Chapter 112 Luxation, Subluxation, and Shearing Injuries of the Tarsal Joint
Luxation, subluxation, and shearing injuries of the tarsus involve damage to the supporting ligaments of the joint. Treatment and prognosis of these injuries depend on the location of the ligament damage and subsequent joint instability. Subluxations can be caused by spontaneous overstress or external trauma. Vehicular trauma usually causes luxations and shear injuries. Conservative treatment of most of these injuries with external coaptation is not advised, because continued instability and the development of degenerative joint disease are the likely outcomes.
ANATOMY AND SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS
General
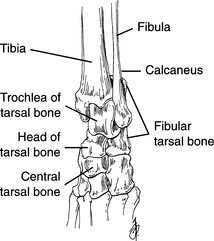
• The tarsus consists of the tibia, fibula, metatarsal bones, and seven specific tarsal bones orderly stacked in levels (Fig. 112-1).
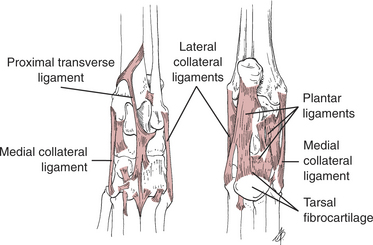
• A multiple complex arrangement of ligaments connects the bones of the joint and helps to prevent luxation (Fig. 112-2).
• The tarsocrural joint is formed by the tibia and fibula at the proximal level and by the talus and calcaneus at the distal level.
• The intertarsal joints are all the articulations between the tarsal bones. Several of these joints are named and include the
• Talocalcaneocentral joint—between the talus and central tarsal bone (includes a small communication with the calcaneus)
• Centrodistal joint (distal intertarsal joint)—between the central tarsal bone and distal numbered tarsal bones
Tarsocrural Joint
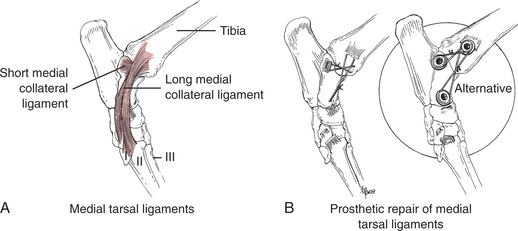
• The major ligaments providing stability on the medial side of the joint are the long medial ligaments and tibiotalar short component ligament (Fig. 112-3A).
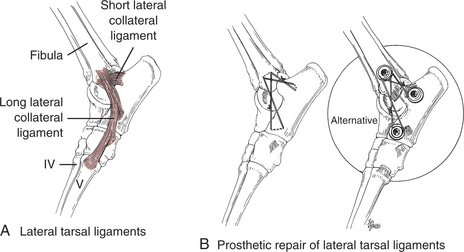
• The major ligaments providing stability on the lateral side of the joint are the long lateral ligament and the calcaneofibular short component ligament (Fig. 112-4A).
• The components of the medial and lateral ligaments complement each other in maintaining the talus in the mortise provided by the tibia and fibula.
• Certain parts of the ligament complexes are tighter in extension (long lateral and long medial ligaments) or flexion (calcaneofibular and tibiotalar short component ligaments).
• The tibiotalar and calcaneofibular short component ligaments of the medial and lateral sides, respectively, are especially important for maintaining stability of the joint. The joint capsule and malleoli also contribute to joint stability.
• The gross anatomy of the medial and lateral collateral ligament complexes is similar (see Figs. 112-3 and 112-4). The components cross at the tarsocrural joint space, providing the greatest amount of ligament and an advantageous spatial arrangement directly over the joint.
Intertarsal and Tarsometatarsal Joints
• The most common injury is damage to the plantar ligaments and tarsal fibrocartilage (see Fig. 112-2).
• Most of the intertarsal joint stability is provided by three distinct plantar ligaments. These ligaments fuse, with a thickening of the joint capsule (the tarsal fibrocartilage), at the tarsometatarsal joint.
• The first ligament originates from the plantar surface of the sustentaculum tali and attaches to the central tarsal bone and tarsometatarsal joint capsule.
• The second ligament originates from the plantar-lateral surface of the calcaneus. It joins with the long component of the lateral collateral ligament complex and attaches to the base of the fifth metatarsal bone.
TARSOCRURAL LUXATION AND SUBLUXATION
Double-Prosthesis Replacement
• Double-prosthesis replacement (described later) closely reproduces the components of the intact medial and lateral collateral ligament complexes, thus allowing nearly normal joint stability to be maintained throughout a functional range of motion.
• Similar to the components of the normal collateral ligaments, double-suture prostheses become taut and lax with flexion and extension. Because of this, wire is not useful. Certain sutures (see later) give more successful results, most likely owing to the retention of elasticity upon cyclic loading.
• Clinically, double-ligament replacement gives results superior to conservative management with splints or non-anatomic single ligament replacement methods. The prognosis is good for long-term function with most closed luxation and subluxation injuries, depending on timely repair (within 5 days of injury) and absence of articular damage.
Preoperative Considerations
• Tarsocrural subluxation usually results from complete rupture or avulsion of either the lateral or medial collateral ligament complex.
• In medial ruptures, the paw tilts abnormally toward the lateral direction with a laterally (valgus) applied force.
• Occasionally, there is rupture of only the long or short components of the medial or lateral ligament complexes. Less joint laxity makes these subluxation injuries more difficult to diagnose. Determine joint laxity using the following methods:
• Place lateral and medial tilt forces on the hock at different joint angles: Laxity in extension but not flexion suggests major damage to the long medial ligament, or long lateral ligament; laxity in only flexion suggests that most damage is isolated to the tibiotalar or calcaneofibular short components.
• Make a dorsoplantar (stress) radiograph while applying lateral and medial tilt forces on the hock: Take the stress radiograph at the tarsocrural joint angle that produces the subluxation; for subtle subluxations, compare this radiograph with a similar radiograph of the contralateral (normal) hock.
Surgical Procedure
Technique
1. Clip the injured limb from the level of the proximal femur, extending distally to include the paw. Include the paw in the sterile field to allow direct manipulation.
2. Place the patient in lateral recumbency, with the injured limb up for lateral replacement or down for medial replacement, and prepare the limb for aseptic surgery.
3. Expose the subluxation through a curved skin incision centered over the medial or lateral malleolus.
4. Inspect the components of the ligament complexes for damage.
a. To help assess the damage, stress the ligament components with a varus or valgus tilt in both flexion and extension.
5. Replace or protect the medial or lateral ligament complexes with two figure-eight heavy sutures fastened to the bone directly, with bone anchors (BoneBiter Suture Anchor System, FlexiTwist Suture Anchor, Innovative Animal Products, Rochester, MN; SECUROS Bone Anchor, SECUROS, Charlton, MA), or with bone screws.
a. Drill bone tunnels in the malleolus in locations similar to the origins of the components of the ligament complex (see Figs. 112-3 and 112-4). Bone tunnels serve as anchors for the suture prostheses.
b. Secure the suture prosthesis that mimics the lateral or medial short components to tags of the torn ligament at the insertion site. Use a locking loop suture pattern to grip the torn ligament (see Chapter 115). A bone anchor or bone screw (see “Shear Injury”) may be needed to fix the prosthesis to the insertion site (see Figs. 112-3B,112-4B).
c. Secure the suture prosthesis that mimics the lateral or medial long components to a drill hole in the tubercle of the distal talus or distal calcaneus (see Figs. 112-3B and 112-4B). A bone anchor or bone screw (see “Shear Injury”) may be used to fix the prosthesis (see Figs. 112-3B and 112-4B).
6. Use one or two (for large patients) strands of #1 to #5 braided polyester or monofilament polybutester sutures for prosthetic replacement or protection.
7. Tie the long and short suture prostheses.
a. Tie the short prosthesis with the tarsocrural joint held in approximately 90 degrees flexion for dogs and 70 degrees for cats.
b. Tie the long suture prosthesis with the joint in a functional standing angle of 135 degrees for dogs (varies with breed) and 120 degrees for cats.
8. Expose the luxation injury through separate surgical incisions on the medial and lateral sides of the joint.
Postoperative Care
• Protect the tarsocrural joints but allow weight-bearing mobilization of the limb with a short, three- to eight-layer semi-supple softcast (3M Scotchcast Soft Cast Casting Tape, St. Paul, MN) coaptation splint. The amount of layers used depends on the size and activity level of the animal and amount of microstrain to be allowed.
• Maintain the semi-supple softcast coaptation splint for 4 to 12 weeks; the length of time depends on the amount of initial trauma, joint instability, and health issues. A longer time is required for luxation and major subluxation injuries and older animals, a shorter time for incomplete tears and partial injuries and younger animals.
• The semi-supple softcast allows for controlled mobilization by progressive unwrapping of layers to increase tissue microstrain as healing advances.
• Once all coaptation is removed, continue progressive controlled mobilization by slowly increasing the animal’s activity over another 4- to 12-week period. During this period, if the animal shows signs of increased lameness or pain, progress more slowly with controlled mobilization in a manner that does not create lameness or discomfort.