CHAPTER 20 Ophthalmic Instruments
This chapter covers instruments that are used in ophthalmic surgery and in neurosurgery, but it is not a comprehensive list of the instruments that an ophthalmologist or neurosurgeon would have.
INSTRUMENT
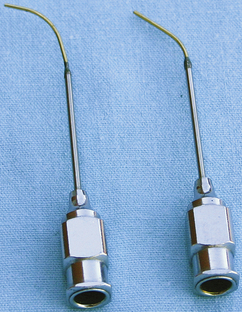
Lacrimal Cannula
| FUNCTION | To flush the lacrimal duct; it can also be used to flush the anal gland duct. |
| CHARACTERISTICS | A regular aluminum hub and needle shaft has a copper tube attached to the end that tapers the diameter of the shaft down to 23- and 30-gauge diameters. The cannula is available with a straight or an angled shaft. |
INSTRUMENT
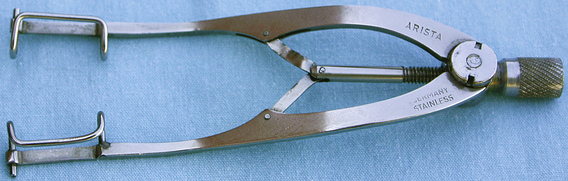
Eye Speculum
| FUNCTION | To hold the eyelids apart for ophthalmic examination or surgery. |
| CHARACTERISTICS | Gently curved ends are designed to slide under each eyelid; a spring device or a turning knob spreads the eyelids apart. There are several versions of eye speculums: Castroviejo, Graefe, and Barraquer. |
INSTRUMENT
Castroviejo Needle Holder with Catch
| FUNCTION | To hold the fine suture needles required for placing sutures in an eye and performing neurosurgery. |
| CHARACTERISTICS | Jaws that hold fine needles are attached to spring-loaded handles that catch or release with gentle pressure. |
INSTRUMENT
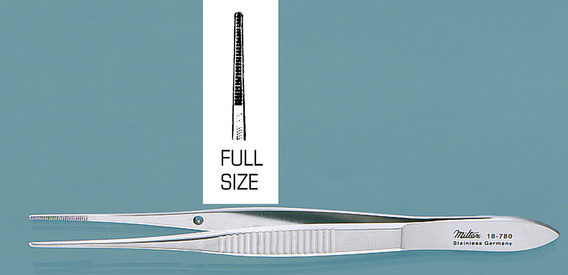
Eye-Dressing Forceps
| FUNCTION | To apply dressing materials to ophthalmic areas. |
| CHARACTERISTICS | This forceps looks exactly like the dressing forceps found in regular surgical packs, but it is smaller and has finer jaws. It causes trauma to tissues and should be used to handle only inanimate objects. It may be straight or curved; sizes range from 4¾ to 6 inches. |
INSTRUMENT
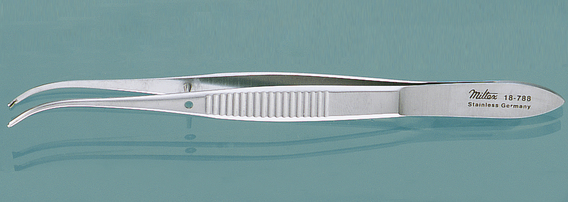
Half-Curved Tissue Forceps (1 × 2 Teeth)
| FUNCTION | To pick up tissue without causing trauma. |
| CHARACTERISTICS | This forceps looks exactly like the tissue forceps found in regular surgical packs, but it is smaller and has finer jaws. The structure of the teeth allows tissue to be picked up without causing trauma. It ranges in length from 4¾ to 6 inches. The teeth in the jaws may be 1 × 2 or 2 × 3. The forceps may be straight or curved. |
INSTRUMENT
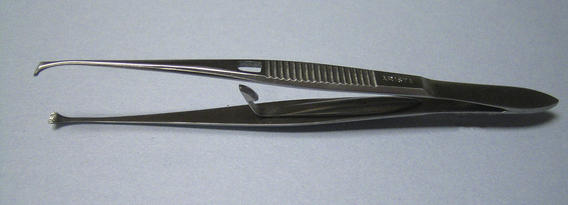
Graefe Eye-Fixation Forceps with Catch
| FUNCTION | To grasp and hold tissues in an atraumatic manner. |
| CHARACTERISTICS | A combination of Allis tissue forceps and tissue forceps, the jaws of the Graefe forceps are configured like the Allis forceps and the handles like the tissue forceps. The catch is designed to hold when the handles are pressed together; it is released by flicking the catch with a finger. |
INSTRUMENT
Serrefine
| FUNCTION | To hold and crush tissues, occlude small vessels, or to tag and hold bridal or fine sutures. |
| COMMON NAME | Bulldog Clamp |
| CHARACTERISTICS | The jaws are similar to those of the other hemostatic forceps and also may be straight or curved. It functions when the handles are squeezed; that opens the jaws in a crossover motion. Similar forceps are known as Dieffenbach, DeBakey, Glover, and Johns Hopkins forceps. |
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree