P
P2 pulmonic second sound. See heart sounds.
p53 a tumor suppressor gene active in the cellular response to DNA damage and cell cycle arrest.
Po2 oxygen partial pressure (tension); also written PO2, pO2 and pO2. See also blood gas analysis.
π pi, small letter; sixteenth letter in the Greek alphabet.
φ phi, small letter; twenty-first letter in the Greek alphabet.
ψ psi, small letter; twenty-third letter in the Greek alphabet.
P-K reaction Prausnitz-Küstner reaction.
P site see peptidyl-tRNA binding site (under tRNA).
Pa chemical symbol, protactinium; symbol, pascal.
PaO2 symbol for partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood. See also blood gas analysis.
PA inhibitor plasminogen activator inhibitor.
PAB, PABA para-aminobenzoic acid.
PAC Political Action Committee.
flying p. a natural gait of Icelandic horses.
p. cells (1) cells within the heart capable of spontaneous discharge.
uterine p. either of the two regulating centers that control uterine contractions.
pachy- word element. [Gr.] thick.
pachyacria [pak″e-ak′re- ] enlargement of the soft parts of the extremities.
] enlargement of the soft parts of the extremities.
pachyblepharon [pak″e-blef′ -ron] thickening of the eyelids.
-ron] thickening of the eyelids.
pachycephaly [pak″e-sef′ -le] abnormal thickness of the bones of the skull.
-le] abnormal thickness of the bones of the skull.
pachycheilia [pak″e-ki′le- ] thickening of the lips.
] thickening of the lips.
pachychromatic [pak″e-kro-mat′ik] having the chromatin in thick strands.
pachydactyly [pak″e-dak′t -le] megalodactyly.
-le] megalodactyly.
pachyderma [pak″e-dur′m ] abnormal thickening of the skin.
] abnormal thickening of the skin.
p. vesicae thickening of the mucous membrane of the bladder.
pachyglossia [pak″e-glo′se- ] abnormal thickness of the tongue.
] abnormal thickness of the tongue.
pachygyria [pak″e-ji′re- ] see macrogyria.
] see macrogyria.
pachyhematous [pak″e-dur′m -t
-t s] pertaining to or having thickened blood.
s] pertaining to or having thickened blood.
pachyleptomeningitis [pak″e-lep″to-men″in-ji′tis] inflammation of all three meningeal layers.
pachymeninges [pak″e-m -nin′jēz] dura mater.
-nin′jēz] dura mater.
pachymeningitis [pak″e-men″in-ji′tis] inflammation of the dura mater; perimeningitis.
ossifying p. see dural ossification.
pachymeningopathy [pak″e-men″in-gop′ -the] noninflammatory disease of the dura mater.
-the] noninflammatory disease of the dura mater.
pachymeninx [pak″e-me′ninks] the dura mater.
pachynsis [p -kin′sis] an abnormal thickening.
-kin′sis] an abnormal thickening.
pachyonychia [pak″e-o-nik′e- ] abnormal thickening of the nails or claws.
] abnormal thickening of the nails or claws.
pachyperitonitis [pak″e-per″ -to-ni′tis] inflammation and thickening of the peritoneum.
-to-ni′tis] inflammation and thickening of the peritoneum.
pachypleuritis [pak″e-pl
 -ri′tis] fibrothorax.
-ri′tis] fibrothorax.
pachysomia [pak″e-so′me- ] thickening of parts of the body.
] thickening of parts of the body.
pachyvaginitis [pak″e-vaj″ -ni′tis] chronic vaginitis with thickening of the vaginal walls.
-ni′tis] chronic vaginitis with thickening of the vaginal walls.
Pacifastacus leniusculus American crayfish; signal crayfish.
Pacific Coast tick see Dermacentor occidentalis.
Pacific labrador tea Ledum columbianum.
pacinian corpuscle [p -sin′e-
-sin′e- n] cutaneous mechanoreceptors that sense pressure and stretch.
n] cutaneous mechanoreceptors that sense pressure and stretch.
packet knot slip knot; useful for the beginning of a continuous suture.
pad [pad] a cushion-like mass of soft material which may be (1) anatomical; (2) surgical.
Mikulicz’s p. a pad made of folded gauze, for packing off viscera in surgical procedures.
pressure p. in surgery, gauze sponges used to apply pressure in the control of minor hemorrhage.
Padda oryzivora see Java sparrow.
paddock a fenced field or enclosure.
P. fumosoroseus associated with cutaneous and disseminated infections in dogs and cats.
P. varioti an opportunistic fungal infection of the respiratory tract of birds.
PAF platelet activating factor.
Pagrus auratus finfish in family Sparidae. Called also snapper, red sea bream.
-pagus word element. [Gr.] conjoined twins.
PAH, PAHA para-aminohippuric acid.
Pahvant Valley fever see tularemia.
Beagle p. syndrome see steroid responsive meningitis-arteritis.
endogenous p. caused by factors within the body, e.g. stretching of mesentery.
p. receptors free nerve endings of tufts of fine points or buttons.
p. threshold the lowest level at which a stimulus can be applied and cause perceptible pain.
p. tolerance the level of stimulation at which pain becomes intolerable.
paint horse [pānt] see American Paint horse.
paired pertaining to data or animals that are matched as being very similar.
p. controls see paired control.
Pajaroello tick see Ornithodorus coriaceus.
pakoein a toxic cycad glycoside found in Bowenia, Cycas etc.
palae(o)- for words beginning thus see pale(o)-.
cleft p. see cleft lip, cleft palate.
midline defect of p. see cleft lip.
p. reflexes swallowing caused by stimulation of the palate.
palatine, palatal pertaining to the palate. See also palate.
p. slit the caudal half of the palate in birds is divided by a median choanal slit.
palatitis [pal″ -ti′tis] inflammation of the palate.
-ti′tis] inflammation of the palate.
palat(o)- word element. [L.] palate.
palatoglossal [pal″ -to-glos′
-to-glos′ l] pertaining to the palate and tongue.
l] pertaining to the palate and tongue.
p. arch see palatoglossal arch.
palatognathous [pal″ -tog′n
-tog′n -th
-th s] having a congenitally cleft palate.
s] having a congenitally cleft palate.
palatomaxillary [pal″ -to-mak′s
-to-mak′s -lar″e] pertaining to the palate and maxilla.
-lar″e] pertaining to the palate and maxilla.
palatopharyngeal [pal″ -to-f
-to-f -rin′je-
-rin′je- l] pertaining to the palate and pharynx.
l] pertaining to the palate and pharynx.
p. arch see palatopharyngeal arch.
palatoplasty [pal′ -to-plas″te] plastic reconstruction of the palate.
-to-plas″te] plastic reconstruction of the palate.
palatoplegia [pal″ -to-ple′j
-to-ple′j ] paralysis of the palate.
] paralysis of the palate.
palatorrhaphy [pal″ -tor′
-tor′ -fe] surgical correction of a cleft palate.
-fe] surgical correction of a cleft palate.
palatoschisis [pal″ -tos′k
-tos′k -sis] cleft palate.
-sis] cleft palate.
palatum [p -la′t
-la′t m] [L.] palate.
m] [L.] palate.
pale lacking the pink color of normal viable tissue that is perfused with blood.
pale soft exudative pork see porcine stress syndrome.
pale(o)- word element. [Gr.] old.
paleocortex [pa″le-o-kor′teks] paleopallium.
pali(n)- word element. [Gr.] again, pathological repetition.
palindromia [pal″in-dro′me- ] a recurrence or relapse.
] a recurrence or relapse.
palisade worms [pal″ -sād′] see Strongylus.
-sād′] see Strongylus.
palisading giving the appearance of palisades, as in a picket fence.
p. crust alternating horizontal layers of keratin and exudate in a crust or scab.
p. granuloma see palisading granuloma.
palladium (Pd) [p -la′de-
-la′de- m] a chemical element, atomic number 46, atomic weight 106.4. See Table 4.
m] a chemical element, atomic number 46, atomic weight 106.4. See Table 4.
palliate [pal′e-āt] to relieve clinical signs.
palliative [pal′e- -tiv] affording relief; also, a drug that so acts.
-tiv] affording relief; also, a drug that so acts.
central p. the lighter staining central area seen in discoid-shaped erythrocytes of dogs.
Palma christi [pahl′m ] see Ricinus communis.
] see Ricinus communis.
p. nerve block see plantar nerve block.
palmitate [pal′m -tāt] salt or ester of palmitic acid, a common dietary fatty acid.
-tāt] salt or ester of palmitic acid, a common dietary fatty acid.
palmus [pa′m s] 1. palpitation. 2. clonic spasm of limb muscles, producing a jumping motion.
s] 1. palpitation. 2. clonic spasm of limb muscles, producing a jumping motion.
palo santo tree see Bulnesia sarmientii.
palomino [pal-o-me′no] not a breed of horse but a color type of gold with white mane and tail.
palpable [pal′p -b
-b l] perceptible by touch.
l] perceptible by touch.
palpate [pal′pāt] to perform palpation.
palpation [pal-pa′sh n] the technique of examining parts of the body by touching and feeling them.
n] the technique of examining parts of the body by touching and feeling them.
motion p. in chiropractic, examination of the range of movement in vertebral joints.
palpebra [pal′p -br
-br ] pl. palpebrae [L.] eyelid.
] pl. palpebrae [L.] eyelid.
palpebra tertia [pal′p -br
-br ] third eyelid, palpebra III; membrane nictitans.
] third eyelid, palpebra III; membrane nictitans.
palpebral [pal′p -br
-br l] pertaining to the eyelid.
l] pertaining to the eyelid.
p. conjunctiva conjunctiva lining the inner aspect of the eyelid.
p. fissure see palpebral fissure.
medial p. ligament the medial canthal ligament which connects the medial canthus to the orbit.
p. nerve a branch of the auriculopalpebral nerve which innervates the orbicularis oculi muscle of the eyelid and effects eyelid closure. See Table 14.
palpebritis [pal″p -bri′tis] blepharitis.
-bri′tis] blepharitis.
PALS periarteriolar lymphoid sheath. See white pulp.
palustrine a toxic alkaloid in Equisetum spp.
PAM, 2-PAM 2-pyridine aldoxime methchloride (pralidoxime chloride).
pampas grass see Cortaderia selloana.
panacea [pan″ -se′
-se′ ] a remedy for all diseases.
] a remedy for all diseases.
Panaeolina foenisecii see Psilocybe.
panangiitis [pan″an″je-i′tis] inflammation involving all the coats of a vessel.
panarteritis nodosa [pan″ahr″t -ri′tis no-dōs′
-ri′tis no-dōs′ ] see periarteritis nodosa.
] see periarteritis nodosa.
panarthritis [pan″ahr-thri′tis] inflammation of all the joints.
panatrophy [pan-at′r -fe] atrophy of several parts; diffuse atrophy.
-fe] atrophy of several parts; diffuse atrophy.
pancarditis [pan″kahr-di′tis] diffuse inflammation of the heart.
pancreatectomy [pan″kre- -tek′t
-tek′t -me] excision of the pancreas.
-me] excision of the pancreas.
acute p. necrosis see acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis.
p. alpha cells alpha cells cells in the islet of Langerhans which secrete glucagon.
p. anomaly includes acinar hypoplasia and congenital Islet of langerhans aplasia.
p. beta cells beta cells comprise the majority of pancreatic islet cell population; secrete insulin.
p. delta cells cells in the islet of Langerhans; known to secrete somatostatin.
p. F cells secrete pancreatic polytpeptide; called also PP cells.
p. fibrosis a sequel to pancreatitis, pancreatic duct obstruction, zinc poisoning.
p. hypertrophy physiological response to diets high in protein and energy.
p. islets islets of cells scattered through the pancreas; contain alpha, beta, C and D cells.
p. islet cell tumor see gastrinoma, insulinoma.
p. lithiasis see pancreatic calculus (above).
p. trypsin inhibitor see trypsin inhibitor.
pancreatic(o)- [pan″kre-at′ik] word element. [Gr.] pancreatic duct.
pancreaticoduodenal [pan″kre-at″ -ko-doo″o-de′n
-ko-doo″o-de′n l] pertaining to the pancreas and duodenum.
l] pertaining to the pancreas and duodenum.
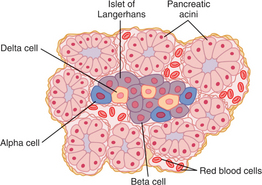
P-3 : Anatomy of pancreatic islets.
From Guyton AC, Hall, JE, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 11th Edition. Saunders, 2005.
pancreatitis [pan″kre-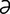 -ti′tis] inflammation of the pancreas; an important disease in dogs and cats.
-ti′tis] inflammation of the pancreas; an important disease in dogs and cats.
chronic p. relapsing or continuing acute pancreatic necrosis. Called also relapsing pancreatitis.
interstitial p. inflammation of the interstitial tissue; may be acute or chronic.
necrotizing p. see acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis (above).
relapsing p. see chronic pancreatitis (see above).
pancreat(o)- word element. [Gr.] pancreas.
pancreatogenous [pan″kre- -toj′
-toj′ -n
-n s] arising in the pancreas.
s] arising in the pancreas.
pancreatolithectomy [pan″kre- -to-l
-to-l -thek′t
-thek′t -me] excision of a calculus from the pancreas.
-me] excision of a calculus from the pancreas.
pancreatolithotomy [pan″kre- -to-l
-to-l -thot′
-thot′ -me] incision of the pancreas for the removal of calculi.
-me] incision of the pancreas for the removal of calculi.
pancreatolysis [pan″kre- -tol′
-tol′ -sis] destruction of pancreatic tissue.
-sis] destruction of pancreatic tissue.
pancreatotomy [pan-kre-at′ -me] incision of the pancreas.
-me] incision of the pancreas.
pancreatotropic [pan″kre- -to-tro′pik] having a special affinity for the pancreas.
-to-tro′pik] having a special affinity for the pancreas.
pancreolithotomy [pan″kre-o-l -thot′
-thot′ -me] pancreatolithotomy.
-me] pancreatolithotomy.
pancreolysis [pan″kre-ol′ -sis] pancreatolysis.
-sis] pancreatolysis.
myelophthisic p. resulting from loss of bone marrow function.
tropical canine p. (TCP) see canine ehrlichiosis.
aplastic p. see aplastic anemia.
pancytopenic relating to pancytopenia.
panda includes the giant panda and red panda (see below).
pandemic [pan-dem′ik] a widespread epidemic, i.e the disease is clustered in time but not in space.
sclerosing p. see old dog encephalitis.
panendoscope [pan-en′do-skōp] a cystoscope that gives a wideangle view of the bladder.
pangola grass Digitaria decumbens.
panhysterectomy [pan″his-t r-ek′t
r-ek′t -me] total hysterectomy.
-me] total hysterectomy.
panhysterosalpingectomy [pan-his″t r-o-sal″pin-jek′t
r-o-sal″pin-jek′t -me] excision of the uterus, cervix and oviducts.
-me] excision of the uterus, cervix and oviducts.
panic grass [pan′ik] grasses that are members of the genus Panicum, e.g. P. antidotale.
bambatsi p.g. Panicum coloratum var. makarikariense.
giant p.g. see Brachiaria mutica.
green p.g. Megathyrsus maximum var. pubiglumis (Panicum maximum var. trichoglume).
panicled redshank Amaranthus cruentus.
P. capillare causes nitrate–nitrite poisoning; called alsowitchgrass.
P. crus-galli reputed to cause photosensitization.
P. purpurascens a coarse, high-producing pasture grass. Called also para grass.
P. virgatum causes hepatogenous photosensitization due probably to steroidal saponins.
panimmunity [pan″ -mu′n
-mu′n -te] immunity to a wide range of bacterial and viral infections.
-te] immunity to a wide range of bacterial and viral infections.
feline p. virus feline parvovirus; the etiologic agent of feline panleukopenia.
panmyeloid [pan-mi′ -loid] pertaining to all elements of the bone marrow.
-loid] pertaining to all elements of the bone marrow.
panmyelophthisis [pan-mi″ -lof′th
-lof′th -sis] aplastic anemia.
-sis] aplastic anemia.
panmyelosis [pan-mi″ -lo′sis] proliferation of all the elements of the bone marrow.
-lo′sis] proliferation of all the elements of the bone marrow.
panniculitis inflammation of the subcutaneous fat. See also opportunistic mycobacterial infection.
lupus p. see lupus erythematosus.
pyogranulomatous p. see opportunist mycobacterial granuloma.
relapsing, febrile, nonsuppurative p. see nodular nonsuppurative panniculitis (above).
sterile p. see nodular nonsuppurative panniculitis (above).
panniculus pl. panniculi [L.] a layer of membrane.
p. muscle see panniculus carnosus (above).
panostosis [pan″os-to′sis] see panosteitis.
panotitis [pan″o-ti′tis] inflammation of all the parts or structures of the ear.
pansinusitis [pan″si-n s-i′tis] inflammation involving all the paranasal sinuses.
s-i′tis] inflammation involving all the paranasal sinuses.
panters atypical interstitial pneumonia of cattle.
panthenol [pan′th -nol] nonproprietary name for pantothenyl alcohol.
-nol] nonproprietary name for pantothenyl alcohol.
p. disease see atypical interstitial pneumonia, Zieria arborescens.
pant(o)- word element. [Gr.] all, the whole.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
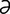 ] a large, plump rodent, brown in color, with three to five lines of white spots down the sides of the body. Called also sooty paca, spotted cavy, Cuniculus paca (formerly Coelogenys spp.).
] a large, plump rodent, brown in color, with three to five lines of white spots down the sides of the body. Called also sooty paca, spotted cavy, Cuniculus paca (formerly Coelogenys spp.).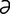 n] enlargements of the arachnoid villi which protrude into the dorsal sagittal sinus, as seen well developed in the horse.
n] enlargements of the arachnoid villi which protrude into the dorsal sagittal sinus, as seen well developed in the horse.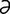 r] 1. an object or substance that controls the rate at which a certain phenomenon occurs; often used alone to indicate an artificial cardiac pacemaker; however, there are other natural and artificial pacemakers. 2. In biochemistry, a pacemaker is a substance whose rate of reaction sets the pace for a series of interrelated reactions.
r] 1. an object or substance that controls the rate at which a certain phenomenon occurs; often used alone to indicate an artificial cardiac pacemaker; however, there are other natural and artificial pacemakers. 2. In biochemistry, a pacemaker is a substance whose rate of reaction sets the pace for a series of interrelated reactions. -chek′ōz] a disease of psittacines caused by a psittacid herpesvirus 1 and characterized by weakness, diarrhea and focal necrosis in the liver and spleen. Intranuclear inclusion bodies in hepatocytes suggest the diagnosis. The disease causes very heavy mortalities.
-chek′ōz] a disease of psittacines caused by a psittacid herpesvirus 1 and characterized by weakness, diarrhea and focal necrosis in the liver and spleen. Intranuclear inclusion bodies in hepatocytes suggest the diagnosis. The disease causes very heavy mortalities. r-mat′o-sēl] plexiform neuroma attaining large size, producing an elephantiasis-like condition.
r-mat′o-sēl] plexiform neuroma attaining large size, producing an elephantiasis-like condition. -ri′tis] chronic inflammation of the ovary and oviduct, with thickening.
-ri′tis] chronic inflammation of the ovary and oviduct, with thickening. -n
-n l-i′tis] inflammation and thickening of the tunica vaginalis of the testis.
l-i′tis] inflammation and thickening of the tunica vaginalis of the testis. -tak′s
-tak′s l] a cell cycle-specific antineoplastic drug; adverse reactions in dogs and cats to the vehicle, Cremophor EL, require careful pretreatment with antihistamines and corticosteroids. Known as TaxolW.
l] a cell cycle-specific antineoplastic drug; adverse reactions in dogs and cats to the vehicle, Cremophor EL, require careful pretreatment with antihistamines and corticosteroids. Known as TaxolW.
 t] the roof of the mouth. The front portion braced by the upper jaw bones (maxillae) is known as the hard palate and forms the partition between the mouth and the nose. The fleshy part arching from the hard palate to the throat is called the soft palate and separates the oropharynx from the nasopharynx. When the animal swallows, the rear of the soft palate swings up against the back of the pharynx and blocks the passage of food and air to the nose. See also soft palate.
t] the roof of the mouth. The front portion braced by the upper jaw bones (maxillae) is known as the hard palate and forms the partition between the mouth and the nose. The fleshy part arching from the hard palate to the throat is called the soft palate and separates the oropharynx from the nasopharynx. When the animal swallows, the rear of the soft palate swings up against the back of the pharynx and blocks the passage of food and air to the nose. See also soft palate. -bel′
-bel′ m] originally, the phylogenetically older parts of the cerebellum; the term is now applied specifically to those parts whose afferent inflow is predominantly supplied by spinocerebellar fibers.
m] originally, the phylogenetically older parts of the cerebellum; the term is now applied specifically to those parts whose afferent inflow is predominantly supplied by spinocerebellar fibers. -net′ik] originated in the past; not newly acquired; said of traits, structures, etc., of species.
-net′ik] originated in the past; not newly acquired; said of traits, structures, etc., of species. -net′ik] old kinetic; a term applied to the nervous motor mechanism concerned in automatic associated movements.
-net′ik] old kinetic; a term applied to the nervous motor mechanism concerned in automatic associated movements. m] that part of the pallium (cerebral cortex) developing with the archipallium in association with the olfactory system; it is phylogenetically older and less stratified than the neopallium, and composed chiefly of the piriform cortex and parahippocampal gyrus. Called also paleocortex.
m] that part of the pallium (cerebral cortex) developing with the archipallium in association with the olfactory system; it is phylogenetically older and less stratified than the neopallium, and composed chiefly of the piriform cortex and parahippocampal gyrus. Called also paleocortex. -thol′
-thol′ -je] study of disease in bodies that have been preserved from ancient times.
-je] study of disease in bodies that have been preserved from ancient times. m] the phylogenetically older portion of the corpus striatum, represented by the globus pallidus.
m] the phylogenetically older portion of the corpus striatum, represented by the globus pallidus. -m
-m s] the phylogenetically older part of the thalamus, i.e. the medial portion which lacks reciprocal connections with the neopallium.
s] the phylogenetically older part of the thalamus, i.e. the medial portion which lacks reciprocal connections with the neopallium. -ko-u′re-
-ko-u′re- ] South American plant genus in the family Rubiaceae; contain fluoroacetate, a cause of myocardial damage and sudden death; includes P. aeneofusca, P. grandiflora, P. juruana, P. marcgravii, cafezinho, cafe bravo, erva cafe, erva de rato, roxa, roxinha, roxona, vick.
] South American plant genus in the family Rubiaceae; contain fluoroacetate, a cause of myocardial damage and sudden death; includes P. aeneofusca, P. grandiflora, P. juruana, P. marcgravii, cafezinho, cafe bravo, erva cafe, erva de rato, roxa, roxinha, roxona, vick. -d
-d m] the globus pallidus, the medial subdivision of the lentiform nucleus, of the brain.
m] the globus pallidus, the medial subdivision of the lentiform nucleus, of the brain. m] the cerebral cortex viewed in its entirety, i.e. the mantle of gray matter covering both cerebral hemispheres. Also, the cerebral cortex during its development.
m] the cerebral cortex viewed in its entirety, i.e. the mantle of gray matter covering both cerebral hemispheres. Also, the cerebral cortex during its development. r] paleness, as of the skin or mucosae. Although it is commonly associated with anemia, many long-term cases show mucosae of normal color; pallor is also a common sign in shock.
r] paleness, as of the skin or mucosae. Although it is commonly associated with anemia, many long-term cases show mucosae of normal color; pallor is also a common sign in shock. r] descriptive of the palm of the human hand, or of the homologous surface or direction of the limbs of other animal species.
r] descriptive of the palm of the human hand, or of the homologous surface or direction of the limbs of other animal species. r] a side effect of some chemotherapy drugs caused by capillary leakage of the drug into tissues, particularly the hands and feet in humans and the paws or feet in animals. Tissue damage results in redness, swelling and blisters. Tingling or burning is reported in humans.
r] a side effect of some chemotherapy drugs caused by capillary leakage of the drug into tissues, particularly the hands and feet in humans and the paws or feet in animals. Tissue damage results in redness, swelling and blisters. Tingling or burning is reported in humans. r] a scheme for charting the position and number of teeth. A horizontal line indicates the occlusal plane and a vertical line in the middle indicates the midline. The teeth in each quadrant are numbered, starting from the point closest to the midline.
r] a scheme for charting the position and number of teeth. A horizontal line indicates the occlusal plane and a vertical line in the middle indicates the midline. The teeth in each quadrant are numbered, starting from the point closest to the midline. -tin] glycerol tripalmitate, one of the common fats in animal fat. A crystallizable and saponifiable substance.
-tin] glycerol tripalmitate, one of the common fats in animal fat. A crystallizable and saponifiable substance. -to-le′ik] a 16-carbon monounsaturated, with a double bond at carbons 7,8, endogenously synthesized nonessential fatty acid.
-to-le′ik] a 16-carbon monounsaturated, with a double bond at carbons 7,8, endogenously synthesized nonessential fatty acid.
 -dro′nāt] a bisphosphonate used in the management of hypercalcemia and to alleviate osteolytic pain of osteosarcomas in dogs.
-dro′nāt] a bisphosphonate used in the management of hypercalcemia and to alleviate osteolytic pain of osteosarcomas in dogs. -gloo′t
-gloo′t -nin] an agglutinin that agglutinates the erythrocytes of all human blood groups.
-nin] an agglutinin that agglutinates the erythrocytes of all human blood groups. -nom′ik] pertaining to or affecting the entire autonomic (sympathetic and parasympathetic) nervous system.
-nom′ik] pertaining to or affecting the entire autonomic (sympathetic and parasympathetic) nervous system. -me] excision of the entire colon, with creation of an outlet from the ileum on the body surface.
-me] excision of the entire colon, with creation of an outlet from the ileum on the body surface. s] a large, elongated, racemose gland located in the anterior abdomen between the liver, kidneys, stomach, spleen and duodenum. The pancreas is composed of both exocrine and endocrine tissue. The acini secrete digestive enzymes, and small ductules leading from the acini secrete ions, mainly sodium and bicarbonate. The combined product, pancreatic juice, enters a long pancreatic duct and from there is transported duct to the duodenum. The pancreatic juice contains enzymes for the breakdown of proteins, carbohydrates and fats. The bicarbonate ions in the pancreatic secretion help neutralize the acidic chyme that is passed along from the stomach to the duodenum. The endocrine functions of the pancreas are related to the islets of Langerhans which occur throughout the pancreas. These small islands contain three major types of cells: the alpha, beta and delta cells. The alpha cells secrete the hormone glucagon, which elevates blood sugar. The beta cells secrete insulin, which affects the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. The delta cells secrete somatostatin, the functions of which are not fully understood, but it is known that it can inhibit the secretion of both glucagon and insulin and may act as a controller of metabolic processes. The somatostatin produced by the delta cells of the pancreas is the same as that produced by the hypothalamus as an inhibitor of the release of growth hormone from the pituitary gland.
s] a large, elongated, racemose gland located in the anterior abdomen between the liver, kidneys, stomach, spleen and duodenum. The pancreas is composed of both exocrine and endocrine tissue. The acini secrete digestive enzymes, and small ductules leading from the acini secrete ions, mainly sodium and bicarbonate. The combined product, pancreatic juice, enters a long pancreatic duct and from there is transported duct to the duodenum. The pancreatic juice contains enzymes for the breakdown of proteins, carbohydrates and fats. The bicarbonate ions in the pancreatic secretion help neutralize the acidic chyme that is passed along from the stomach to the duodenum. The endocrine functions of the pancreas are related to the islets of Langerhans which occur throughout the pancreas. These small islands contain three major types of cells: the alpha, beta and delta cells. The alpha cells secrete the hormone glucagon, which elevates blood sugar. The beta cells secrete insulin, which affects the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats. The delta cells secrete somatostatin, the functions of which are not fully understood, but it is known that it can inhibit the secretion of both glucagon and insulin and may act as a controller of metabolic processes. The somatostatin produced by the delta cells of the pancreas is the same as that produced by the hypothalamus as an inhibitor of the release of growth hormone from the pituitary gland. -ko-en″t
-ko-en″t r-os′t
r-os′t -me] anastomosis of the pancreatic duct to the intestine.
-me] anastomosis of the pancreatic duct to the intestine. -ko-me″zo-j
-ko-me″zo-j -joo′n
-joo′n l] an anomalous structure that extends between the pancreaticoduodenal vein, under the ileum and colon, to the left side of the mesojejunum. Reported to be the cause of diarrhea in kittens.
l] an anomalous structure that extends between the pancreaticoduodenal vein, under the ileum and colon, to the left side of the mesojejunum. Reported to be the cause of diarrhea in kittens. -tin] a substance from the pancreas of the hog or ox containing enzymes, principally amylase, protease and lipase; used in the treatment of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency.
-tin] a substance from the pancreas of the hog or ox containing enzymes, principally amylase, protease and lipase; used in the treatment of pancreatic exocrine insufficiency. -to-doo″o-d
-to-doo″o-d -nek′t
-nek′t -me] excision of the head of the pancreas along with the encircling loop of the duodenum.
-me] excision of the head of the pancreas along with the encircling loop of the duodenum.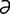 -to-l
-to-l -thi′
-thi′ -sis] the presence of calculi in the ductal system or parenchyma of the pancreas.
-sis] the presence of calculi in the ductal system or parenchyma of the pancreas. m] a non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent, used as the bromide salt.
m] a non-depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent, used as the bromide salt. ] abnormal depression of all the cellular elements of the blood. Results from the depression of activity of bone marrow, spleen and lymph nodes such as occurs in radiation injury and a number of poisonings, e.g. Pteridium aquilinum, trichlorethylene extracted soybean meal, nitrofurans and stachybotrytoxicosis.
] abnormal depression of all the cellular elements of the blood. Results from the depression of activity of bone marrow, spleen and lymph nodes such as occurs in radiation injury and a number of poisonings, e.g. Pteridium aquilinum, trichlorethylene extracted soybean meal, nitrofurans and stachybotrytoxicosis. n-sef″
n-sef″ -li′tis] encephalitis with parenchymatous lesions of both the gray and white matter of the brain.
-li′tis] encephalitis with parenchymatous lesions of both the gray and white matter of the brain. ] a genus of flies in the family Tabanidae; some feed on blood and cause insect worry in horses and cattle. Called also deer fly. Do not suck blood but will mop up spilled blood.
] a genus of flies in the family Tabanidae; some feed on blood and cause insect worry in horses and cattle. Called also deer fly. Do not suck blood but will mop up spilled blood. -too′
-too′ -t
-t -riz-
-riz- m] generalized hypopituitarism due to absence or damage to the pituitary gland, which in its complete form, leads to absence of gonadal function and insufficiency of thyroid and adrenal function. When cachexia is a prominent feature, it is called Simmonds′ disease or pituitary cachexia.
m] generalized hypopituitarism due to absence or damage to the pituitary gland, which in its complete form, leads to absence of gonadal function and insufficiency of thyroid and adrenal function. When cachexia is a prominent feature, it is called Simmonds′ disease or pituitary cachexia. r-o-sal″ping-go-o″of-
r-o-sal″ping-go-o″of- – rek′t
– rek′t -me] excision of the uterus, cervix, oviducts and ovaries.
-me] excision of the uterus, cervix, oviducts and ovaries. -kum] a genus of grasses in the family Poaceae. May contain sufficient nitrate or oxalate to cause poisoning with these substances. They are highly productive and popular annual and perennial grasses and cereal crops but many of them cause hepatogenous photosensitization due probably to a high content of steroidal saponins in the plants. Edematous enlargement and icteric staining of the cranial tissues gives rise to the common names of yellow bighead and yellow thickhead. Some contain calcium oxalate crystals and cause equine nutritional secondary hyperparathyroidism. See also Megathrysus.
-kum] a genus of grasses in the family Poaceae. May contain sufficient nitrate or oxalate to cause poisoning with these substances. They are highly productive and popular annual and perennial grasses and cereal crops but many of them cause hepatogenous photosensitization due probably to a high content of steroidal saponins in the plants. Edematous enlargement and icteric staining of the cranial tissues gives rise to the common names of yellow bighead and yellow thickhead. Some contain calcium oxalate crystals and cause equine nutritional secondary hyperparathyroidism. See also Megathrysus. ] 1. abnormal depression in numbers of white blood cells. 2. the name of a disease caused by feline parvovirus; see feline panleukopenia.
] 1. abnormal depression in numbers of white blood cells. 2. the name of a disease caused by feline parvovirus; see feline panleukopenia. s] 1. chronic superficial keratitis. 2. an inflammatory exudate overlying synovial cells on the inside of a joint capsule, usually occurring in rheumatoid arthritis or related articular rheumatism. 3. panniculus adiposus.
s] 1. chronic superficial keratitis. 2. an inflammatory exudate overlying synovial cells on the inside of a joint capsule, usually occurring in rheumatoid arthritis or related articular rheumatism. 3. panniculus adiposus.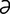 l-mi′tis] inflammation of ocular structures and tissues from within all three of the tunics. Compare with endophthalmitis.
l-mi′tis] inflammation of ocular structures and tissues from within all three of the tunics. Compare with endophthalmitis. -ti′tis] 1. inflammation of body fat. 2. a disease of cats and aquarium fish fed on a diet high in polyunsaturated fats and low in vitamin E. In cats there is inflammation of all fat tissues; in fish there is also thickening of the swim bladder. See also yellow fat disease.
-ti′tis] 1. inflammation of body fat. 2. a disease of cats and aquarium fish fed on a diet high in polyunsaturated fats and low in vitamin E. In cats there is inflammation of all fat tissues; in fish there is also thickening of the swim bladder. See also yellow fat disease.