Surface microcirculation
Pial arterial RBC flow
Biomicroscopic observation
Microcinematography
High-speed microcinematography
Television biomicroscopy
Photoelectric method
Pial arterial plasma flow
Fluorescence angiography
Coomassie blue infusion technique
Infrared absorption angiography
Pial arterial blood flow
Laser-Doppler flowmetry
Pial arterial pressure
Micropipet method
Parenchymal microcirculation
Regional hemoglobin content and mean transit time: photoelectric method
Regional hemoglobin oxygen saturation: absorption spectrophotometry
Regional RBC and plasma content: radioisotope technique
In addition, the evaluation of capillary density has been performed in the research for cerebral ischemia. Capillary density can be evaluated through alkaline phosphatase staining method (1), infusion of fluorescent dextran or plasma (2), and Evans blue infusion (3). However, these techniques are explained in section dealing with cerebral ischemia in this book and so they have been skipped in this chapter.
2 Materials
2.
Observation of microvascular architecture.
(a)
Casting method.
Polyester resin (Mercox): kept at room temperature.
Slightly harmful for inhalation.
20% NaOH: dissolved before use.
Harmful for contact.
(b)
Carbon black injection.
Gelatin: powder. dissolved before use.
India ink: kept at room temperature.
Methyl salicylate: kept at room temperature.
Glycerol: kept at room temperature.
(c)
Microangiography.
Microbarium (micropaque, baroperse, chromopaque, etc.): powder.
Dissolves before use.
Gelatin.
3 Methods
1.
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Out of intraparenchymal vessels, the arteriole can be an object for evaluation, since capillary had better be observed as its density. Evaluation should be done taking the depth from brain surface into account since intraparenchymal microvessels are distributed as shown in Fig. 1.
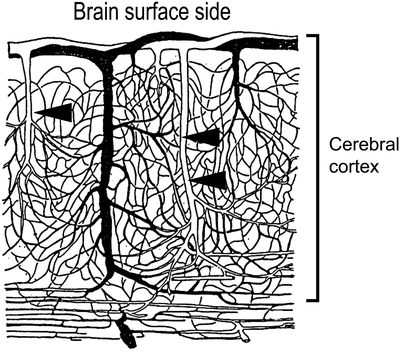

Fig. 1.
Distribution of intraparenchymal microvessels.
In light microscopy, paraffin-embedded brain is sliced from the brain surface with the brain surface on the top. The depth from the brain surface is grossly calculated by slice counts and slice thickness (Fig. 2a).
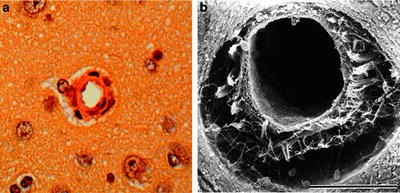





Fig. 2.
(a) Light microscopy of canine intraparenchymal arteriole, (b) scanning electron microscopy of canine intraparenchymal arteriole.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


