O
O chemical symbol, oxygen; [L.] oculus (eye); [L.] octarius (pint); opening.
Ω the Greek capital letter omega; symbol for ohm.
ω omega, small letter; twenty-fourth letter in the Greek alphabet.
O-F test see oxidation-fermentation test.
poison o. Toxicodendron diversilobum, T. quercifolium.
oat [ōt] member of the plant genus Avena in the family Poaceae.
o. grass Avena pubescens. See also oatgrass.
o. hulls a high-fiber, low-protein, low-energy feed.
oaten pertaining to or emanating from oats.
ob- word element. [L.] against, in front of, towards.
obcecation [ob“se-ka’sh n] incomplete blindness.
n] incomplete blindness.
Obeliscoides a genus of nematodes in the family Trichostrongylidae.
O. cuniculi found in the stomach of rabbits; in heavy infestations causes gastritis.
obese [o-bēs’] characterized by obesity.
o. fold pyoderma see fold dermatitis.
obligate [ob’l -gāt] necessary, essential.
-gāt] necessary, essential.
o. accumulators see accumulator plants.
obligatory [ b-lig’
b-lig’ -tor“e] unavoidable; something that is bound to occur.
-tor“e] unavoidable; something that is bound to occur.
oblique [o-blēk’ ] slanting; inclined.
obliquity [o-blik’w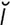 -te] the state of being oblique or slanting.
-te] the state of being oblique or slanting.
oblongata [ob“long-gah’t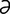 ] medulla oblongata. See also brain.
] medulla oblongata. See also brain.
Obodhiang virus a rhabdovirus closely related to rabies virus.
obstetric, obstetrical [ob-stet’rik] pertaining to or emanating from obstetrics.
o. chains see obstetric chain.
o. saw wire saw used in fetotomes. There are two types, Swedish and Gigli wire saws.
obstipation [ob“st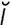 -pa’sh
-pa’sh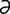 n] intractable constipation.
n] intractable constipation.
ventricular outflow o. see ventricular outflow obstruction.
obstructive having the characteristic of obstruction.
o. pulmonary disease see chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
obstruent [ob’stroo- nt] 1. causing obstruction. 2. any agent or agency that causes obstruction.
nt] 1. causing obstruction. 2. any agent or agency that causes obstruction.
obtund [ob-tund’] to render dull or blunt.
obtundation [ob“t n-da’sh
n-da’sh n] depression as a result of intracranial disease.
n] depression as a result of intracranial disease.
obturating pertaining to, having the characteristic of obturation.
o. muscles the muscles that rotate the thigh laterally. See also Table 13.
o. nerve degeneration causes permanent obturator nerve paralysis (below).
o. bone the unpaired bone constituting the back and part of the base of the skull. See also Table 10.3.
o. crest see external occipital crest.
o. fracture see basisphenoid fracture.
occipitalization [ok-sip“ -t
-t l-
l- -za’sh
-za’sh n] synostosis of the atlas with the occipital bone.
n] synostosis of the atlas with the occipital bone.
occipitoatlantal of or relating to the occipital bone of the skull and the atlas cervical vertebrae.
occipitoatlantoaxial pertaining to the occiput, the atlas and the axis.

O-1: Obturator paralysis.
From Dyce KM, Sack W, Wensing CJG, Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy, 3rd Edition. Saunders, 2002.
o. malformation see atlanto-occipital malformation of Arab horses.
occipitocervical [ok-sip“ -to-sur’v
-to-sur’v -k
-k l] pertaining to the occiput and neck.
l] pertaining to the occiput and neck.
occipitofrontal [ok-sip“ -to-fron’t
-to-fron’t l] pertaining to the occiput and the forehead.
l] pertaining to the occiput and the forehead.
occipitomastoid [ok-sip“ -to-mas’toid] pertaining to the occipital bone and mastoid process.
-to-mas’toid] pertaining to the occipital bone and mastoid process.
occipitomental [ok-sip“ -to-men’t
-to-men’t l] pertaining to the occiput and chin.
l] pertaining to the occiput and chin.
occipitotemporal [ok-sip“ -to-tem’p
-to-tem’p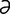 -r
-r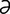 l] pertaining to the occipital and temporal bones or regions.
l] pertaining to the occipital and temporal bones or regions.
occipitothalamic [ok-sip“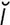 -to-th
-to-th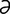 -lam’ik] pertaining to the occipital lobe and thalamus.
-lam’ik] pertaining to the occipital lobe and thalamus.
occlude [ -klōōd’ ] to fit close together; to close tight; to obstruct or close off.
-klōōd’ ] to fit close together; to close tight; to obstruct or close off.
occlusio pupillae pupil occlusion; a complete fibrovascular membrane across the pupil.
coronary o. see coronary occlusion.
traumatic o. any abnormality of occlusion which causes injury to structures within the mouth.
occlusive [ -kloo’siv] pertaining to or effecting occlusion.
-kloo’siv] pertaining to or effecting occlusion.
occult [ -kult’] obscure or hidden from view.
-kult’] obscure or hidden from view.
occupation time parameter for usage of pens in a feedlot.
OCD osteochondrosis dissecans.
ocelli simple eyes of insects.
Ochroconis galloparvum a genus of dematiaceous members of the Fungi Imperfecti.
ochrometer [o-krom’ -t
-t r] an instrument for measuring capillary blood pressure.
r] an instrument for measuring capillary blood pressure.
Ochsner forceps a strongly built, curved hemostat with rat-tooth tips to the blades.
OCT ornithine carbamoyl transferase, a liver specific enzyme.
octa- word element. [Gr., L.] eight.
octachloronaphthalene one of the toxic highly chlorinated naphthalenes.
octadepsipeptides see emodepside.
octan occurring on the eighth day (every 7 days).
13C-o. acid breath test an indirect measure of gastric emptying.
octavalent [ok“t -va’l
-va’l nt] having a valency of 8.
nt] having a valency of 8.
ocular [ok’u-l r] 1. pertaining to the eye. 2. eyepiece (of a microscope).
r] 1. pertaining to the eye. 2. eyepiece (of a microscope).
extrinsic o. muscles see extraocular muscles. See also Table 13.1F.
o. filariasis see thelaziasis, onchocercosis.
o. lymphomatosis see Marek’s disease.
o. neurectoderm ectoderm which gives rise to ocular tissues.
o.-skeletal dysplasia see oculoskeletal dysplasia.
ocul(o)- word element. [L.] eye.
oculocentesis paracentesis of the eye (aqueocentesis, sub-retinal aspirate, vitreocentesis).
oculocephalic reflex see doll’s eye reflex.
oculocutaneous [ok“u-lo-ku-ta’ne- s] pertaining to or affecting both the eyes and the skin.
s] pertaining to or affecting both the eyes and the skin.
oculofacial [ok“u-lo-fa’sh l] pertaining to the eyes and face.
l] pertaining to the eyes and face.
oculogyration [ok“u-lo-ji-ra’sh n] the movement of the eye about the anteroposterior axis.
n] the movement of the eye about the anteroposterior axis.
oculomotor [ok“u-lo-mo’t r] pertaining to or affecting eye movements.
r] pertaining to or affecting eye movements.
o. nerve the third cranial nerve; it contains motor and parasympathetic fibers. Various branches of the oculomotor nerve provide for muscle movement in most of the extraocular and intraocular muscles and resulting in globe movement, constriction of the pupil, accommodation and eyelid opening. See also Table 14.
oculomotorius the oculomotor nerve.
oculomycosis [ok“u-lo-mi-ko’sis] any fungal disease of the eye.
oculonasal [ok“u-lo-na’s l] pertaining to the eye and the nose.
l] pertaining to the eye and the nose.
oculopupillary [ok“u-lo-pu’p -lar-e] pertaining to the pupil of the eye.
-lar-e] pertaining to the pupil of the eye.
oculovestibulocephalic reflex [ok“u-lo-ves-tib’u-lo-s -fal’ik re’fleks] see doll’s eye reflex.
-fal’ik re’fleks] see doll’s eye reflex.
oculozygomatic [ok“u-lo-zi“go-mat’ik] pertaining to the eye and the zygoma.
oculus [ok’u-l s] pl. oculi [L.] eye.
s] pl. oculi [L.] eye.
OD 1. [L.] oculus dexter (right eye). 2. overdose.
oddi sphincter see sphincter of Oddi.
oddments in wool marketing includes locks, bellies, crutchings, stained wool.
posterior o. probability determined after consideration of the results of a study.
Odland’s bodies keratinosomes.
Odocoileostrongylus tenuis see Parelaphostrongylus tenuis.
odontalgia [o-don-tal’j ] pain in a tooth; toothache.
] pain in a tooth; toothache.
odontectomy [o“don-tek’t -me] extraction of a tooth.
-me] extraction of a tooth.
odontic [o-don’tik] pertaining to the teeth.
odont(o)- word element. [Gr.] tooth.
odontoblastic emanating from or pertaining to odontoblast.
o. layer the epithelioid layer of odontoblasts in contact with the dentin of teeth.
o. processes see dentinal fibers.
odontogenesis [o-don“to-jen’ -sis] the origin and development of the teeth.
-sis] the origin and development of the teeth.
o. imperfecta dentinogenesis imperfecta.
odontogenic [o-don“to-jen’ik] 1. forming teeth. 2. arising in tissues that give origin to the teeth.
odontoid [o-don’toid] like a tooth.
o. process see odontoid process.
odontologist [o“don-tol’ -jist] dentist.
-jist] dentist.
odontology [o“don-tol’ -je] 1. scientific study of the teeth. 2. dentistry.
-je] 1. scientific study of the teeth. 2. dentistry.
odontolysis [o-don-tol’ -sis] the resorption of dental tissue.
-sis] the resorption of dental tissue.
ameloblastic o. contains true neoplastic ameloblastic tissue. See ameloblastic odontoma.
complex o. all the dental tissues are represented but not in an organized form.
composite o. one consisting of both enamel and dentin in an abnormal pattern.
compound o. all the dental tissues are present and organized into denticles, tooth-like structures.
radicular o. one associated with a tooth root, or formed when the root was developing.
odontopathy [o“don-top’ -the] any disease of the teeth.
-the] any disease of the teeth.
odontoplasty [o-don’to-plas“te] remodeling of a tooth involving the removal of enamel.
odontoprisis [o-don“to-pri’sis] see bruxism.
odontosis [o“don-to’sis] formation or eruption of the teeth.
odontotomy [o“don-tot’ -me] incision of a tooth.
-me] incision of a tooth.
butyric acid o. odor of rancid butter.
irradiation o. meat sterilized by irradiation may develop a hydrogen sulfide odor.
odorant [o’d r-
r- nt] any substance capable of stimulating the sense of smell.
nt] any substance capable of stimulating the sense of smell.
-odynia word element. [Gr.] pain.
odynometer [o“din-om’ -t
-t r] an instrument for measuring pain; see also algometer.
r] an instrument for measuring pain; see also algometer.
odynophagia [od“ -no-fa’j
-no-fa’j ] painful swallowing of food.
] painful swallowing of food.
oe- for words beginning thus, see also those beginning e-.
Oedemagena a genus of flies similar to Hypoderma spp.
oenanthetol one of the poisonous alcohols in the plant Oenanthe crocata.
oenanthetone one of the poisonous alcohols in the plant Oenanthe crocata.
Oesophagodontus [e-sof“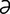 -go-don’t
-go-don’t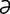 s] a nematode genus in the family Strongylidae.
s] a nematode genus in the family Strongylidae.
O. robustus one of the large strongyles of horses. Causes strongylosis.
oesophagus [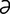 -sof’
-sof’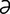 -g
-g s] see esophagus.
s] see esophagus.
Oestromyia leporina a fly similar to Hypoderma spp. Which parasitizes moles and muskrats.
Oestrus a genus of bot flies in the family Oestridae.
off feed the animal’s food intake is less than normal.
off-flavor abnormal unappetizing flavor.
off-patent drugs see generic (2).
off-shears said of sheep which have been recently shorn.
Office International des Epizooties (OIE) see World Organisation for Animal Health.
offspring progeny generally; includes calf, lamb, kid, pig, foal, chicken, poult, duckling, puppy, kitten, cria. See also Table 16.
ofloxacin [o-flok’s -sin] a second generation fluoroquinolone antibiotic.
-sin] a second generation fluoroquinolone antibiotic.
Ogmocotyle a genus of intestinal flukes (digenetic trematodes) in the family Notocotylidae.
Ohara’s disease [o-hah’rah] see tularemia.
OHE medical record abbreviation for ovariohysterectomy.
ohmmeter [ōm’me-t r] an instrument that measures electrical resistance in ohms.
r] an instrument that measures electrical resistance in ohms.
-oid suffix meaning resembling.
OIE Office International des Epizooties. See World Organisation for Animal Health.
OIF ovulation induction factor.
automobile o. see crankcase oil (below).
o. of chenopodium extracted from the plant Chenopodium ambrosioides. An old-time anthelmintic.
diesel and fuel o. see crude oil.
ethereal o. see essential oil (above).
fixed o. an oil that does not evaporate on warming and occurs as a solid, semisolid or liquid.
o. gland see uropygial glands.
irritant o. occurs in plants; causes gastroenteritis; includes bryonin, croton and castor oils.
sump o. see crankcase oil (above).
sweet birch o. see methyl salicylate.
turpentine o. see turpentine oil.
o. of Wintergreen see methyl salicylate.
yew o. an irritant oil in Taxus spp., but not the principal toxin in that plant—taxine is.
OL [L.] oculus laevus (left eye).
-ol word termination indicating an alcohol or a phenol.
olamine [ol’ -mēn] USAN contraction for ethanolamine.
-mēn] USAN contraction for ethanolamine.
olaquindox a growth stimulant used as a feed additive for pigs.
Olax benthamiana Australian plant in the family Olacaceae; causes cyanide poisoning.
old dog encephalitis see old dog encephalitis.
Old English mastiff see Mastiff.
old man’s beard Clematis vitalba.
old tuberculin see tuberculin.
oleaginous [o“le-aj’ -n
-n s] oily; greasy.
s] oily; greasy.
oleander [o“le-an’d r] Nerium oleander, but also used in the common name of other plants.
r] Nerium oleander, but also used in the common name of other plants.
yellow o. Cascabela thevetia (Thevetia peruviana).
oleandroside a digitoxin-like glycoside, one of the toxic substances in Nerium oleander.
oleate [o’le-āt] 1. a salt of oleic acid. 2. a solution of a substance in oleic acid.
olecranarthritis [o-lek“r n-ahr-thri’tis] inflammation of the elbow joint.
n-ahr-thri’tis] inflammation of the elbow joint.
olecranarthropathy [o-lek“r n-ahr-throp’ah-the] disease of the elbow joint.
n-ahr-throp’ah-the] disease of the elbow joint.
olecranoid [o-lek’r -noid] resembling the olecranon.
-noid] resembling the olecranon.
olecranon [o-lek’r -non] the bony projection of the ulna at the elbow.
-non] the bony projection of the ulna at the elbow.
ole(o)- word element. [L.] oil.
oleo oil the oily fraction of rendered animal fat.
oleostearin a firm fraction of rendered animal fat, used in margarine manufacture.
oleotherapy [o“le-o-ther’ -pe] treatment with oil, particularly by injection.
-pe] treatment with oil, particularly by injection.
oleothorax [o“le-o-tho’raks] intrapleural injection of oil to compress and inactivate the lung.
oleum [o’le-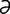 m] pl. olea [L.] oil.
m] pl. olea [L.] oil.
olfact- [ol’fakt] prefix meaning sense of smell.
olfaction [ol-fak’sh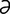 n] 1. the act of smelling. 2. the sense of smell.
n] 1. the act of smelling. 2. the sense of smell.
olfactology [ol“fak-tol’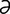 -je] the science of the sense of smell.
-je] the science of the sense of smell.
olfactometer [ol“fak-tom’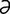 -tre] an instrument for testing the sense of smell.
-tre] an instrument for testing the sense of smell.
olfactory [ol-fak’t -re] pertaining to the sense of smell.
-re] pertaining to the sense of smell.
o. hair modified cilia projecting from olfactory cells in the mucosa of the nasal olfactory area.
o. nerve the first cranial nerve made up of about 20 bundles and concerned with the sense of smell. The cell bodies are situated in the olfactory mucous membrane of the nose. Nerve fibers lead caudad through openings in the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone and connect with the cells of the olfactory bulb. From there the fibers pass inward to the cerebrum. See also Table 14.
olifantvel [Af.] the thickened, wrinkled, alopecic skin caused by Besnoitia besnoiti in cattle.
olig(o)- word element. [Gr.] few, little, scanty.
oligochromasia [ol“ -go-kro-ma’se-
-go-kro-ma’se- ] deficiency of hemoglobin in the blood.
] deficiency of hemoglobin in the blood.
oligochymia [ol“ -go-kī’me-
-go-kī’me- ] deficiency of chyme.
] deficiency of chyme.
oligocythemia [ol“ -go-si-the’me-
-go-si-the’me- ] deficiency of the cellular elements of the blood.
] deficiency of the cellular elements of the blood.
oligodactyly [ol“ -go-dak’t
-go-dak’t -le] congenital absence of one or more digits. Called also hypodactyly.
-le] congenital absence of one or more digits. Called also hypodactyly.
oligodendroglia [ol“ -go-d
-go-d n-drog’le-
n-drog’le- ] oligodendrocyte.
] oligodendrocyte.
oligodipsia [ol“ -go-dip’se-
-go-dip’se- ] abnormally diminished thirst.
] abnormally diminished thirst.
oligogalactia [ol“ -go-g
-go-g -lak’she-
-lak’she- ] deficient secretion of milk.
] deficient secretion of milk.
oligohydramnios [ol“ -go-hi-dram’ne-os] deficiency in the amount of amniotic fluid.
-go-hi-dram’ne-os] deficiency in the amount of amniotic fluid.
oligohydruria [ol“ -go-hi-droo’re-
-go-hi-droo’re- ] hypersthenuria.
] hypersthenuria.
oligomer [ol’ -go-m
-go-m r] a short polymer.
r] a short polymer.
o. ligation assay a technique for detecting a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) allele in a gene.
oligopeptides [ol“ -go-pep’tīd] small peptides containing mixtures of amino acids.
-go-pep’tīd] small peptides containing mixtures of amino acids.
oligophosphaturia [ol“ -go-fos“f
-go-fos“f -tu’re-
-tu’re- ] deficiency of phosphates in the urine.
] deficiency of phosphates in the urine.
oligoplasmia [ol“ -go-plaz’me-
-go-plaz’me- ] deficiency of blood plasma.
] deficiency of blood plasma.
oligoptyalism [ol“ -go-ti’
-go-ti’ -liz-
-liz- m] diminished secretion of saliva.
m] diminished secretion of saliva.
oligotrophia, oligotrophy a state of poor (insufficient) nutrition.
oligozoospermia [ol“ -go-zo“o-spur’me-
-go-zo“o-spur’me- ] low number of spermatozoa in the ejaculate.
] low number of spermatozoa in the ejaculate.
olivary [ol’ -var“e] shaped like an olive.
-var“e] shaped like an olive.
o. body called also olivary nucleus; see olive (2).
o. oil an emollient lubricant and mild laxative.
olivifugal [ol“ -vif’u-g
-vif’u-g l] moving or conducting away from the olive.
l] moving or conducting away from the olive.
olivipetal [ol“ -vip’
-vip’ -t
-t l] moving or conducting toward the olive.
l] moving or conducting toward the olive.
Ollier’s disease [o-le-a’] multiple enchondromatosis, dyschrondroplasia.
Ollulanus [ol“u-lan’us] a genus of trichostrongyloid nematodes in the family Ollulanidae.
olsalazine [ol-sal’ -zēn] 5-amino-salicylate; used in the treatment of ulcerative colitis.
-zēn] 5-amino-salicylate; used in the treatment of ulcerative colitis.
-oma word element. [Gr.] tumor, neoplasm.
omarthritis [o“mahr-thri’tis] inflammation of the shoulder joint.
omasal [o-ma’s l] pertaining to or emanating from the omasum.
l] pertaining to or emanating from the omasum.

O-6: Olson-Hegar needle holder–scissors combination.
From Sonsthagen TF, Veterinary Instruments and Equipment: A Pocket Guide, 2nd Edition. Mosby, 2011.
 -te] excessive accumulation of fat in the body; increase in weight beyond that considered desirable with regard to species, age and bone structure, and to a degree greater than that regarded as overweight. A quantitative definition is 15% above optimal weight in dogs and 20% in cats. See also overweight, body condition score.
-te] excessive accumulation of fat in the body; increase in weight beyond that considered desirable with regard to species, age and bone structure, and to a degree greater than that regarded as overweight. A quantitative definition is 15% above optimal weight in dogs and 20% in cats. See also overweight, body condition score. r-a’sh
r-a’sh n] complete removal, by disease, degeneration, surgical procedure, irradiation, etc.
n] complete removal, by disease, degeneration, surgical procedure, irradiation, etc. n] thumb-operated fixation tissue forceps similar to O’Brien forceps except that there is a slide catch that keeps the teeth locked together.
n] thumb-operated fixation tissue forceps similar to O’Brien forceps except that there is a slide catch that keeps the teeth locked together.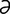 n] thumb-operated tissue forceps with blades tipped by long rat-teeth, two on one side, one on the other.
n] thumb-operated tissue forceps with blades tipped by long rat-teeth, two on one side, one on the other.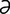 b-ses’iv-k
b-ses’iv-k m-pul’siv] normal activities or behavior for the species, but repetitive or constant, even to the point of being damaging to the animal. Includes tail chasing, flank licking and licking.
m-pul’siv] normal activities or behavior for the species, but repetitive or constant, even to the point of being damaging to the animal. Includes tail chasing, flank licking and licking. -tr
-tr ’sh
’sh n] a veterinarian who specializes in obstetrics and reproductive medicine, in general. See also theriogenologist.
n] a veterinarian who specializes in obstetrics and reproductive medicine, in general. See also theriogenologist. n] the act of blocking or clogging; state of being clogged; refers usually to a tubular structure. See intestinal, laryngeal, nasolacrimal duct obstruction, esophageal, oviductal, urethral, ureteral obstruction.
n] the act of blocking or clogging; state of being clogged; refers usually to a tubular structure. See intestinal, laryngeal, nasolacrimal duct obstruction, esophageal, oviductal, urethral, ureteral obstruction. nt] 1. aware of environment, but decreased responsiveness to normal stimuli. 2. a soothing or partially anesthetic agent.
nt] 1. aware of environment, but decreased responsiveness to normal stimuli. 2. a soothing or partially anesthetic agent. -ra’t
-ra’t r] 1. a disk or plate that closes an opening, e.g. to close a cleft palate temporarily or permanently; the obturator foramen is the large opening in each os coxae that in many species is almost entirely occluded by a sheet of fibrous tissues, the obturator membrane. 2. a sharp or blunt probe used within an endoscopic sheath to assist gaining access to an anatomical regions, for example in the placement of an arthroscope. See also trocar.
r] 1. a disk or plate that closes an opening, e.g. to close a cleft palate temporarily or permanently; the obturator foramen is the large opening in each os coxae that in many species is almost entirely occluded by a sheet of fibrous tissues, the obturator membrane. 2. a sharp or blunt probe used within an endoscopic sheath to assist gaining access to an anatomical regions, for example in the placement of an arthroscope. See also trocar.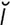 -t
-t l] pertaining to the occiput; located near the occipital bone, such as the occipital lobe.
l] pertaining to the occiput; located near the occipital bone, such as the occipital lobe. -to-p
-to-p -ri’
-ri’ -t
-t l] pertaining to the occipital and parietal bones or lobes of the brain.
l] pertaining to the occipital and parietal bones or lobes of the brain. -p
-p t] the back of the skull. The external occipital protruberance and the occipital crests; may normally be very prominent in some dogs. Sometimes traumatized with hematoma formation resulting.
t] the back of the skull. The external occipital protruberance and the occipital crests; may normally be very prominent in some dogs. Sometimes traumatized with hematoma formation resulting. -kloo’z
-kloo’z l] pertaining to closure; applied to the masticating surfaces of the teeth. The cat does not have any teeth with occlusal surfaces.
l] pertaining to closure; applied to the masticating surfaces of the teeth. The cat does not have any teeth with occlusal surfaces. n] 1. the act of closure or state of being closed; an obstruction or a closing off. 2. the relation of the teeth of both jaws when in functional contact during activity of the mandible. A system for classification of occlusion in carnivores exists: Class 0 is normal occlusion (called also orthoclusion); Class I is a malocclusion in which the jaws are of normal length, but there are abnormalities in the position of individual teeth; includes anterior and posterior crossbites, base-wide and base-narrow canines, rotated teeth (called also neutroclusion); Class II malocclusion includes those due to a short mandible or long maxilla (called also distoclusion); Class III malocclusion includes those due to a long mandible or short maxilla (called also mesioclusion); Class IV malocclusions have Class II on one side and Class III on the other (called also mesiodistoclusion).
n] 1. the act of closure or state of being closed; an obstruction or a closing off. 2. the relation of the teeth of both jaws when in functional contact during activity of the mandible. A system for classification of occlusion in carnivores exists: Class 0 is normal occlusion (called also orthoclusion); Class I is a malocclusion in which the jaws are of normal length, but there are abnormalities in the position of individual teeth; includes anterior and posterior crossbites, base-wide and base-narrow canines, rotated teeth (called also neutroclusion); Class II malocclusion includes those due to a short mandible or long maxilla (called also distoclusion); Class III malocclusion includes those due to a long mandible or short maxilla (called also mesioclusion); Class IV malocclusions have Class II on one side and Class III on the other (called also mesiodistoclusion).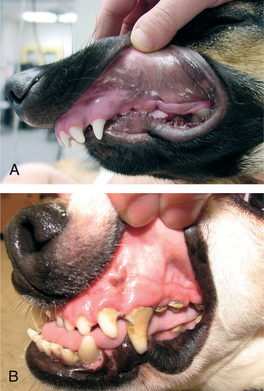
 -tok“s
-tok“s -ko’sis] the nephropathy caused by poisoning by the mycotoxin ochratoxin A. Characterized by degeneration of renal epithelium, polydipsia, polyuria, diarrhea and uremia. Pigs most affected. Resembles Balkan nephropathy in humans.
-ko’sis] the nephropathy caused by poisoning by the mycotoxin ochratoxin A. Characterized by degeneration of renal epithelium, polydipsia, polyuria, diarrhea and uremia. Pigs most affected. Resembles Balkan nephropathy in humans. -tok“sin] mycotoxin synthesized by Aspergillus ochraceous and some Penicillium fungi with nephrotoxic, immunotoxic, teratogenic and hepatotoxic activities and found in a wide variety of climates and geographical regions as a natural contaminant of poultry and livestock feedstuffs. Causes nephropathy in all species tested with large species differences in potency, pigs being most sensitive. Teratogenicity and immunotoxicity occur only at doses higher than those causing nephrotoxicity. Categorized as a group 2 carcinogen by the WHO.
-tok“sin] mycotoxin synthesized by Aspergillus ochraceous and some Penicillium fungi with nephrotoxic, immunotoxic, teratogenic and hepatotoxic activities and found in a wide variety of climates and geographical regions as a natural contaminant of poultry and livestock feedstuffs. Causes nephropathy in all species tested with large species differences in potency, pigs being most sensitive. Teratogenicity and immunotoxicity occur only at doses higher than those causing nephrotoxicity. Categorized as a group 2 carcinogen by the WHO. -no’sis] a yellow, brown or chocolate discoloration of cartilage, tendon sheaths and ligaments but not bone. Caused by deposit of alkapton bodies as the result of a metabolic disorder. Affected parts must be condemned as not suitable for human consumption.
-no’sis] a yellow, brown or chocolate discoloration of cartilage, tendon sheaths and ligaments but not bone. Caused by deposit of alkapton bodies as the result of a metabolic disorder. Affected parts must be condemned as not suitable for human consumption. -p
-p s] cephalopod in the order Octopoda; has eight legs and eats crustaceans and shellfish.
s] cephalopod in the order Octopoda; has eight legs and eats crustaceans and shellfish. -t
-t l dis-pla’zh
l dis-pla’zh ] a syndrome of disproportionate dwarfism and retinal dysplasia sometimes with retinal detachment and blindness reported in Labrador retrievers and Samoyeds.
] a syndrome of disproportionate dwarfism and retinal dysplasia sometimes with retinal detachment and blindness reported in Labrador retrievers and Samoyeds.
 -lo-blas-to’m
-lo-blas-to’m ] a tumor containing areas of ameloblastic epithelium and compound or complex odontoma.
] a tumor containing areas of ameloblastic epithelium and compound or complex odontoma.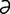 sis’ti-k
sis’ti-k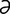 k
k njen’
njen’ – t
– t ] a disease of calves recorded in Germany and thought to be due to environmental influences; characterized by abortion or stillbirth and congenital fibrous, cystic enlargement of mandibles and maxillae, and absence or deformity of some teeth.
] a disease of calves recorded in Germany and thought to be due to environmental influences; characterized by abortion or stillbirth and congenital fibrous, cystic enlargement of mandibles and maxillae, and absence or deformity of some teeth. ] a non-neoplastic malformation, a hamartoma, consisting of a mixture of enamel, dentin and cementum.
] a non-neoplastic malformation, a hamartoma, consisting of a mixture of enamel, dentin and cementum. r] a volatile emanation, usually unpleasant, perceived by the olfactory sense of the clinician. See also taint.
r] a volatile emanation, usually unpleasant, perceived by the olfactory sense of the clinician. See also taint.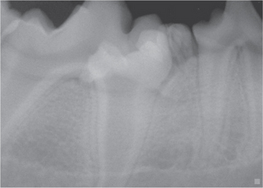
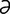 -k
-k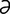 s] the cliff swallow bug, possibly an overwintering vector for the western equine encephalomyelitis virus.
s] the cliff swallow bug, possibly an overwintering vector for the western equine encephalomyelitis virus. -gos’to-m
-gos’to-m m] a genus of roundworms in the family Chabertiidae. Found in the large intestine. Cause the important disease esophagostomosis (esophagostomiasis) in sheep. Includes O. aculeatum, syn. O. apiosternum (monkeys); O. asperum, syn. O. indicum (goats, sheep); O. bifurcum (monkeys); O. brevicaudatum (pig); O. columbianum (sheep, goats, camels and wild antelopes); O. dentatum (pig); O. georgianum (pig), O. granatensis (pig), O. hsiungi (pig), O. longicaudatum,. O. quadrispinulatum (pig), O. maplestonei (pig), O. multifoliatum (goat, sheep), O. okapi (okapi); O. quadrispinulatum (pig), O. radiatum (water buffalo, cattle); O. rousseloti (pig); O. staphanostomum (monkeys), O. venulosum (camel, deer, goat, sheep), O. walkeri (eland).
m] a genus of roundworms in the family Chabertiidae. Found in the large intestine. Cause the important disease esophagostomosis (esophagostomiasis) in sheep. Includes O. aculeatum, syn. O. apiosternum (monkeys); O. asperum, syn. O. indicum (goats, sheep); O. bifurcum (monkeys); O. brevicaudatum (pig); O. columbianum (sheep, goats, camels and wild antelopes); O. dentatum (pig); O. georgianum (pig), O. granatensis (pig), O. hsiungi (pig), O. longicaudatum,. O. quadrispinulatum (pig), O. maplestonei (pig), O. multifoliatum (goat, sheep), O. okapi (okapi); O. quadrispinulatum (pig), O. radiatum (water buffalo, cattle); O. rousseloti (pig); O. staphanostomum (monkeys), O. venulosum (camel, deer, goat, sheep), O. walkeri (eland).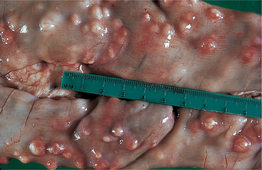
 -’sh
-’sh l] medicines authorized by pharmacopeias and recognized formularies. Use of drugs other than these could be regarded by a court of law as being experimental.
l] medicines authorized by pharmacopeias and recognized formularies. Use of drugs other than these could be regarded by a court of law as being experimental. nt] a semisolid preparation for external application to the body. Official ointments consist of medicinal substances incorporated in suitable vehicles (bases).
nt] a semisolid preparation for external application to the body. Official ointments consist of medicinal substances incorporated in suitable vehicles (bases). -fin] see alkene.
-fin] see alkene. -min] a preparation of fat-soluble vitamins in fish liver or edible vegetable oil.
-min] a preparation of fat-soluble vitamins in fish liver or edible vegetable oil. -je’me-
-je’me- ] deficiency in volume of the blood. Estimation of the degree of oligemia, the severity of dehydration, is a vital assessment in many diseases of animals. See packed cell volume, dehydration.
] deficiency in volume of the blood. Estimation of the degree of oligemia, the severity of dehydration, is a vital assessment in many diseases of animals. See packed cell volume, dehydration. -go-den’dro-sīt] non-neuronal (glial) cell of the central nervous system that produces myelin in the developing brain and maintains it thereafter.
-go-den’dro-sīt] non-neuronal (glial) cell of the central nervous system that produces myelin in the developing brain and maintains it thereafter. -go-den“dro-gli-o’m
-go-den“dro-gli-o’m ] brain or spinal cord tumor thought to arise from oligodendrocytes.
] brain or spinal cord tumor thought to arise from oligodendrocytes. -go-don’sh
-go-don’sh ] congenital absence of some of the teeth. Considered a serious fault of conformation in some dog breeds.
] congenital absence of some of the teeth. Considered a serious fault of conformation in some dog breeds. -go-di-nam’ik] active in a small quantity; refers to the antimicrobial effect of very dilute solutions of metals such as silver and copper.
-go-di-nam’ik] active in a small quantity; refers to the antimicrobial effect of very dilute solutions of metals such as silver and copper. -go-meg’
-go-meg’ -n
-n -fro’ne-
-fro’ne- ] congenital renal hypoplasia in which there is a reduction in the total number of nephrons, and hypertrophy of the nephrons.
] congenital renal hypoplasia in which there is a reduction in the total number of nephrons, and hypertrophy of the nephrons. -go-mu’k
-go-mu’k s] a cell which develops into a goblet cell in the intestinal epithelium.
s] a cell which develops into a goblet cell in the intestinal epithelium. -go-mi’sin] antibiotic inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation, acting at the O-sensitive subunit of F0F1-ATPase.
-go-mi’sin] antibiotic inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation, acting at the O-sensitive subunit of F0F1-ATPase. -go-noo’kle-o-tīd] a polymer made up of a few to a hundred or more nucleotides. Can be made synthetically to a specified sequence.
-go-noo’kle-o-tīd] a polymer made up of a few to a hundred or more nucleotides. Can be made synthetically to a specified sequence. -gop-ne’
-gop-ne’ ] hypoventilation. Usually refers to reduced rate; apnea is complete cessation.
] hypoventilation. Usually refers to reduced rate; apnea is complete cessation. -go-sak’
-go-sak’ -rīd] a carbohydrate which yields only a small number, usually 3 to 10, of monosaccharides on hydrolysis.
-rīd] a carbohydrate which yields only a small number, usually 3 to 10, of monosaccharides on hydrolysis. -go-spur’me-
-go-spur’me- ] low volume of ejaculate; not to confuse with oligozoospermia, which is low number of spermatozoa in the ejaculate.
] low volume of ejaculate; not to confuse with oligozoospermia, which is low number of spermatozoa in the ejaculate. -gu’re-
-gu’re- ] reduced daily output of urine, which may be physiologic or pathologic. This has veterinary significance if the net intake is normal or if water is available ad lib; then it is a sign of renal insufficiency.
] reduced daily output of urine, which may be physiologic or pathologic. This has veterinary significance if the net intake is normal or if water is available ad lib; then it is a sign of renal insufficiency. -vo-ser“
-vo-ser“ -bel’
-bel’ r] nerve fibers passing from olive to contralateral cerebellum.
r] nerve fibers passing from olive to contralateral cerebellum. -vo-pon“to-ser“
-vo-pon“to-ser“ -bel’
-bel’ r] pertaining to the olive, the middle peduncles and the cerebellar cortex.
r] pertaining to the olive, the middle peduncles and the cerebellar cortex.


