Q
Q abbreviation for ubiquinone (CoQ).
q symbol for (1) the long arm of a chromosome or (2) the frequency of the rarer allele of a pair.
Q banding a laboratory technique for staining a karyotype with quinacrine dye.
q.d. [L.] quaque die (every day); once daily.
Q fever [ku fe′v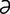 r] (query fever) an infection of most animal species, including humans, and some birds. It is caused by Coxiella burnetii and spread by inhalation, especially of inspissated reproductive exudates, and by ticks, and by the ingestion of raw infected milk. The disease is inapparent in most infected animals but can cause abortion in sheep and goats, and probably cattle. Called also Queensland fever. A disease notifiable to the OIE (see Table 12).
r] (query fever) an infection of most animal species, including humans, and some birds. It is caused by Coxiella burnetii and spread by inhalation, especially of inspissated reproductive exudates, and by ticks, and by the ingestion of raw infected milk. The disease is inapparent in most infected animals but can cause abortion in sheep and goats, and probably cattle. Called also Queensland fever. A disease notifiable to the OIE (see Table 12).
QBC 1. quantitative buffy coat. 2. quantitative blood count.
q.h. [L.] quaque hora (every hour).
q.i.d. [L.] quater in die (four times a day).
Qinchuan cattle red or yellow Chinese draft cattle with a cervical hump.
q.q.h. [L.] quaque quarta hora (every 4 hours).
q.s. [L.] quantum satis (a sufficient amount).
quackery [kwak′ f-e] the practice or methods of a quack.
f-e] the practice or methods of a quack.
quadrangular [kwod-rang′gu-l r] having four angles.
r] having four angles.
quadrate [kwod′rāt] square or squared.
quadr(i)- word element. [L.] four.
quadriceps [kwod′r -seps] having four heads; refers to quadriceps muscle. See also Table 13.
-seps] having four heads; refers to quadriceps muscle. See also Table 13.
q. reflex see patellar reflex.
quadrigemina the corpora quadrigemina.
quadrigeminal [kwod“r -jemĩ-n
-jemĩ-n l] fourfold; in four parts; forming a group of four.
l] fourfold; in four parts; forming a group of four.
quadrilateral [kwod″r -lat’
-lat’ r-
r- l] having four sides.
l] having four sides.
quadrilocular [kwod″ri-lok′u-l r] having four cavities.
r] having four cavities.
quadripartite [kwod″r -pahr′tīt] divided into four.
-pahr′tīt] divided into four.
hereditary amblyopia with q. see hereditary amblyopia with quadriplegia.
quadrisect [kwod′r -sekt] to cut into four parts.
-sekt] to cut into four parts.
quadritubercular [kwod″r -too-bur′ku-l
-too-bur′ku-l r] having four tubercles or cusps.
r] having four tubercles or cusps.
quadrivalent [kwod″r -va’l
-va’l nt] having a valence of four.
nt] having a valence of four.
quadruped [kwod′roo-p d] four-footed; an animal having four feet. See also biped, tetrapod.
d] four-footed; an animal having four feet. See also biped, tetrapod.
q. disease see ulcerative enteritis.
qualimeter an early instrument for measuring the penetrating power of X-rays; penetrometer.
q. data data measured on a categorical scale.
q. trait see qualitative trait.
quality purity of contents, care in presentation and finish of a product.
q. characters features of animal productivity or performance which can be measured quantitatively.
q. inheritance genetic transmission of phenotypes which are quantitative and continuous.
q. trait see quantitative trait.
plain q’s. a horse with fat, rounded hindquarters resembling those of a pig.
quartipara [kwor-tip′ -r
-r ] quadripara.
] quadripara.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
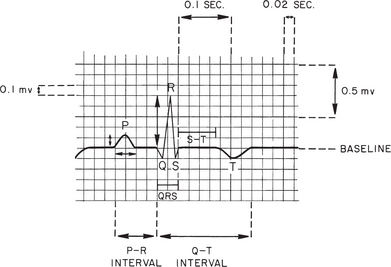
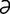 nt] 1. one-quarter of the circumference of a circle. 2. one of four corresponding parts, or quarters, as of the surface of the abdomen or of the field of vision.
nt] 1. one-quarter of the circumference of a circle. 2. one of four corresponding parts, or quarters, as of the surface of the abdomen or of the field of vision.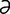 -r
-r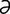 ] a female which has had four pregnancies that resulted in viable offspring; para IV.
] a female which has had four pregnancies that resulted in viable offspring; para IV. -ple′j
-ple′j ] paralysis of all four limbs; tetraplegia. Indicative of spinal cord injury in the upper cervical area. May be acute or gradual in onset depending on the nature of the lesion.
] paralysis of all four limbs; tetraplegia. Indicative of spinal cord injury in the upper cervical area. May be acute or gradual in onset depending on the nature of the lesion. t] one of four offspring produced at one birth. Said of species that normally have single births.
t] one of four offspring produced at one birth. Said of species that normally have single births. -t
-t r] an instrument for measuring the quantity of X-rays generated by a Coolidge tube. The first hot-cathode tube.
r] an instrument for measuring the quantity of X-rays generated by a Coolidge tube. The first hot-cathode tube. -ta“tiv] pertaining to observations of a numerical kind, e.g. 50 kg, 2 m, 24 hands.
-ta“tiv] pertaining to observations of a numerical kind, e.g. 50 kg, 2 m, 24 hands. -te] 1. a characteristic, as of energy or mass, susceptible of precise physical measurement. 2. a measurable amount.
-te] 1. a characteristic, as of energy or mass, susceptible of precise physical measurement. 2. a measurable amount. m] pl. quanta [L.] an elemental unit of energy; the amount emitted or absorbed at each step when energy is emitted or absorbed by atoms or molecules.
m] pl. quanta [L.] an elemental unit of energy; the amount emitted or absorbed at each step when energy is emitted or absorbed by atoms or molecules. n-tēn, kwahr′
n-tēn, kwahr′ n-tēn] 1. a place or period of detention of ships or aircraft coming from infected or suspected ports. 2. restrictions placed on entering or leaving premises or regions where a case of communicable disease exists or is suspected.
n-tēn] 1. a place or period of detention of ships or aircraft coming from infected or suspected ports. 2. restrictions placed on entering or leaving premises or regions where a case of communicable disease exists or is suspected. n] 1. recurring in 4-day cycles (every third day). 2. a variety of intermittent fever of which the paroxysms recur on every third day.
n] 1. recurring in 4-day cycles (every third day). 2. a variety of intermittent fever of which the paroxysms recur on every third day. r] 1. hindquarter. 2. lateral or medial sides of the wall of the hoof of the horse. 3. one of the four individual glands in the udder of a cow.
r] 1. hindquarter. 2. lateral or medial sides of the wall of the hoof of the horse. 3. one of the four individual glands in the udder of a cow. r] an American light horse of compact build and muscular hindquarters, about 15.2 hands high, often chestnut but any solid color. It originated from Thoroughbred and Criollo. Primarily a cattle horse but also used in short sprint races.
r] an American light horse of compact build and muscular hindquarters, about 15.2 hands high, often chestnut but any solid color. It originated from Thoroughbred and Criollo. Primarily a cattle horse but also used in short sprint races.