N
ν nu, small letter; thirteenth letter of the Greek alphabet.
N-3-pyridylmethyl N1-p-nitrophenyl urea see valor.
N-CAMs nerve-cell adhesion molecules.
N-methylconiine plant toxin found in Conium maculatum.
N5,N10-methylene H4 folate form of tetrahydrolate essential to the synthesis of purines.
Na chemical symbol, sodium (L. natrium).
Na+ gradient the rate of increase or decrease of sodium ion concentration.
Naalehu [Hawaiian] see enzootic calcinosis.
Naboth’s cyst [nah′bot] see cervical cyst.
nacreous [na′kre- s] having a pearl-like luster.
s] having a pearl-like luster.
NAD in medical records, an abbreviation for no abnormalities detected.
NAD+ the oxidized form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.
NAD+ malate dehydrogenase see malate dehydrogenase.
NADC National Animal Disease Center.
NADH the reduced form of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide.
nadolol [na-do′lol] an adrenergic blocking agent that affects both β1– and β2-receptors.
NADP nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
NADP-linked malic enzyme see malic enzyme.
Naegleria [na-gler′e-a] a genus of protozoa in the family Vahlkamp- fiidae.
naftifine an antifungal drug in the allylamine class, closely related to terbinafine.
nag vernacular for horse; called also steed, cayuse, neddy.
NAHMS National Animal Health Monitoring System.
n. bed infection see paronychia.
n. dermatophytosis see onychomycosis.
Nairobi bleeding disease [ni-ro′be] canine ehrlichiosis.
Nairobi sheep disease [ni-ro′be] an infectious disease of sheep caused by an arbovirus in the genus Nairovirus and transmitted by the tick Rhipicephalus appendiculatus and possibly other ticks. It is characterized by acute hemorrhagic gastroenteritis and blood-stained purulent nasal discharge. A disease notifiable to the OIE (see Table 22).
Nairovirus [ni″ro-vi′r s] a genus in the family Bunyaviridae; includes Nairobi sheep disease virus.
s] a genus in the family Bunyaviridae; includes Nairobi sheep disease virus.
naive [nah-ēv′] in immunology, an individual that has not been exposed to a particular antigen.
naked ladies see Colchicum autumnale.
Nakuru grass Cynodon aethiopicus.
nalbuphine [nal′bu-fēn] a synthetic κ-agonist-μ-antagonist opioid analgesic.
naled [nah′led] an organophosphorus insecticide.
name [nām] title; identifying word(s).
International Nonproprietary Name (INN) see International Nonproprietary Name (INN).
United States Adopted Name (USAN) see United States Adopted Name (USAN).
nanism [na′niz- m] dwarfism or marked small size from any cause.
m] dwarfism or marked small size from any cause.
Nannizia [nd-niz′e- ] see Microsporum.
] see Microsporum.
nanocephaly [nan″o-sef′ –le] microcephaly.
–le] microcephaly.
nanocormia [nan″o-kor′me- ] abnormal smallness of the body or trunk.
] abnormal smallness of the body or trunk.
nanogram [nan′o-gram] one-thousand-millionth (10−9) gram.
nanomelus [nan-om′ -l
-l s] micromelus.
s] micromelus.
nanophthalmia [nan″of-thal′me- ] nanophthalmos.
] nanophthalmos.
nanophthalmus [nan″of-thal′m s] 1. nanophthalmos. 2. an animal affected with nanophthalmos.
s] 1. nanophthalmos. 2. an animal affected with nanophthalmos.
nanophyetiasis [nan″o-fi″ -ti′
-ti′ -sis] see salmon poisoning.
-sis] see salmon poisoning.
nanosecond (ns, nsec) [nan′o-sek″ond] one-thousand-millionth (lO-9) second.
nanosomia [nan″o-so′me- ] dwarfism.
] dwarfism.
nanous [nan′ s] dwarfed; stunted.
s] dwarfed; stunted.
Nantucket fever human babesiosis.
Nanyang cattle Chinese draft cattle, usually red with gray or white spots.
nape [nāp] the back of the neck. Called also nucha.
naphthalene [naf′thd-lēn] a hydrocarbon from coal tar oil.
chlorinated n. see chlorinated naphthalenes.
naphthlindandione an anticoagulant rodenticide, related to warfarin.
2-naphthylamine an industrial chemical identified as a urinary bladder carcinogen.
Napier grass Pennisetum purpureum. Called also elephant grass.
narc(o)- word element. [Gr.] stupor, stuporous state.
narcosis [nahr-ko′sis] a reversible state of central nervous system depression induced by a drug.
basal n., basis n. narcosis with complete unconsciousness, amnesia and analgesia.
n. analgesics opiate derivatives such as morphine and etorphine.
n. antitussives cough suppressants, usually containing codeine.
narcotize [nahr′ko-tīz] to put under the influence of a narcotic.
nardoo see Marsilea drummondii.
nares [na′re] [L.] plural of naris; the openings of the nasal cavity. See also nostril, choana.
narrow-leaved sumpweed see Iva angustifolia.
n. breath flow of the breath from the nostrils as distinct from the breath from the mouth.
n. cavity erectile tissue erectile tissue present only in some patients; usually collapsed.
n. cavity hemorrhage see epistaxis.

N-2: Nasal deviation in a horse.
From Knottenbelt DC, Pascoe RR, Diseases and Disorders of the Horse. Saunders, 2003.
n. cavity-sinuses see paranasal sinuses.
n. cavity vestibular region place of transition from skin to respiratory epithelium.
n. diverticulum see nasal diverticulum.
n. fundus the caudal part of the nasal cavity, close to the ethmoid bone.
n. granuloma see enzootic nasal granuloma, mycotic nasal granuloma,Schistosoma nasalis.
n. hemorrhage see epistaxis. Called also rhinorrhagia, nose bleed.
n. mucosal inflammation see rhinitis.
n. odor smell of the nasal breath; may be necrotic, smell of ketones.
progressive n. hematoma see progressive ethmoidal hematoma.
n. turbinates nasal conchae; see Table 10.
n. vestibule the part of the nasal cavity just inside the nostrils that is lined with skin.
nasion [na′ze-on] a landmark found at the middle point of the frontonasal suture.
nas(o)- word element. [L.] nose.
nasociliary [na″zo-sil′e-ar″e] pertaining to the eyes, brow, and root of the nose.
nasofrontal [na″zo-fron′t l] pertaining to the nasal and frontal bones.
l] pertaining to the nasal and frontal bones.
nasogastric [na″zo-gas′trik] pertaining to the nasal cavity and the stomach.
nasolabial [na″zo-la′be- l] pertaining to the nose and lip.
l] pertaining to the nose and lip.
nasolacrimal [na″zo-lak′r -m
-m l] pertaining to the nose and lacrimal apparatus.
l] pertaining to the nose and lacrimal apparatus.
n. apparatus see lacrimal apparatus.
n. groove nasolacrimal furrow.
n. radiography see dacryocystorhinography.
n. system see lacrimal apparatus.
nasomaxillary pertaining to the maxilla and the nasal cavity.
n. aperture see nasomaxillary aperture.
nasomyiasis infection of the nasal cavity by fly larvae. See Oestrus ovis.
naso-oral pertaining to the nose and mouth.
nasopalatine [na″zo-pal′ -tīn] pertaining to the nose and palate.
-tīn] pertaining to the nose and palate.
nasopharyngeal [na″zo-f -rin′je-
-rin′je- l] pertaining to the nasal and pha- ryngeal cavities.
l] pertaining to the nasal and pha- ryngeal cavities.
n. meatus see nasopharyngeal meatus.
n. polyp see nasopharyngeal polyp.
nasopharyngitis [na″zo-far″in-ji′tis] inflammation of the nasopharynx.
nasopharynx [na″zo-far′inks] the part of the pharynx above the soft palate.
nasosinusitis [na″zo-si″n s-i′tis] inflammation of the paranasal sinuses.
s-i′tis] inflammation of the paranasal sinuses.
natal [na′t l] 1. pertaining to birth. 2. pertaining to the nates (buttocks).
l] 1. pertaining to birth. 2. pertaining to the nates (buttocks).
natality [na-talĩ-te] the birth rate.
nates [na′tēz] [L.] the buttocks.
natimortality [na″t -mor-talĩ-te] the proportion of stillbirths to the general birth rate.
-mor-talĩ-te] the proportion of stillbirths to the general birth rate.
National Formulary (NF) see United States National Formulary.
natremia [n -tre′me-
-tre′me- ] see hypernatremia.
] see hypernatremia.
natriuresis [na″tre-u-re′sis] the excretion of abnormal amounts of sodium in the urine.
natural [nach′ -r
-r l] occurs in nature, without the intervention of humans.
l] occurs in nature, without the intervention of humans.
naturally bred see bull-bred herd.
naturopath [na′ch r-o-path″] a practitioner of naturopathy.
r-o-path″] a practitioner of naturopathy.
n. ill see omphalitis. Called also omphalophlebitis.
navelwort Cotyledon umbilicus.
n. bursa inflammation in the horse may contain Brucella abortus; a cause of intermittent lameness.
NAVLE North American Veterinary Licensing Examination.
NAVTA National Association of Veterinary Technicians in America.
NBE net base excretion in urine. See net acid excretion.
NCS not clinically significant.
Nd chemical symbol, neodymium.
Neapolitan farcy see epizootic lymphangitis.
near-drowning nonfatal water inhalation. There is severe injury to the lungs and hypoxia.
near-side a horse’s left-hand side.
nearthrosis [ne″ahr-thro′sis] a false or artificial joint.
neat an archaic word for cattle.
neatsfoot oil an oil manufactured by boiling cattle hooves. Used in leather maintenance.
Nebraska virus the calf diarrheaRotavirus.
nebula [neb′u-l ] a small corneal opacity. See also macula and leukoma.
] a small corneal opacity. See also macula and leukoma.
nebulization [neb″u-l -za′sh
-za′sh ] 1. conversion into a spray. 2. treatment by a spray.
] 1. conversion into a spray. 2. treatment by a spray.
nebulizer [neb′u-li″z r] an atomizer; a device for creating an aerosol.
r] an atomizer; a device for creating an aerosol.
Necator [ne-ka′tor] a genus of hookworm in the subfamily Necatorinae.
N. americanus the common hookworm of humans, found also in pigs and dogs.
N. suillus see N. americanus (above), found in pigs.
ewe n. a concave neck; a fault in conformation in most species except sheep.
femoral n. the column of bone connecting the head of the femur its shaft.
humeral n. the constriction of the humerus just distal to its head.
n. twist injury see head twist injury.
uterine n., n. of uterus cervix uteri.
wry n. see torticollis. n. yoke see headstock.
neck stab [nek] see evernazione.
neckbread butcher’s term for the cervical segment of the thymus.
necklace [nek′l s] bands of color across the lower neck and chest of cats.
s] bands of color across the lower neck and chest of cats.
necrectomy [nek-rek′t -me] excision of necrosed tissue.
-me] excision of necrosed tissue.
necr(o)- word element. [Gr.] death.
interdigital n. see bovine footrot.
ruminal n. see ruminal necrobacillosis.
necrocytosis [nek″ro-si-to′sis] death and decay of cells.
necrogenic [nek″ro-jen′ik] productive of necrosis or death.
necrogenous [n -kroj′
-kroj′ -n
-n s] originating or arising from dead matter.
s] originating or arising from dead matter.
necrology [n -krol′
-krol′ -je] statistics or records of death.
-je] statistics or records of death.
necrolysis [n -krolĩ-sis] separation or exfoliation of necrotic tissue.
-krolĩ-sis] separation or exfoliation of necrotic tissue.
necroparasite an organism that lives in dead tissue.
necrophagous [n -krof ′
-krof ′ -g
-g s] feeding upon dead flesh.
s] feeding upon dead flesh.
necrophilous [n -krof′
-krof′ -l
-l s] showing a preference for dead tissue; said of microorganisms.
s] showing a preference for dead tissue; said of microorganisms.
necropneumonia [nek″ro-noo-mo′ne- ] gangrenous pneumonia.
] gangrenous pneumonia.
necropsy [nek′rop-se] examination of a body after death. See also autopsy.
necrose [nek′rōs] to become necrotic or to undergo necrosis.
necrosis [n -kro′sis] pl. necroses [Gr.] death of tissues or individual cells within a living animal.
-kro′sis] pl. necroses [Gr.] death of tissues or individual cells within a living animal.
aseptic n. necrosis without infection.
central n. necrosis affecting the central portion of an affected organ, cell or lobule of the liver.
cheesy n. see caseous necrosis (above).
colliquative n. see liquefactive necrosis (below).
ischemic n. necrosis of any tissue due to interruption of its blood supply.
moist n. necrosis in which the dead tissue is wet and soft.
n. necrosis see Roeckl’s granuloma.
Zenker’s n. hyaline degeneration and necrosis of striated muscle; called also Zenker’s degeneration.
necrotic [n -krot′ik] of or pertaining to cell death.
-krot′ik] of or pertaining to cell death.
n. cervicovaginitis necrosis in cows and ewes, usually as a result of trauma during parturition.
n. colitis common in older cats as a cause of chronic, foul, bloody diarrhea.
n. glossitis necrosis and loss of the tip of the tongue in feeder steers; cause unknown.
n. hepatitis see infectious necrotic hepatitis.
n. laryngitis see calf diphtheria.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
 -fēn] a parenteral opiate receptor antagonist used to reverse the effects of opiates.
-fēn] a parenteral opiate receptor antagonist used to reverse the effects of opiates. r] a unit of linear measure or wave length equal to one-thousand-millionth (lO-9) of a meter; nm; millimicron.
r] a unit of linear measure or wave length equal to one-thousand-millionth (lO-9) of a meter; nm; millimicron. s] congenital abnormal smallness in all dimensions of one or both eyes in the absence of other ocular defects. Called also pure microphthalmos.
s] congenital abnormal smallness in all dimensions of one or both eyes in the absence of other ocular defects. Called also pure microphthalmos. -t
-t s] a genus of digenetic trematodes in the family Nanophyetidae, parasites in the intestines of mammals.
s] a genus of digenetic trematodes in the family Nanophyetidae, parasites in the intestines of mammals. -prok′s
-prok′s n] a propionic acid derivative with analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory activity (a nonsteroidal anti- inflammatory agent); associated with severe gastrointestinal toxic- ity in dogs and cats.
n] a propionic acid derivative with analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory activity (a nonsteroidal anti- inflammatory agent); associated with severe gastrointestinal toxic- ity in dogs and cats. -lāt] USAN contraction for 2-naphthalenesulfonate. narasin [nar′
-lāt] USAN contraction for 2-naphthalenesulfonate. narasin [nar′ -sin] an ionophore (polyether of monocarboxylic acid produced by Streptomyces aureofaciens) used as an aid to gastrointestinal absorption and to improve weight gains as for monensin. Causes poisoning similar to monensin poisoning.
-sin] an ionophore (polyether of monocarboxylic acid produced by Streptomyces aureofaciens) used as an aid to gastrointestinal absorption and to improve weight gains as for monensin. Causes poisoning similar to monensin poisoning. s] European genus of plants in the family Liliaceae. Includes the daffodil and narcissus. Can be poisonous if plant residues, especially bulbs, are ingested by animals because of the high content of lycorine, which causes salivation, vomiting and diarrhea.
s] European genus of plants in the family Liliaceae. Includes the daffodil and narcissus. Can be poisonous if plant residues, especially bulbs, are ingested by animals because of the high content of lycorine, which causes salivation, vomiting and diarrhea. m] toxic plant genus in the family Liliaceae; contain steroidal saponins which cause alveld, a crystal-associated cholangiohepatopathy and a resulting jaundice and photosensitive dermatitis; contain 3-methoxy-2(5H)-furanone causing nephrosis; includes N. asiaticum, N. ossifragum (bog asphodel).
m] toxic plant genus in the family Liliaceae; contain steroidal saponins which cause alveld, a crystal-associated cholangiohepatopathy and a resulting jaundice and photosensitive dermatitis; contain 3-methoxy-2(5H)-furanone causing nephrosis; includes N. asiaticum, N. ossifragum (bog asphodel).
 nt, na′s
nt, na′s nt] 1. being born; just coming into existence. 2. just liberated from a chemical reaction, and hence more reactive.
nt] 1. being born; just coming into existence. 2. just liberated from a chemical reaction, and hence more reactive. -ring″go-l
-ring″go-l -ring′go-skōp] a flexible fiberoptic endoscope for examining the nasopharynx and larynx.
-ring′go-skōp] a flexible fiberoptic endoscope for examining the nasopharynx and larynx. -pe] visual examination of the pharynx via a fiberscope passed up the nostril.
-pe] visual examination of the pharynx via a fiberscope passed up the nostril. s] [L.] nose.
s] [L.] nose. -mi′sin] a polyene antibiotic used in topical treatment of fungal infections of the skin, eye and nasal cavity.
-mi′sin] a polyene antibiotic used in topical treatment of fungal infections of the skin, eye and nasal cavity. r-op′
r-op′ -the] an early American system of healing that views disease as a manifestation of alterations in the processes by which the body naturally heals itself. It emphasizes health restoration as well as disease treatment using diet modification, nutritional supplements, herbal medicine, acupuncture, Chinese medicine, hydrotherapy, massage, joint manipulation and lifestyle counseling.
-the] an early American system of healing that views disease as a manifestation of alterations in the processes by which the body naturally heals itself. It emphasizes health restoration as well as disease treatment using diet modification, nutritional supplements, herbal medicine, acupuncture, Chinese medicine, hydrotherapy, massage, joint manipulation and lifestyle counseling.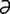 ] a subjective sensation in humans which probably occurs in animals. It is an unpleasant sensation, vaguely referred to the epigastrium and abdomen, with a tendency to vomit. In dogs and cats, observed as hypersalivation with repeated licking and swallowing. Nausea may be a symptom of a variety of disorders, some minor and some more serious. Nausea is usually felt when nerve endings in the stomach and other parts of the body are irritated, e.g. in motion sickness. The irritated nerves send messages to the center in the brain that controls the vomiting reflex. When the nerve irritation becomes intense, vomiting results.
] a subjective sensation in humans which probably occurs in animals. It is an unpleasant sensation, vaguely referred to the epigastrium and abdomen, with a tendency to vomit. In dogs and cats, observed as hypersalivation with repeated licking and swallowing. Nausea may be a symptom of a variety of disorders, some minor and some more serious. Nausea is usually felt when nerve endings in the stomach and other parts of the body are irritated, e.g. in motion sickness. The irritated nerves send messages to the center in the brain that controls the vomiting reflex. When the nerve irritation becomes intense, vomiting results. l] the umbilicus, the scar marking the site of entry of the umbilical cord into the fetal belly.
l] the umbilicus, the scar marking the site of entry of the umbilical cord into the fetal belly. -vik′u-l
-vik′u-l r] boat-shaped; applied to certain bones, such as the navicular bones of the horse’s foot and human ankle.
r] boat-shaped; applied to certain bones, such as the navicular bones of the horse’s foot and human ankle. -sis] infection with organisms of the genus Necator; hookworm disease. Manifested by anemia and melena.
-sis] infection with organisms of the genus Necator; hookworm disease. Manifested by anemia and melena.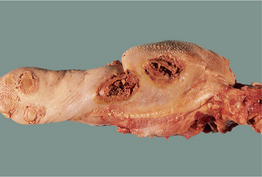
 ] a condition in which the spermatozoa are dead or motionless. See also immotile cilia syndrome.
] a condition in which the spermatozoa are dead or motionless. See also immotile cilia syndrome.