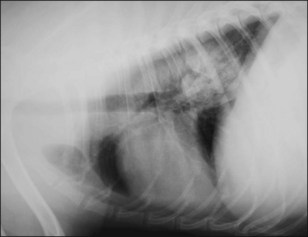
6 Oesophageal foreign body in a dog
Problem list and discussion of problems
Differential diagnosis
Causes of regurgitation include:
• Pharyngeal disorders
• pharyngeal obstructive disorders, such as foreign bodies, tonsillar neoplasia or retropharyngeal lymphadenopathy
• Oesophageal disorders
• oesophageal obstructive disorders, such as foreign bodies, stricture, neoplasia, vascular ring anomalies, perioesophageal masses
Differential diagnoses for halitosis include:
Minimum data base
Imaging
Thoracic and abdominal radiographs showed a foreign body of mineral density in the caudal oesophagus at the level of the diaphragmatic hiatus (Figs 6.1 and 6.2) and another foreign body of mineral bone density inside the stomach. There was no evidence of aspiration pneumonia and no evidence of mediastinitis or pneumomediastinum, so the foreign body did not appear to have penetrated the oesophagus.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree