi syndrome.
t. cellulosum a type of tapetum lucidum made of cells called iridocytes, as found in carnivores.
bass tapeworm see Proteocephalus ambloplitis.
broad t. Diphyllobothrium latum.
broad fish tapeworm see Diphyllobothrium latum.
dwarf t. see Hymenolepis nana.
fish t. Diphyllobothrium latum.
fringed tapeworm see Thysanosoma actinioides.
hydatid t. Echinococcus granulosus.
coal t. pitch see coal tar pitch.
hot t. a cause of burns in dogs and cats, usually made more severe because it sticks to the skin.
Stockholm t. see Stockholm tar.
Tarai a black Indian dairy buffalo with a white tail; occasionally brown in color.
tarbush see Flourensia cernua.
Tarentaise cattle fawn to yellow, dual-purpose cattle from the French Alps.
t.–film distance the distance from the target of the X-ray tube and the plane of the X-ray film.
tarichatoxin [tar’ik- -tok″sin] a neurotoxin from the newt (Taricha), identical with tetrodotoxin.
-tok″sin] a neurotoxin from the newt (Taricha), identical with tetrodotoxin.
taro Colocasia esculenta, Xanthosoma spp.
giant t. Alocasia brisbanensis.
tarry [tahr’e] said of feces that are black and glutinous. See also melena.
tarsal [tahr’s l] pertaining to the tarsal plate of an eyelid or of the foot. See also Table 10.
l] pertaining to the tarsal plate of an eyelid or of the foot. See also Table 10.
t. adenitis see meibomian adenitis.
t. hydrarthrosis see bog spavin.
t. sheath the synovial sheath around the deep flexor tendon in the horse.
tarsalia [tahr-sa’le- ] the bones of the tarsus.
] the bones of the tarsus.
tarsalis [tahr-sa’lis] [L.] tarsal.
tars(o)- word element. [Gr.] edge of eyelid, tarsus of the foot.
tarsoclasis [tahr-sok’l -sis] surgical fracture of the tarsus.
-sis] surgical fracture of the tarsus.
tarsoconjunctiva [tahr″so-k n-j
n-j nk’ti-v
nk’ti-v ] the tarsal plate and palpebral conjunctiva.
] the tarsal plate and palpebral conjunctiva.
tarsocrural [tahr″so-krōōr’ l] pertaining to the tarsal bones and the tibia and fibula.
l] pertaining to the tarsal bones and the tibia and fibula.
t. joint the articulation between the tibial tarsal bone (talus) and the tibia and fibula.
tarsomalacia [tahr″so-m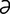 -la’sh
-la’sh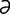 ] softening of the tarsal plate of an eyelid.
] softening of the tarsal plate of an eyelid.
tarsometatarsal [tahr″so-met″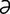 -tahr’s
-tahr’s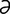 l] pertaining to the tarsus and metatarsus.
l] pertaining to the tarsus and metatarsus.
tarsophyma any tumor of the tarsus.
tarsoplasty [tahr’so-plas″te] plastic repair of the tarsal plate of the eyelid.
tarsotomy [tahr-sot’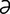 -me] surgical incision of a tarsus, or the tarsal plate of an eyelid.
-me] surgical incision of a tarsus, or the tarsal plate of an eyelid.
Tarui disease [tah’roo-e] 6-phosphofructokinase 1 deficiency.
T-8 Accumulation of dental tartar and resulting perialveolar gingivitis in cat.
From Greene CE, Infectious Diseases of the Dog and Cat, 3rd Edition. Saunders, 2008.
 -nid] a fly of the family Tabanidae, including the genera Chrysops, Haematopota, Pangonia and Tabanus.
-nid] a fly of the family Tabanidae, including the genera Chrysops, Haematopota, Pangonia and Tabanus. -ba’n
-ba’n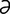 s] a genus of blood-sucking biting flies (horse flies, deer flies or march flies) in the family Tabanidae which transmit trypanosomes and anthrax to various animals and have a painful bite.
s] a genus of blood-sucking biting flies (horse flies, deer flies or march flies) in the family Tabanidae which transmit trypanosomes and anthrax to various animals and have a painful bite. -ch
-ch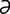 r] separation of the chief cranial bones into inner and outer tables, separated by a diploë.
r] separation of the chief cranial bones into inner and outer tables, separated by a diploë.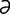 l] 1. a flat layer or surface, e.g. smooth surface on top of (occlusal surface of) teeth especially on the incisors of the horse, used in telling the age of the horse. 2. a collection of related records in a data base.
l] 1. a flat layer or surface, e.g. smooth surface on top of (occlusal surface of) teeth especially on the incisors of the horse, used in telling the age of the horse. 2. a collection of related records in a data base. l-sp n] a household unit of volume or capacity; equivalent to three teaspoons or approximately 15 mL; in metric measurement, equal to 20 mL.
l-sp n] a household unit of volume or capacity; equivalent to three teaspoons or approximately 15 mL; in metric measurement, equal to 20 mL. t] a solid dosage form containing a medicinal substance with or without a suitable diluent.
t] a solid dosage form containing a medicinal substance with or without a suitable diluent. -rith’me-
-rith’me- ] tachycardia associated with an irregularity in the normal heart rhythm. Includes atrial tachycardia, sinus tachycardia, premature ventricular contractions, atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia.
] tachycardia associated with an irregularity in the normal heart rhythm. Includes atrial tachycardia, sinus tachycardia, premature ventricular contractions, atrial flutter, atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia.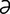 -lak’sis] 1. rapid immunization against the effect of toxic doses of an extract by previous injection of small doses of it. 2. rapidly decreasing response to a drug or physiologically active agent after administration of a few doses.
-lak’sis] 1. rapid immunization against the effect of toxic doses of an extract by previous injection of small doses of it. 2. rapidly decreasing response to a drug or physiologically active agent after administration of a few doses. ; tak″e-ne’
; tak″e-ne’ ] very rapid respirations. The rate is fast and the depth shallow, as in heat stroke, because the initiating mechanism is hyperthermia and there is no hypercapnia.
] very rapid respirations. The rate is fast and the depth shallow, as in heat stroke, because the initiating mechanism is hyperthermia and there is no hypercapnia.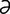 -rol] an isomer of ergosterol, an antirachitic substance, produced by irradiaton of ergosterol.
-rol] an isomer of ergosterol, an antirachitic substance, produced by irradiaton of ergosterol.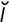 -zo’īt] a fast multiplication stage of zoites in the life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii or Neospora caninum; found in tissues.
-zo’īt] a fast multiplication stage of zoites in the life cycle of Toxoplasma gondii or Neospora caninum; found in tissues. s] an immunosuppressive agent used in allogenic organ transplant to reduce the risk of rejection. It is derived from Streptomyces tsukabaensis. It selectively binds FK-binding proteins and the complex inhibits calcineurin. There is a slightly increased risk of cutaneous carcinogensis when used topically on humans, rodents and monkeys. It is used topically in the treatment of inflammatory and immune-mediated skin diseases of dogs and cats.
s] an immunosuppressive agent used in allogenic organ transplant to reduce the risk of rejection. It is derived from Streptomyces tsukabaensis. It selectively binds FK-binding proteins and the complex inhibits calcineurin. There is a slightly increased risk of cutaneous carcinogensis when used topically on humans, rodents and monkeys. It is used topically in the treatment of inflammatory and immune-mediated skin diseases of dogs and cats. ] a genus of cyclophyllidean tapeworms of the family Taeniidae. The adult tapeworm inhabits the intestine of carnivores, the larval stage (metacestode) invades the tissues of a variety of animals, in some cases humans. They cause some economic loss due to condemnation of offal, but their greatest importance is their zoogenetic potential, and the preoccupation of humans with the danger of becoming infected. Tapeworms and their hosts are listed below, but species whose intermediate hosts are unknown are: T. bubesi (lion), T. crocutae (spotted hyena), T. erythraea (black-backed jackal), T. gongamai and T. hlosei (lion and cheetah), T. lycaontis (hunting dog), T. regis (lion).
] a genus of cyclophyllidean tapeworms of the family Taeniidae. The adult tapeworm inhabits the intestine of carnivores, the larval stage (metacestode) invades the tissues of a variety of animals, in some cases humans. They cause some economic loss due to condemnation of offal, but their greatest importance is their zoogenetic potential, and the preoccupation of humans with the danger of becoming infected. Tapeworms and their hosts are listed below, but species whose intermediate hosts are unknown are: T. bubesi (lion), T. crocutae (spotted hyena), T. erythraea (black-backed jackal), T. gongamai and T. hlosei (lion and cheetah), T. lycaontis (hunting dog), T. regis (lion).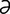 ] see tenia.
] see tenia.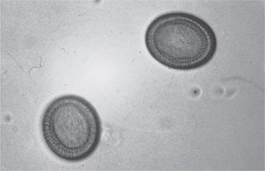

 -se’t
-se’t m] genus in the plant family Asteraceae; reported to be associated with abortion in cattle; includes T. axillare, T. parthenium (feverfew), T. vulgare (tansy).
m] genus in the plant family Asteraceae; reported to be associated with abortion in cattle; includes T. axillare, T. parthenium (feverfew), T. vulgare (tansy). -poks″] a poxvirus that infects African nonhuman primates, but may also cause disease in humans. Named after the Tana River Valley in Kenya.
-poks″] a poxvirus that infects African nonhuman primates, but may also cause disease in humans. Named after the Tana River Valley in Kenya. -sīt] special cell in the ependyma lining the third ventricle in the brain; the function is unknown.
-sīt] special cell in the ependyma lining the third ventricle in the brain; the function is unknown. -pe’t
-pe’t m] pl. tapeta [L.] 1. a covering structure or layer of cells. 2. a stratum in the human brain composed of fibers from the body and splenium of the corpus callosum sweeping around the lateral ventricle. 3. common abbreviation for tapetum lucidum (see below).
m] pl. tapeta [L.] 1. a covering structure or layer of cells. 2. a stratum in the human brain composed of fibers from the body and splenium of the corpus callosum sweeping around the lateral ventricle. 3. common abbreviation for tapetum lucidum (see below). rm] a class of the phylum Platyhelminthes, class Eucestoda, or flatworms; includes members of the genera Taenia, Diphyllobothrium, Dipylidium and Echinococcus. Most adult tapeworm infestations have little apparent effect on the health of farm livestock (with the exception of Anoplocephala perfoliata in horses) and are mostly esthetic problems in companion animals.
rm] a class of the phylum Platyhelminthes, class Eucestoda, or flatworms; includes members of the genera Taenia, Diphyllobothrium, Dipylidium and Echinococcus. Most adult tapeworm infestations have little apparent effect on the health of farm livestock (with the exception of Anoplocephala perfoliata in horses) and are mostly esthetic problems in companion animals.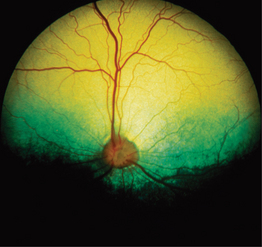
 -ran’tu-l
-ran’tu-l ] a large group of hairy spiders in the family Theraphosidae. Although known for the large size and a fearsome reputation, they are also kept as pets.
] a large group of hairy spiders in the family Theraphosidae. Although known for the large size and a fearsome reputation, they are also kept as pets.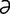 -rak’s
-rak’s -k
-k m] a plant in the family Asteraceae suspected to cause some incidents of stringhalt in horses in the absence of H. radicata, for example in South America. Called also dandelion. See Hypochaeris radicata.
m] a plant in the family Asteraceae suspected to cause some incidents of stringhalt in horses in the absence of H. radicata, for example in South America. Called also dandelion. See Hypochaeris radicata.

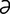 t] 1. an object or area toward which something is directed, e.g. target animal, population, level or nucleotide sequence. 2. the area of the anode of an X-ray tube where the electron beam collides causing the emission of X-rays. 3. a cell or organ that is affected by a particular agent, e.g. a hormone or drug.
t] 1. an object or area toward which something is directed, e.g. target animal, population, level or nucleotide sequence. 2. the area of the anode of an X-ray tube where the electron beam collides causing the emission of X-rays. 3. a cell or organ that is affected by a particular agent, e.g. a hormone or drug.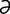 t-ing] mechanisms whereby proteins are sorted and transported to particular sites in the cell required for their synthesis or function.
t-ing] mechanisms whereby proteins are sorted and transported to particular sites in the cell required for their synthesis or function. -ni’tis] inflammation of the tarsal plate and the meibomian glands of the eyelid.
-ni’tis] inflammation of the tarsal plate and the meibomian glands of the eyelid. -me] 1. excision of one or more bones of the tarsus. 2. excision of the tarsal plate of the eyelid.
-me] 1. excision of one or more bones of the tarsus. 2. excision of the tarsal plate of the eyelid.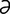 -tahr’s
-tahr’s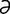 s] the bone of the lower shank of birds made up of fused tarsal and metatarsal bones.
s] the bone of the lower shank of birds made up of fused tarsal and metatarsal bones. -fe] temporary or permanent joining with suture of a portion or the entire upper and lower eyelids for the purpose of protecting the cornea by shortening or closing the palpebral fissure.
-fe] temporary or permanent joining with suture of a portion or the entire upper and lower eyelids for the purpose of protecting the cornea by shortening or closing the palpebral fissure. s] 1. the hock or ankle made up of up to seven bones–talus, calcaneus, navicular, medial, intermediate and lateral cuneiform, and cuboid–comprising the articulation between the cannon bone and the tibia. 2. the fibrous layer forming the framework of either (upper or lower) eyelid. See tarsal plate.
s] 1. the hock or ankle made up of up to seven bones–talus, calcaneus, navicular, medial, intermediate and lateral cuneiform, and cuboid–comprising the articulation between the cannon bone and the tibia. 2. the fibrous layer forming the framework of either (upper or lower) eyelid. See tarsal plate.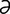 r] 1. the recrystallized sediment of wine casks; crude potassium bitartrate. 2. a yellowish film formed of calcium phosphate and carbonate, food particles, and other organic matter, deposited on the teeth by the saliva. See also dental calculus.
r] 1. the recrystallized sediment of wine casks; crude potassium bitartrate. 2. a yellowish film formed of calcium phosphate and carbonate, food particles, and other organic matter, deposited on the teeth by the saliva. See also dental calculus.


