Fig. 1.
The optimal position of neck during perfusion fixation.
The animal is placed in a supine position. Position of neck should be kept at physiological angle. Neck super-extension should be avoided, since it causes stretch and compression of the basilar artery between the pons and clivus, which cause it fixed as transformed appearance.
2.
Perfusion fixation (Figs. 2 and 3):
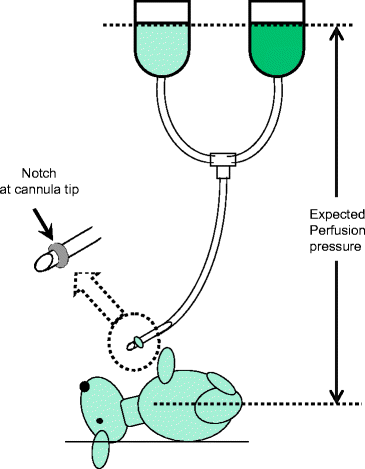
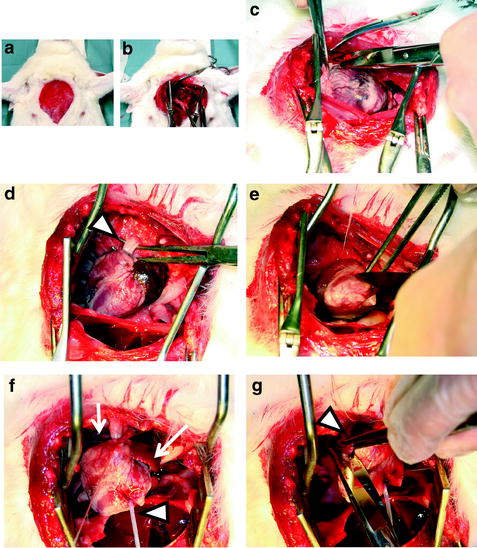

Fig. 2.
The bag, the tube, and the cannula for perfusion.

Fig. 3.
(a) Skin incision at the anterior chest. (b) Thoracotomy. (c) Pericardium is opened (d) Ascending aorta (open arrowhead) is taken. (e) Left ventricle apex is cut and opened. (f) Cannula (open arrowhead) is inserted and ligated at ascending aorta. (g) Right atrium (arrow head ) is cut and opened.
The bag with heparinized saline or phosphate buffer, the bag with fixative solution, the tube, and the cannula inserted into the ascending aorta are connected and prepared for perfusion (Fig. 2). The notch should be placed at the cannula tip. The position of solution surface in the bag should be set at height from the animal heart that is expected as perfusion pressure.
Under deep analgesia and anesthesia or after euthanasia (see Note 1), thoracotomy is performed by skin incision from upper limb of breast bone to epigastrium followed by cutting of midline of breast bone or left costae near the breast bone. Lung is pressed laterally, and the pericardium is widely opened. At first, the ascending aorta is exposed and the aorta should be loosely coiled with thread (*1). During this procedure, injury of aorta wall should be avoided, since its injury prohibits effective perfusion of fluid due to leakage of fluid. After that, the descending aorta is taken, if you require its cramped during perfusion fixation.
Second, the apex of left ventricle of heart is widely opened, and cannula is upwardly inserted. Insertion of cannula into the ascending aorta is easily recognized by touch sensation of tip of cannula. The ascending aorta is ligated with the thread (see the previous step *1) together with the cannula inside it at just below the notch of cannula.
Next, the descending aorta is cramped if you require it. Right atrium is widely cut for draining the fixative fluid.
Perfusion is started with heparinized saline or Ringer solution. The duration of those fluids and/or their volume are varied according to the literature and the kinds of animal. Usually, the duration is between 10 and 25 min. Of course, draining fluids from the atrium becoming transparent is one of the indications of completion of this step.
After that, infusion of fixation solution is started. Whether perfusion of fixation solution to the tissues is effective or not can be judged at this point. When the descending aorta is cramped, the muscles of neck and upper extremities show contracture just after infusion of fixative solution. When the descending aorta is not cramped, contracture of lower limb is seen just after the contracture of the body.
According to the progress of fixation, drip speed becomes slow. It is caused by decreased vessel lumen due to compaction of vessel wall and decreased elasticity of vessel wall, which is caused by fixative solution.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue



