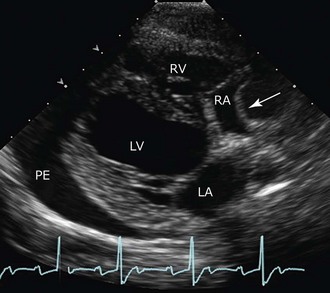
Chapter 182 Echocardiography is especially useful in determining the severity and impact of the effusion, which correlates with clinical severity. The echocardiographic correlate of clinical cardiac tamponade is seen as diastolic collapse of the right atrium and sometimes the right ventricle and is a direct reflection of intrapericardial relative to intracardiac pressures and diminished cardiac filling (Figure 182-1). Prolonged diastolic compression or inversion of the right atrial and ventricular chamber walls is especially notable and usually an indication for immediate pericardiocentesis. Figure 182-1 Image of a 10-year-old golden retriever with signs of cardiac tamponade (from mesothelioma). Arrow shows right atrial wall collapse associated with tamponade. (Right parasternal long axis image at onset of systole.) LA, Left atrium; LV, left ventricle; PE, pericardial effusion; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle.
Pericardial Effusion
Diagnostic Evaluation
Echocardiography
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Pericardial Effusion
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
