M
m symbol, meter; symbol milli-.
μ mu, the twelfth letter of the Greek alphabet; symbol for micro-; micron (μm).
M-CSF macrophage colony-stimulating factor.
M-mode motion mode. See M-mode ultrasonography.
M-plasty a technique for suturing a fusiform incision.
M protein myeloma protein; membrane protein.
MA test microscopic agglutination test.
Macaca [m -kah′k
-kah′k ] genus of Old World monkeys in the subfamily Cercopithecinae; includes the macaques.
] genus of Old World monkeys in the subfamily Cercopithecinae; includes the macaques.
McArdle disease [m k-ahr′d
k-ahr′d l] glycogenosis type V
l] glycogenosis type V
m. wasting disease see proventricular dilatation disease.
McBurney incision [m k-bur′ne] see grid incision.
k-bur′ne] see grid incision.
macerate [mas′ r-āt] to soften by wetting or soaking.
r-āt] to soften by wetting or soaking.
Mackenzie River disease [m -ken′ze] Australian name for poisoning by Terminalia oblongata.
-ken′ze] Australian name for poisoning by Terminalia oblongata.
McNemar’s chi-square test see chi-square test.
M. catalinum found in the small intestine of dogs, wolves, badgers and foxes.
M. ingens found in the small intestine of wild mammals including skunk, mink, raccoon and mole.
macrencephalia [mak-ren″s -fa′le-
-fa′le- ] hypertrophy of the brain.
] hypertrophy of the brain.
macr(o)- word element. [Gr.] large, long.
macroamylasemia [mak″ro-am″ l-
l- -se′me-
-se′me- ] the presence of macroamylase in the blood.
] the presence of macroamylase in the blood.
macroblepharia [mak″ro-bl -far′e-
-far′e- ] abnormal largeness of the eyelid.
] abnormal largeness of the eyelid.
macrocardius [mak″ro-kahr′de- s] a fetus with an extremely large heart.
s] a fetus with an extremely large heart.
macrocarpa Cupressus macrocarpa.
macrocephalous [mak″ro-sef′ -l
-l s] having an abnormally large head.
s] having an abnormally large head.
macrocephaly [mak″ro-sef′ -le] abnormal enlargement of the cranium.
-le] abnormal enlargement of the cranium.
macrochromosomes [mak″ro-kro′mo-sōmz] a pair of normal chromosomes.
macrocolon [mak′ro-ko″l n] see megacolon.
n] see megacolon.
macrocrania [mak″ro-kra′ne- ] abnormal increase in size of the skull in relation to the face.
] abnormal increase in size of the skull in relation to the face.
macrocyte [mak′ro-sīt] an abnormally large erythrocyte.
macrocythemia [mak″ro-si-the′me- ] the presence of macrocytes in the blood. See macrocytosis.
] the presence of macrocytes in the blood. See macrocytosis.
macrocytic [mak″ro-sit′ik] manifested by or pertaining to the presence of macrocytes.
macrodactyly [mak″ro-dak′t -le] abnormal largeness of the digits.
-le] abnormal largeness of the digits.
macrodontia [mak″ro-don′sh ] one or more abnormally large teeth.
] one or more abnormally large teeth.
macroglobulinemia [mak″ro-glob″u-l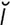 -ne′me-
-ne′me-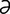 ] increased levels of immunoglobulin M in the blood.
] increased levels of immunoglobulin M in the blood.
macroglossia [mak″ro-glos′e-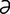 ] excessive size of the tongue.
] excessive size of the tongue.
macrognathia [mak″ro-na′the-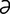 ] abnormal overgrowth of the jaw.
] abnormal overgrowth of the jaw.
macrogols [mak′ro-gols] a polyethylene glycol used in the manufacure of drugs as solvents.
macromastia [mak″ro-mas′te- ] excessive size of the mammary glands.
] excessive size of the mammary glands.
macromelanosomes [mak″ro-mel′ -no-sōm″] large pigment granules; seen in color dilution alopecia.
-no-sōm″] large pigment granules; seen in color dilution alopecia.
macromelia [mak″ro-me′le- ] enlargement of one or more limbs.
] enlargement of one or more limbs.
macromelus [mak-rom′ -l
-l s] a fetus with abnormally large or long limbs.
s] a fetus with abnormally large or long limbs.
macrometeorology measurement of the macroclimate.
macromonocyte [mak″ro-mon′o-sīt] a giant monocyte.
macromyeloblast [mak″ro-mi′ -lo-blast] a large myeloblast.
-lo-blast] a large myeloblast.
macronormoblast [mak″ro-nor′mo-blast] a very large nucleated erythrocyte; macroblast.
macronucleus [mak″ro-noo′kle- s] the larger nucleus when there are two in the cell.
s] the larger nucleus when there are two in the cell.
macronychia [mak″ro-nik′e- ] abnormally enlarged claws or hooves.
] abnormally enlarged claws or hooves.
macropenis [mak″ro-pe′nis] megalopenis.
m. activating factor (MAF) a lymphokine that activates macrophages, for example interferon.
angry m. see activated macrophage (above).
m. chemotactic factor (MCF) a lymphokine that attracts macrophages.
m. colony-stimulating factor see colony-stimulating factors.
macrophthalmia [mak″rof-thal′me- ] abnormal enlargement of the eye.
] abnormal enlargement of the eye.
macropod [mak″ro-pod] members of the marsupial family Macropodidae.
macropodia [mak″ro-po′de- ] excessive size of the feet.
] excessive size of the feet.
macroprosopia [mak″ro-pro-so′pe- ] excessive size of the face.
] excessive size of the face.
macrorhabdosis infection by Macrorhabdus ornithogaster; see megabacteriosis.
macroscopic [mak″ro-skop′ik] of large size; visible to the unaided eye.
macroscopy [m -kros′k
-kros′k -pe] examination with the unaided eye.
-pe] examination with the unaided eye.
macrosigmoid [mak″ro-sig′moid] excessive size of the sigmoid colon.
macrosomatia, macrosomia [mak″ro-so-ma′she- , mak″ro-so′me-
, mak″ro-so′me- ] great bodily size.
] great bodily size.
macrotia [mak-ro′sh ] abnormal enlargement of the pinna of the ear.
] abnormal enlargement of the pinna of the ear.
m. acusticae terminations of the vestibulocochlear nerve in the utricle and saccule.
m. atrophica a white atrophic patch on the skin.
m. corneae see macula (4) (above).
m. densa a zone of heavily nucleated cells in the distal renal tubule.
m. germinativa germinal area; the part of the conceptus where the embryo is formed.
m. lutea retinae see macula retinae (below).
maculate [mak′u-lāt] spotted or blotched.
macule [mak′ūl] a discolored spot on the skin that is not raised above the surface.
maculocerebral [mak″u-lo-ser′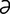 -br
-br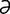 l] pertaining to the macula lutea and the brain.
l] pertaining to the macula lutea and the brain.
maculopapular [mak″u-lo-pap′u-l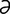 r] both macular and papular.
r] both macular and papular.
mad cow disease see bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE).
mad itch see Aujeszky’s disease.
madarosis [mad″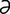 -ro′sis] loss of eyelashes or eyebrows.
-ro′sis] loss of eyelashes or eyebrows.
madeira vine see Anredera cordifolia.
Madura foot [m -doo′r
-doo′r ] see maduromycosis.
] see maduromycosis.
maduramicin, maduramycin a polyether ionophore used in poultry feed as a coccidiostat.
Madurella [mad″u-rel′ ] a genus of fungi associated with the lesions of maduromycosis in humans.
] a genus of fungi associated with the lesions of maduromycosis in humans.
maduromycetoma [m -doo′r
-doo′r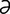 ] maduromycotic mycetoma.
] maduromycotic mycetoma.
maduromycotic [m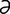 -doo′r
-doo′r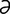 -mi-kot-ik] pertaining to or emanating from maduromycosis.
-mi-kot-ik] pertaining to or emanating from maduromycosis.
maedi a chronic pneumonia of sheep caused by a lentivirus, which also causes visna when it invades the brain of sheep. In maedi the characteristic features are a prolonged incubation period of more than 2 years, a progressive pneumonia which lasts for about 6 months, initially with dyspnea and respiratory distress at exercise but terminally also at rest, and at the inevitable death, an abnormally high density and heaviness of the lungs. Some sheep show chronic wasting and/or have indurative mastitis. A disease notifiable to the OIE (see Table 22). Called also maedi–visna, Graaff–Reinet disease, la bouhite, ovine progressive pneumonia and lymphoid interstitial pneumonia.
MAF macrophage activating factor.
MAFF [formerly] Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food, in the UK. See DEFRA.
wool m. see cutaneous myiasis.
Magill circuit [m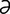 gil′] see Magill circuit.
gil′] see Magill circuit.
magnesemia [mag″n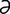 -se′me-
-se′me-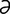 ] hypermagnesemia.
] hypermagnesemia.
magnesia [mag-ne′zh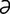 ] magnesium oxide; aperient and antacid.
] magnesium oxide; aperient and antacid.
magnesium (Mg) [mag-ne′ze-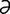 m] a chemical element, atomic number 12, atomic weight 24.312. See Table 4. Its salts are essential in nutrition, being required for the activity of many enzymes, especially those concerned with oxidative phosphorylation. It is found in the intra- and extracellular fluids and is excreted in urine and feces.
m] a chemical element, atomic number 12, atomic weight 24.312. See Table 4. Its salts are essential in nutrition, being required for the activity of many enzymes, especially those concerned with oxidative phosphorylation. It is found in the intra- and extracellular fluids and is excreted in urine and feces.
m. ammonium phosphate (MAP) a common constituent of urinary calculi. See urolithiasis.
blood m. concentration of magnesium in the blood. See hypermagnesemia, hypomagnesemia.
m. carbonate, m. hydroxide, m. oxide, m. phosphate, m. trisilicate compounds used as antacids.
endogenous m. magnesium contributed to the feces by the intestinal secretions.
m. gluconate a magnesium replenisher.
m. sulfate–chloral hydrate mixture see chloral hydrate and magnesium sulfate.
magnet [mag′n t] an object having polarity and capable of attracting iron.
t] an object having polarity and capable of attracting iron.
oral dose m. see reticular magnet.
magnetism [mag′n -tiz-
-tiz- m] magnetic attraction or repulsion.
m] magnetic attraction or repulsion.
Maine-Anjou red, red-and-white, or red-roan dual-purpose cattle originating in northern France.
m. r. for energy see energy requirements.
major histocompatibility complex [ma′j r] see major histocompatibility complex.
r] see major histocompatibility complex.
mal [mahl] [Fr.] illness. disease.
m. de caderas see Trypanosoma equinum.
m. de playa South American name for Lantana poisoning.
m. des mains sales see hydatid disease.
m. do eucalipto disease caused by poisoning with the fungus Ramaria spp.
petit m. momentary loss of consciousness without convulsive movements. See also partial seizure.
m. seco [Span.] South American name for grass sickness, dysautonomia.
mala [ma′l ] the cheek or cheek bone.
] the cheek or cheek bone.
malabsorption [mal″ b-sorp′sh
b-sorp′sh n] impaired intestinal absorption of nutrients.
n] impaired intestinal absorption of nutrients.
malaccol an insecticidal substance present in the roots of Derris spp. plants.
malacoma an abnormally soft part or spot.
m. vesicae a flat yellow growth on the mucosa of the bladder.
malacosis [mal″ -ko′sis] malacia.
-ko′sis] malacia.
malacosteon [mal″ -kos′te-on] osteomalacia.
-kos′te-on] osteomalacia.
maladie [mahl″ah-de′] see mal.
m. du jeune âge du chat feline panleukopenia.
maladjustment syndrome [mal″ -just′m
-just′m nt] see neonatal maladjustment syndrome.
nt] see neonatal maladjustment syndrome.
malady [mal′ -de] a disease or illness.
-de] a disease or illness.
Malamute, malemute see Alaskan malamute.
malar [ma′l r] pertaining to mala. See also zygomatic, jugal.
r] pertaining to mala. See also zygomatic, jugal.
malaris muscle the cutaneous muscle which depresses the lower eyelid.
Malassez named after L.C. Malassez (1842–1909), a French physiologist.
M. disease cyst of the testis.
malate [ma′lāt] a salt of malic acid.
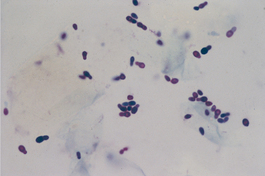
M-6: Malassezia pachydermatis from a dog ear (modified Wright-Giemsa stain).
From Gotthelf LN, Small Animal Ear Diseases, 2nd Edition. Saunders, 2005.
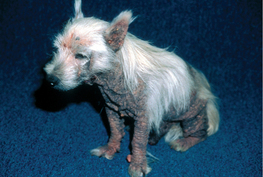
M-7: Malasseziasis in a West Highland white terrier.
From Medleau L, Hnilica KA, Small Animal Dermatology, 2nd Edition. Saunders, 2006.
malaxate [mal′ k-sāt] to knead, as in making pills.
k-sāt] to knead, as in making pills.
malaxation [mal″ k-sa′sh
k-sa′sh n] an act of kneading.
n] an act of kneading.
maldescent faulty descent of the testicle into the scrotum.
maldevelopment [mal″d -vel′
-vel′ p-m
p-m nt] abnormal growth or development.
nt] abnormal growth or development.
male [māl] an individual of the sex that produces spermatozoa.
m. castrate see barrow, capon, gelding, steer, wether.
m. feminizing syndrome see feminizing syndrome.
m. pseudohermaphrodite see pseudohermaphrodite.
maleberry see Lyonia ligustrina.
maleruption [mal″ -rup′sh
-rup′sh n] see teeth maleruption.
n] see teeth maleruption.
m. aphtha see contagious ecthyma.
m. carbuncle a form of anthrax in humans.
m. head catarrh malignant catarrhal fever.
m. histiocytosis see malignant histiocytosis.
m. hyperthermia see malignant hyperthermia, porcine stress syndrome.
m. lymphoma tautology for lymphoma; all lymphomas are malignant.
m. pustule see malignant carbuncle (above).
m. theileriosis theileriosis caused by Theileria hirci.
malignin a protein fragment present in the serum of human patients with malignant glial tumors.
Malinois see Belgian Malinois.
mallard see Anas platyrhynchos.
malleable susceptible of being beaten out into a thin plate.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
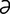 -kahk′] members of the genus Macaca, of the family Cercopithecoidae, the Old World monkeys. They are generally medium to large-sized, heavily built, and their tails range in length from long to absent. Many species have been important in biomedical research. Includes stump-tailed macaque (M. arctoides); long-tailed or crab-eating macaque (M. fascicularis); rhesus macaque (M. mulatta), see rhesus monkey; pig-tailed macaque (M. nemestrina); crested black macaque (M. nigra); bonnet macaque or bonnet monkey (M. radiata); liontailed macaque (M. silensus); Barbary macaque or Barbary ape (M. sylvana).
-kahk′] members of the genus Macaca, of the family Cercopithecoidae, the Old World monkeys. They are generally medium to large-sized, heavily built, and their tails range in length from long to absent. Many species have been important in biomedical research. Includes stump-tailed macaque (M. arctoides); long-tailed or crab-eating macaque (M. fascicularis); rhesus macaque (M. mulatta), see rhesus monkey; pig-tailed macaque (M. nemestrina); crested black macaque (M. nigra); bonnet macaque or bonnet monkey (M. radiata); liontailed macaque (M. silensus); Barbary macaque or Barbary ape (M. sylvana). k-don′
k-don′ ld] a purse-string retention technique for correction of cervical incompetence in breeding mares.
ld] a purse-string retention technique for correction of cervical incompetence in breeding mares. r-a′sh
r-a′sh n] the softening of a solid by soaking. In histology, the softening of a tissue by soaking, especially in acids, until the connective tissue fibers are dissolved so that the tissue components can be teased apart. In obstetrics, the degenerative changes with discoloration and softening of tissues, and eventual disintegration, of a fetus retained in the uterus after its death. In herbal medicine, certain herbs may require cold water to make produce infusions or decoctions if the active ingredient is susceptible to inactivation by heat.
n] the softening of a solid by soaking. In histology, the softening of a tissue by soaking, especially in acids, until the connective tissue fibers are dissolved so that the tissue components can be teased apart. In obstetrics, the degenerative changes with discoloration and softening of tissues, and eventual disintegration, of a fetus retained in the uterus after its death. In herbal medicine, certain herbs may require cold water to make produce infusions or decoctions if the active ingredient is susceptible to inactivation by heat. -ken′ze] a method of collecting samples from the haircoat, particularly of cats, for diagnosis of dermatophytosis. A sterile toothbrush is used to brush the hair thoroughly and is then pressed onto a plate or slant of Sabouraud’s agar and incubated.
-ken′ze] a method of collecting samples from the haircoat, particularly of cats, for diagnosis of dermatophytosis. A sterile toothbrush is used to brush the hair thoroughly and is then pressed onto a plate or slant of Sabouraud’s agar and incubated. -kan″tho-ring′k
-kan″tho-ring′k s] a genus of large acanthocephalans in the family Oligacanthorhynchidae.
s] a genus of large acanthocephalans in the family Oligacanthorhynchidae.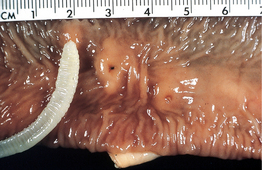
 -lās] a complex in which normal serum amylase is bound to a variety of specific binding proteins, forming a complex too large for renal excretion. It is not correlated with any specific disease state; however, in hyperamylasemia or pancreatitis, it can result in urinary amylase concentrations not rising concomitantly with serum concentrations.
-lās] a complex in which normal serum amylase is bound to a variety of specific binding proteins, forming a complex too large for renal excretion. It is not correlated with any specific disease state; however, in hyperamylasemia or pancreatitis, it can result in urinary amylase concentrations not rising concomitantly with serum concentrations. m] pl. macroconidia; a large conidium produced by some fungi such as Microsporum spp.
m] pl. macroconidia; a large conidium produced by some fungi such as Microsporum spp.
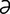 -ment] any of the macronutrients that are chemical elements, including calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, potassium, sodium and chloride.
-ment] any of the macronutrients that are chemical elements, including calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, potassium, sodium and chloride. -me′to-sīt] 1. a cell that produces macrogametes. 2. the female gametocyte of ampicomplexan protozoa that matures into a macrogamete.
-me′to-sīt] 1. a cell that produces macrogametes. 2. the female gametocyte of ampicomplexan protozoa that matures into a macrogamete. ] neuroglial cells of ectodermal origin, i.e. the astrocytes and oligodendrocytes considered together.
] neuroglial cells of ectodermal origin, i.e. the astrocytes and oligodendrocytes considered together. ] moderate reduction in the number of sulci of the cerebrum, sometimes with increase in the brain substance, resulting in excessive size of the gyri.
] moderate reduction in the number of sulci of the cerebrum, sometimes with increase in the brain substance, resulting in excessive size of the gyri. r-
r- l] the major minerals in animal nutrition (as distinct from trace minerals). Includes calcium, phosphorus, sodium, chlorine, potassium, magnesium, sulfur.
l] the major minerals in animal nutrition (as distinct from trace minerals). Includes calcium, phosphorus, sodium, chlorine, potassium, magnesium, sulfur. -kūl] a very large molecule having a polymeric chain structure, as in proteins, polysaccharides, nucleic acids, etc.
-kūl] a very large molecule having a polymeric chain structure, as in proteins, polysaccharides, nucleic acids, etc. -br
-br l fish′
l fish′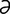 r] an abnormally large eyelid aperture that allows greater exposure of cornea, conjunctiva and sclera. Commonly seen in the brachycephalic dog breeds. Causes abnormal distribution of the tear film and lagophthalmos and predisposes to proptosis and exposure keratitis.
r] an abnormally large eyelid aperture that allows greater exposure of cornea, conjunctiva and sclera. Commonly seen in the brachycephalic dog breeds. Causes abnormal distribution of the tear film and lagophthalmos and predisposes to proptosis and exposure keratitis.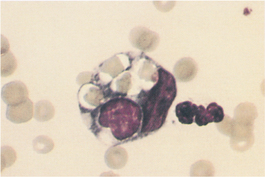
 ] one of the endemic Australian genera of the cycads in the family Zamiaceae; contain cycad glycosides (e.g. macrozamin) and cause liver necrosis, gastroenteritis and zamia staggers. Species associated with poisoning include M. communis, M. diplomera, M. heteromera, M. lucida, M. miquelii, M. moorei, M. mountperriensis, M. pauli-guilielmi, M. riedlei.; others are suspected. Called also burrawang, zamia.
] one of the endemic Australian genera of the cycads in the family Zamiaceae; contain cycad glycosides (e.g. macrozamin) and cause liver necrosis, gastroenteritis and zamia staggers. Species associated with poisoning include M. communis, M. diplomera, M. heteromera, M. lucida, M. miquelii, M. moorei, M. mountperriensis, M. pauli-guilielmi, M. riedlei.; others are suspected. Called also burrawang, zamia. ] pl. maculae [L.] 1. a stain, spot, or thickening; 2. an area distinguishable by color or otherwise from its surroundings. Often used alone to refer to the macula retinae. 3. a moderate size corneal opacity that can be seen without special optical aids; presenting as a gray spot intermediate between a nebula and a leukoma. 4. macula lutea.
] pl. maculae [L.] 1. a stain, spot, or thickening; 2. an area distinguishable by color or otherwise from its surroundings. Often used alone to refer to the macula retinae. 3. a moderate size corneal opacity that can be seen without special optical aids; presenting as a gray spot intermediate between a nebula and a leukoma. 4. macula lutea.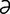 -doo′r
-doo′r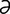 -mi-ko′sis ] a chronic disease due to various fungi or actinomycetes, affecting various body tissues, particularly the feet; called also mycetoma. The most common form in humans affects the foot (Madura foot) and is characterized by sinus formation, necrosis and swelling. The disease is recorded in the horse, in which there are nasal granulomas and similar lesions in the skin. The fungi Helminthosporium spp., Allescheria spp. and Curvularia spp. are present in the lesions. See also mycetoma.
-mi-ko′sis ] a chronic disease due to various fungi or actinomycetes, affecting various body tissues, particularly the feet; called also mycetoma. The most common form in humans affects the foot (Madura foot) and is characterized by sinus formation, necrosis and swelling. The disease is recorded in the horse, in which there are nasal granulomas and similar lesions in the skin. The fungi Helminthosporium spp., Allescheria spp. and Curvularia spp. are present in the lesions. See also mycetoma. n-īd] a sulfonamide that is not inhibited by the presence of pus and necrotic tissue; used mostly for local application to infected wounds, especially burns. Called also homosulfanilamide, sulfamylon.
n-īd] a sulfonamide that is not inhibited by the presence of pus and necrotic tissue; used mostly for local application to infected wounds, especially burns. Called also homosulfanilamide, sulfamylon. ] 1. a suspension of finely divided material in a small amount of water. 2. a thin, paste-like substance composed of organic material.
] 1. a suspension of finely divided material in a small amount of water. 2. a thin, paste-like substance composed of organic material.
 m] a growth response in a nonmotile organism under the influence of a magnet.
m] a growth response in a nonmotile organism under the influence of a magnet. -f
-f -ka′sh
-ka′sh n] 1. apparent increase in size, as under the microscope. 2. the process of making something appear larger, as by use of lenses. 3. the ratio of apparent (image) size to real size. 4. radiologicalmagnification; a factor of object to film distance.
n] 1. apparent increase in size, as under the microscope. 2. the process of making something appear larger, as by use of lenses. 3. the ratio of apparent (image) size to real size. 4. radiologicalmagnification; a factor of object to film distance. m] the highly coiled, second zone of the hen’s left oviduct. About 30 cm long. The albumen-secreting zone. The egg takes about 3 hours to pass through this part.
m] the highly coiled, second zone of the hen’s left oviduct. About 30 cm long. The albumen-secreting zone. The egg takes about 3 hours to pass through this part. -nans] in terms of animal nutrition, the amount and quality of the diet required to maintain an adult animal without providing additional nutriment for production, reproduction or weight gain.
-nans] in terms of animal nutrition, the amount and quality of the diet required to maintain an adult animal without providing additional nutriment for production, reproduction or weight gain.
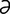 -līn′m
-līn′m nt] displacement, especially of the teeth from their normal relation to the line of the dental arch.
nt] displacement, especially of the teeth from their normal relation to the line of the dental arch. -se′zh
-se′zh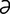 ] a lipophilic yeast which is commonly found on the skin and particularly in normal and diseased ears of dogs and cats. Includes M. pachydermatis, M. canis. Called also Pityrosporum canis.
] a lipophilic yeast which is commonly found on the skin and particularly in normal and diseased ears of dogs and cats. Includes M. pachydermatis, M. canis. Called also Pityrosporum canis.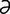 -se′zh
-se′zh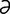 sis] infection with the yeast, Malassezia. In dogs and rarely cats, skin and ear infections occur, usually secondary to allergic skin disease or an underlying systemic disease, resulting in overgrowth of yeasts which are otherwise normal inhabitants. There is alopecia, erythema, seborhea, and intense pruritus; with chronicity, the skin becomes hyperpigmented, hyperkeratotic and lichenified.
sis] infection with the yeast, Malassezia. In dogs and rarely cats, skin and ear infections occur, usually secondary to allergic skin disease or an underlying systemic disease, resulting in overgrowth of yeasts which are otherwise normal inhabitants. There is alopecia, erythema, seborhea, and intense pruritus; with chronicity, the skin becomes hyperpigmented, hyperkeratotic and lichenified.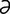 -sim″
-sim″ -la′sh
-la′sh n] 1. imperfect, faulty or disordered assimilation. 2. the inability of the gastrointestinal tract to take up one or more ingested nutrients, whether due to faulty digestion (maldigestion) or to impaired intestinal mucosal transport (malabsorption).
n] 1. imperfect, faulty or disordered assimilation. 2. the inability of the gastrointestinal tract to take up one or more ingested nutrients, whether due to faulty digestion (maldigestion) or to impaired intestinal mucosal transport (malabsorption). -thi′on] one of the least toxic and most widely used organophosphorus insecticides in companion animals. Toxicity when it occurs is usually due to gross overconcentration of the compound in the topical preparation used. See also organophosphorus compound.
-thi′on] one of the least toxic and most widely used organophosphorus insecticides in companion animals. Toxicity when it occurs is usually due to gross overconcentration of the compound in the topical preparation used. See also organophosphorus compound. n] incomplete digestion such as occurs in pancreatic exocrine or bile salt deficiency. In ruminants a defect in ruminal microflora could have the same effect. See also malassimilation.
n] incomplete digestion such as occurs in pancreatic exocrine or bile salt deficiency. In ruminants a defect in ruminal microflora could have the same effect. See also malassimilation. n] defective or abnormal formation; deformity; an anatomical aberration, especially one acquired during development.
n] defective or abnormal formation; deformity; an anatomical aberration, especially one acquired during development. -lig′n
-lig′n n-se] a tendency to progress in virulence. In popular usage, any condition that, if uncorrected, tends to worsen so as to cause serious illness or death. Malignant neoplasia is the best known example.
n-se] a tendency to progress in virulence. In popular usage, any condition that, if uncorrected, tends to worsen so as to cause serious illness or death. Malignant neoplasia is the best known example. -lig′n
-lig′n nt] tending to become progressively worse and to result in death; having the properties of anaplasia, invasiveness, virulence and metastasis; said of tumors and fulminating infections.
nt] tending to become progressively worse and to result in death; having the properties of anaplasia, invasiveness, virulence and metastasis; said of tumors and fulminating infections. -lig′n
-lig′n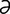 nt k
nt k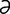 -tahr′
-tahr′ l fe′v
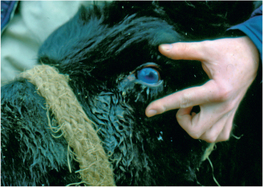
l fe′v r] an acute highly infectious, fatal herpesvirus disease of cattle, farmed deer and occasionally pigs characterized by an erosive stomatitis and gastroenteritis, erosions on the mucosa of the upper respiratory tract, keratoconjunctivitis, encephalitis, lymphadenopathy and lymphoproliferative vasculitis in multiple tissues. There are at least two viruses involved both of which cause inapparent infection in their reservoir hosts. A wildebeest-associated form of the disease is caused by alcephaline herpesvirus 1. It occurs in most African countries in cattle which co-mingle with clinically normal wildebeest and hartebeest. It is epizootic and seasonal. It can also occur in zoological gardens in other countries. Sheep-associated MCF is caused by a poorly characterized virus, presumably ovine herpesvirus 2 (OvHV-2). Cases mostly occur when cattle have had contact with lambing ewes and usually start 1–2 months later. Goats can also act as a source of OvHV-2 infection for cattle. Cases without apparent or recent exposure to sheep do occur but are uncommon. Called also bovine malignant catarrh, malignant head catarrh.
r] an acute highly infectious, fatal herpesvirus disease of cattle, farmed deer and occasionally pigs characterized by an erosive stomatitis and gastroenteritis, erosions on the mucosa of the upper respiratory tract, keratoconjunctivitis, encephalitis, lymphadenopathy and lymphoproliferative vasculitis in multiple tissues. There are at least two viruses involved both of which cause inapparent infection in their reservoir hosts. A wildebeest-associated form of the disease is caused by alcephaline herpesvirus 1. It occurs in most African countries in cattle which co-mingle with clinically normal wildebeest and hartebeest. It is epizootic and seasonal. It can also occur in zoological gardens in other countries. Sheep-associated MCF is caused by a poorly characterized virus, presumably ovine herpesvirus 2 (OvHV-2). Cases mostly occur when cattle have had contact with lambing ewes and usually start 1–2 months later. Goats can also act as a source of OvHV-2 infection for cattle. Cases without apparent or recent exposure to sheep do occur but are uncommon. Called also bovine malignant catarrh, malignant head catarrh.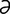 -lig′n
-lig′n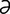 nt
nt  -de′m
-de′m ] an acute infection of wounds by Clostridium chauvoei, C. novyi, C. perfringens, C. septicum or C. sordellii. The inflammation causes severe swelling and discoloration of skin and exposed tissues. There may be local subcutaneous emphysema and a frothy exudate, depending on the identity of the invading organism. There is a high fever and a profound toxemia; death follows within a few hours if treatment is not provided. Special occurrences are when a large number of animals are affected at one time. These include involvement of the vulva in recently lambed ewes, of shearing or docking wounds, and of the umbilicus or eyes of recently born lambs.
] an acute infection of wounds by Clostridium chauvoei, C. novyi, C. perfringens, C. septicum or C. sordellii. The inflammation causes severe swelling and discoloration of skin and exposed tissues. There may be local subcutaneous emphysema and a frothy exudate, depending on the identity of the invading organism. There is a high fever and a profound toxemia; death follows within a few hours if treatment is not provided. Special occurrences are when a large number of animals are affected at one time. These include involvement of the vulva in recently lambed ewes, of shearing or docking wounds, and of the umbilicus or eyes of recently born lambs.