PLAGUE
Plague is an acute, highly infectious disease transmitted to humans and animals by the bite of a rat flea. It has been known as bubonic plague and black death.
TRANSMISSION
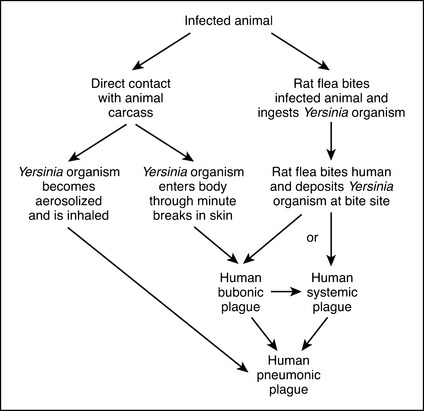
Plague is characterized by periodic outbreaks in a rodent population. A flea transmits Y. pestis bacteria from one animal to another or to humans. When a flea takes a blood meal from an infected host, such as a ground squirrel, it also ingests some of the bacteria that are living in the blood of that host. The bacteria stay in the intestines of the flea, and when it takes another meal it deposits some of the Y. pestis organisms into a new host (Figure 29).
In a population of rodents, some of the rodents are resistant to Y. pestis infection, and others are highly susceptible. As the susceptible rodents become infected and die, the rodent population decreases, and the fleas will look to other animals, or people, as a blood source.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree