CHAPTER 27 Pharmacologic Considerations in the Young Patient
Drug Absorption
Transplacental Transfer
The transfer of drugs from mother to fetus has been demonstrated for a number of drugs, which is a greater concern for drugs with high lipid solubility or that reach high systemic concentrations. The main forces that favor drug transfer from mother to fetus are the lipid solubility of the drug and a steep maternal-fetal drug concentration. However, other properties of the drug may also affect the extent of drug transfer; a list of properties and effects are presented in Table 27-1.
TABLE 27-1 Drug effects on fetus
| Drug property | Effect on drug exposure to the fetus |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight (MW) | |
| Lipid solubility | Only lipid-soluble drugs cross the placental barrier. |
| Ionization | Only nonionized drugs are able to cross the placenta. Weak acid drugs are more likely to transfer.* |
| Protein binding | Only unbound substances are likely to cross the placenta. Decreased maternal albumin increases the amount of free drug and may increase fetal exposure for highly bound drugs. |
* Because fetal circulation is generally more acidic than maternal circulation, weak acid drugs can ionize in the fetus and be trapped. This results in fetal accumulation of weak acid drugs.
Data from Syme MR, Paxton JW, Keelan JA: Drug transfer and metabolism by the human placenta, Clin Pharmacokinet 43(8):487-514, 2004.
Transfer from Milk
Like transplacental transfer of drugs to the fetus, the transfer of drugs from mother’s milk to the neonate can also be a concern. The transfer of the drug to milk is similar to placental transfer of drugs. Weakly acidic drugs that are nonionized and nonprotein bound rapidly transfer from the maternal circulation to milk. Animal milk tends to be more acidic than the plasma pH, therefore drugs that make their way into milk may accumulate because they become ionized and “trapped” in the milk. The neonate may receive a significant dose of drug while nursing, although the amount of drug is generally less than 2% of the maternal dose. It is important to note, however, that the drug present in milk is not necessarily bioavailable and depends again on possible interactions in the neonate’s gastrointestinal tract that might limit drug absorption. Examples of drugs that cross the placenta include anesthetics, such as lidocaine; salicylates and nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs); beta-lactam antibiotics; many narcotics; and anticonvulsants, including phenytoin and diazepam (Table 27-2).
TABLE 27-2 Drugs to avoid in the preterm and lactating animal
| Preterm | Lactating |
|---|---|
Drug Distribution
One obvious difference between neonates and adult animals is the difference in proportion of head-to-body sizes. Body weight is also distributed differently in puppies and kittens, and these differences lead to changes that can present challenges to drug therapy. For example, the proportion of extracellular fluid as a percentage of total body weight changes significantly during the life of a maturing puppy. As seen in Figure 27-1, the changes occurring in the growing puppy (and similarly in the kitten) are a result of the total water alterations as a proportion of body weight. This water is found primarily in the extracellular fluid compared to percent intracellular fluid and will have significant effects on the absorption and distribution of drugs within the animal, including decreased plasma concentrations and longer half-lives. Plasma concentrations of water-soluble compounds are lower in pediatric patients compared with adults because the volume into which the compound is distributed is greater in the young. Unbound lipid-soluble compounds have the same type of distribution because they are distributed into the total body of water.
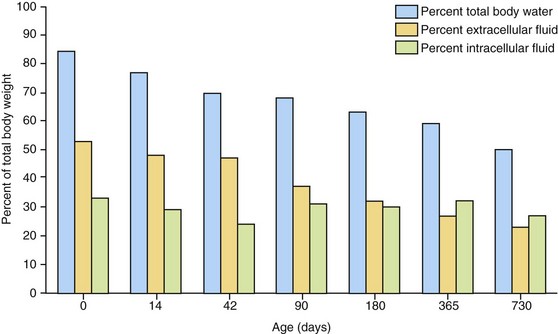
Figure 27-1 Changes in proportion of body weight in extracellular vs. intracellular fluid in maturing puppy.
(Adapted from Boothe DM, Hoskins JD: Drug and blood component therapy. In Hoskins JD: Veterinary pediatrics: dogs and cats from birth to six months, ed 3, Philadelphia, 2001, Saunders, Table 3-2.)
Drug Responses
There is relatively little information on the risks to the fetus associated with giving medications during pregnancy; much of the information available is limited to human medicine. However, there are some general guidelines that have been developed that may be helpful in assessing the impact of drug therapy in this population. Table 27-3 shows drug categories and a description of the effects of the different categories. Table 27-4 lists the general safety of a variety of drugs for use in neonates.
TABLE 27-3 Drug category and description of effects
| Drug category | Description |
|---|---|
| A | Adequate, well-controlled studies in pregnant women have not shown an increased risk of fetal abnormalities. |
| B | Animal studies have revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus; however, there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|