15 Poisoning
Introduction
Excellent texts on veterinary toxicology and poisoning of domestic animals and free-living species are available.1–6 This short chapter makes no attempt to provide a guide to poisons and their effects, but merely addresses a number of practical issues related to the investigation of alleged poisonings.
The source of the toxic product may, initially, be obscure, as in the case of percutaneous absorption of phenolics from pentachlorophenol-treated wood shaving used for bedding.7 Similarly, suspicious deaths in cage birds may be related to inadvertent poisoning caused by overheating of cooking ware coated with polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or by acrolein or other vapours associated with cooking fats and oils.8
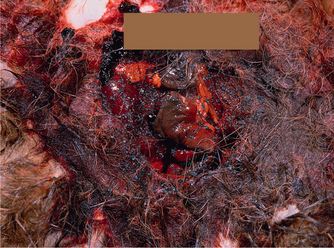
Malicious poisoning of wildlife and domestic animals – raptors, foxes, dogs and cats – is depressingly common and often involves agrochemicals or rodenticides. These deliberate poisonings rely on the target species, or individual, taking bait. Examples are dead rabbits contaminated with carbofuran (Fig. 15.1), or eggs laced with strychnine or organophosphorus insecticide. These baits are, however, indiscriminate and it may be a family dog out for a walk with the children that finds and consumes the poison.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree