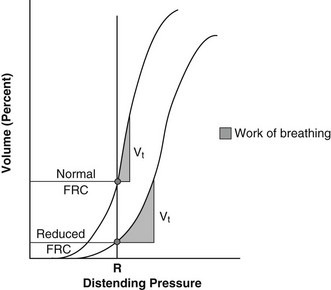
Chapter 8 The resting lung volume is a balance between the elastic properties of the lung (favoring alveolar collapse) and the elastic properties of the chest wall (favoring alveolar expansion). This resting lung volume, understood as the volume of air remaining in the lungs at the end of a normal breath, is called the functional residual capacity (FRC). At the normal FRC, the lung is very compliant. Compliance or stiffness is the change in lung volume for any given applied pressure. In a healthy state with compliant lungs, small changes in intrapleural pressure cause a large change in lung volume, subsequently drawing fresh air into the respiratory tract. A pressure-volume curve of the lung shows the change in the work of breathing at normal and reduced lung volumes (Figure 8-1). Most common pulmonary parenchymal diseases (e.g., pulmonary edema, pneumonia) increase FRC, flatten the pressure-volume curve, and decrease compliance. Significant pleural space disease resulting in lung collapse (e.g., pneumothorax, diaphragmatic hernia) produces similar changes in lung compliance and FRC. Figure 8-1 Pulmonary compliance equals the slope of the pressure volume curve at the functional residual capacity (FRC) or resting volume of the lung. The x-axis, R, is the pressure required to move a volume of air (shown in the y-axis). With a reduced FRC, a greater distending pressure is required to move an equal tidal volume. This requires more work and therefore more energy. Vt, Tidal volume. Impaired respiration occurs secondary to inadequate ventilation or inadequate gas exchange. If sufficiently severe, this impairment can progress to respiratory failure, a life-threatening situation that often necessitates aggressive intervention. Failure of ventilation is the inability to move fresh air into the pulmonary alveoli, resulting in high blood carbon dioxide levels (hypercarbia) and low blood oxygen levels (hypoxemia). Failure of gas exchange occurs at the level of the blood-air barrier, resulting in hypoxemia with or without hypercarbia. In cases of impaired gas exchange, the hypoxemic patient initially hyperventilates in an effort to improve oxygenation. This results in low blood carbon dioxide levels and a respiratory alkalosis. With progression of disease and onset of respiratory failure, effective exchange of both oxygen and carbon dioxide is lost, resulting in hypoxemia and hypercarbia. Appropriate differentiation of the type of respiratory failure is critical when moving forward with proper medical intervention. Close observation of respiratory pattern and physical examination findings are especially helpful in determining the likely cause and appropriate therapeutic interventions (Table 8-1). TABLE 8-1 Common Causes of Respiratory Distress in Dogs and Cats
Stabilization of the Patient with Respiratory Distress
Pathophysiology of Respiratory Distress
Respiratory Failure
Problem
Phase Affected/Respiratory Pattern
Emergency Treatment
Upper Airway Obstruction
Laryngeal paralysis
Inspiratory/Obstructive
O2, sedation, antiinflammatory, +/− tracheostomy
Extrathoracic tracheal collapse
Inspiratory/Obstructive
O2, sedation, antitussive
Airway mass lesion
Fixed/Obstructive
O2, sedation, +/− tracheostomy
Airway foreign body
Fixed/Obstructive
O2, sedation, Heimlich maneuver
Laryngeal stenosis
Fixed/Obstructive
O2, sedation, +/− tracheostomy
Lower Airway Obstruction
Intrathoracic tracheal collapse
Expiratory/Obstructive
O2, sedation, antitussive
Bronchitis
Expiratory/Obstructive
O2, sedation, antiinflammatory, bronchodilator
Airway mass lesion
Fixed/Obstructive
O2, sedation
Airway foreign body
Fixed/Obstructive
O2, sedation, Heimlich maneuver
Pulmonary Parenchymal Disease
Pneumonia
Inspiratory/Restrictive
O2, IV fluids, antibiotic, physical therapy
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema
Inspiratory/Restrictive
O2, sedation, fluid restriction/diuretics
Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema
Inspiratory/Restrictive
O2, sedation
Pulmonary hemorrhage
Inspiratory/Restrictive
O2, sedation, FFP
Pulmonary neoplasia
Inspiratory/Restrictive
O2, sedation
Pleural Space Disease
Chylothorax
Inspiratory/Restrictive/Inverse
O2, thoracocentesis
Pneumothorax
Inspiratory/Restrictive/Inverse
O2, thoracocentesis
Pyothorax
Inspiratory/Restrictive/Inverse
O2, thoracocentesis
Pleural hemorrhage
Inspiratory/Restrictive/Inverse
O2, FFP, thoracocentesis
Diaphragmatic hernia
Inspiratory/Restrictive/Inverse
O2, sedation, surgical correction
Pulmonary Thromboembolism
Hyperventilation
O2, sedation, thrombolytic, anticoagulation
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


