CHAPTER 129 Reproductive Management of Fallow Deer
Fallow deer are the most widely distributed deer in the world and are primarily farmed for meat. Venison from fallow deer is fine grained and cut sizes are particularly suited to the restaurant trade, which usually prefers chilled rather than frozen product. To provide year-round availability of chilled product of consistent quality, a range of reproductive management strategies and production techniques, including selective slaughter of males and females at different times of the year, castration of some males for slaughter during the breeding season, and the use of hybridization, is required.
A number of factors need to be considered for the development of an efficient fallow deer farm. Assessment of body score of both breeding and slaughter stock combined with information on nutritional requirements of different age and sex classes of stock at various stages of the production cycle are essential elements of reproductive management on both stud and commercial farms. The integration of information on reproductive biology, behavior, nutrition, genetics, lactation, and animal management of farmed fallow deer provided in this chapter will assist practitioners to advise owners of both small and large farms on how to optimize production for maximum profit.
THE BREEDING SEASON
Fallow deer exhibit highly seasonal patterns of reproduction calibrated by photoperiod. They are short-day breeders, with the rut (peak of mating activity) occurring in October/November in the Northern Hemisphere (NH) and April/May in the Southern Hemisphere (SH). Breeding pattern within regions is highly synchronized in any one year, and reproductive management of this species on pastoral farms must therefore align feed supply with seasonal demands of late pregnancy and lactation. Patterns of reproduction also vary slightly at different latitudes, and local benchmarks for reproductive behavior and onset of the rut need to be established. Description of the estrous cycle, estrus, length of the breeding season, and gestation length are provided by Asher in Chapter 123.
REPRODUCTIVE BEHAVIOR
Bucks
If bucks are placed in adjoining paddocks they will fight vigorously through a fence and can make large holes in it. The fighting will also create holes in the top soil on either side of the fence, as the bucks attempt to hold ground during their pushing and shoving. This enormous energy expenditure leads to rapid weight loss, and adult bucks can lose 20 to 30 kg in a period of 6 to 8 weeks just prior to and during the rut. This equates to a change in body condition score from 3.5 to 1.5 (on a scale of 5) and leaves the buck vulnerable to winter death syndrome if low body condition is combined with poor quality feed and cold-snap weather conditions.7 Losses among sire bucks can be minimized by providing high-quality feed to sires immediately following the rut. This ensures protection of valuable genetics in preparation for subsequent breeding seasons.
Does
Estrous behavior in does appears quite passive compared with that of other livestock species.1 It is rare for does in estrus to mount other does or be mounted, and the most obvious characteristic of fallow deer estrus is simply that a doe will stand to be mounted by the buck. A nonestrous doe will generally avoid close contact with the rutting buck and will run short distances if a buck approaches.
REPRODUCTIVE BIOLOGY
Fallow deer have a highly synchronized mating season. The does are polyestrous but most (∼95%) conceive in their first or second estrous cycle. Pregnancy testing using ultrasonography is 100% accurate from 50 days of gestation, and a high level of accuracy is achievable earlier than this by experienced operators. Rapid fetal growth takes place in the third trimester of pregnancy when daily energy requirements increase by 25%. Basic information on the reproductive biology of fallow deer is presented in Table 129-1.
Table 129-1 Fallow Deer Reproduction
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Onset of puberty | Does: 16 months (weight dependent, 35 to 40 kg) |
| Bucks: 14 months (motile sperm first detected) | |
| Onset of breeding season | Mid-April Southern Hemisphere, mid-October Northern Hemisphere |
| Duration of breeding season | 6 estrous cycles in adult does |
| 4–5 estrous cycles in younger does | |
| Duration of rut | 6 weeks (2–3 estrous cycles) |
| Length of estrous cycle | 21 ± 0.6 days (1st cycle of breeding season) |
| 25 ± 1.5 days (last cycle of breeding season) | |
| Length of estrous | 12 to 24 hours |
| Matings per estrous | Repeated mounting (16 ± 7) prior to final ejaculatory mount |
| Courtship | 4 to 50 minutes (mean ± SD = 15 ± 10) |
| Gestation length | 234 ± 2 days |
| Onset of fawning | Last week of spring |
| Duration of parturition | 30–180 minutes from appearance of membranes |
| Fawning rate | 88–92% of does joined |
| Male-female ratio at birth | 1:1 |
| Weaning rate | 80–84% of does joined |
| Birth weight | Females: 4–4.2 kg |
| Males: 4.2–4.6 kg | |
| Twinning rate | <1:200 |
The buck-doe ratio used by most fallow deer farmers is 1 : 40 for experienced adult bucks and 1 : 20 for rising 2- and 3-year-old bucks. Higher buck-doe ratios can lead to subfertility in males and prolong the breeding season. This may lead to the birth of late fawns (conceived in fourth or fifth estrous cycle), and these fawns will grow slower than their counterparts, be subject to winter conditions earlier in their development, and usually do not attain the adult body weights expected. Late fawns might not conceive at 16 months of age as expected, because their body weight will not be sufficiently high by then to support the onset of puberty, pregnancy, and then lactation. Fallow does are highly fertile and will continue to breed after 12 years of age, depending on conditions, although there is some evidence that they are most efficient between 3 and 8 years of age.10
Fallow does will usually miss one or more breeding seasons throughout their reproductive life even when environmental conditions seem favorable.10 Stress may play a role in inducing this reproductive spell, and may originate from the heavy demands of lactation in drought years or from feeding the rapidly growing male fawn through to weaning the previous year, from introducing deer to new surroundings at the start of the rut, or changed environmental conditions.
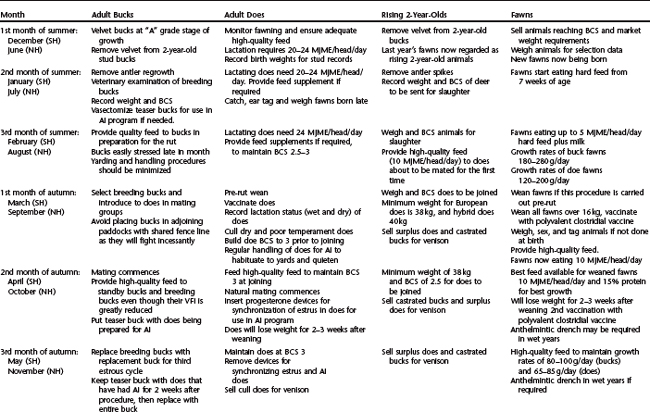
Fawn growth rates between 100 and 200 g/head/day are usually attained in the first 12 weeks of life, but slow to average between 50 and 100 g/head/day for the following 9 months up to yearling age. Growth profiles for female and male fawns up to 12 months of age are shown in the annual management calendar in Table 129-2. Castration of males at 6 months of age reduces growth rate by 10% compared with their male counterparts, but this is compensated for by increasing ease of management of slaughter animals during the following breeding season.
WEANING
Weaning can be carried out pre-rut or later in the breeding season in fallow deer, as lactation does not appear to inhibit ovulation and conception. However, the procedure should not be carried out without consideration of factors/stressors that can impact on behavioral and growth changes in weaned animals and their dams, such as unfavorable weather patterns (drought, wet, cold), body condition of dam or fawn, and introduction to unfamiliar surroundings of fawns, in particular after separation from their mother. If does become emaciated due to poor nutrition during lactation, it is probable that subsequent reproductive performance will be low if poor body condition is maintained throughout the rutting period, and pre-rut weaning is recommended under such conditions.1 Studies have shown positive effects of pre-rut weaning on hind conception date and hind condition in red deer in New Zealand, but it was acknowledged that weaned calves grew more slowly.14
Weight loss occurs in fawns immediately after weaning and persists for 2 to 3 weeks whether the procedure occurs pre-rut or post-rut. Comparative evaluation of weight recovery in fallow deer weaned pre-rut compared with deer weaned post-rut has shown no difference between the groups by 12 to 14 months of age owing to compensatory weight gains that occurred during spring (9–12 months of age).11 However, the availability of nutritious feed during this time is necessary to facilitate weight recovery. Minimization of weight loss at weaning is assisted by (i) weaning dams from their fawns so that fawns remain in familiar surroundings, (ii) adding two or three older animals of quiet temperament and who are used to human contact to the group of weaned deer, to assist in training of weaned deer to use of laneways, gates, and concentrate feeding points if required, and (iii) moving dams out of calling range of their fawns for 3 to 4 weeks. This may not be possible if deer are being weaned indoors, where appropriate strategies may need to be developed according to the size of the facility.
Controlled mating practices may require considerable pre-rut sorting and handling of breeding stock, and under these circumstances fawns are better removed from the breeding herd. The opportunity to preferentially feed weaned deer, and to carry out routine animal health management, without disturbance to breeding animals is facilitated by pre-rut weaning. In situations where concentrate feeding of deer is routinely practiced such as in-winter systems and indoors it is likely that young animals will not compete equally for feed with adult animals and their growth and development will not be optimal unless they are managed separately to adult stock. However, under extensive pastoral conditions where access to feed is not a limiting factor, where the mating policy involves joining a number of breeding bucks with the total breeding herd, and where reproductive performance data are not routinely recorded, separation of sub-yearling animals can take place in late winter/early spring without apparent production consequences.
NUTRITION AND BODY CONDITION SCORE
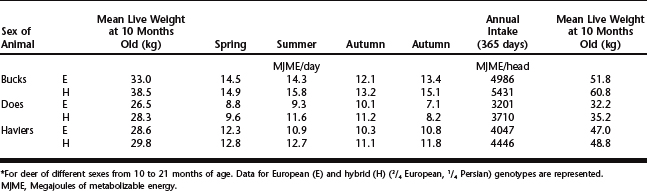
Seasonal variations in energy intake, and the annual energy intake for European fallow deer (E) bucks, does, and haviers (castrated male deer) and ¼ bred hybrids (¾ European and ¼ Persian) (H) between 10 and 21 months of age are shown in Table 129-3, and daily energy intake and live weight change for the same animals are shown in Figure 129-1. The pronounced reduction in voluntary feed intake and associated reduction in live weight in bucks during autumn corresponds with the rut (peak breeding period), and this reduction is significantly increased in older males, particularly those being used for breeding when up to 30% of live weight may be lost during this time. Calculated energy requirements for adult fallow bucks of different ages and weights over seasons of the year are shown in Table 129-4, although these data are interpolated from information derived for red deer stags in the winter in New Zealand.3
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree