Fig. 1.
In order to slice the artery in a right angle in its axis, the specimen should be embedded in a right angle on the plate.
The embedded specimen is sliced using a microtome on thickness of 4–6 μm, the slice is mounted on a glass, and it is deparaffinized with xylene, rehydrated with a graded ethanol, and rinsed in distilled water.
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

1.
HE staining (Fig. 2a)
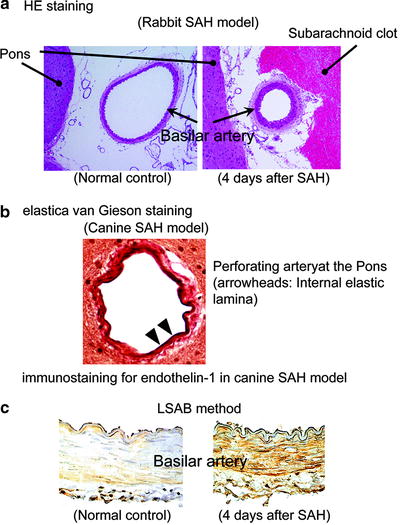

Fig. 2.
(a) HE staining of rabbit basilar artery. (b) Elastica van Gieson staining of canine perforating artery at the Pons. (c) Immunostaining for endothelin-1 of canine basilar artery.
HE staining has been most frequently used to evaluate the degree of cerebral vasospasm. Hematoxylin stains cell nuclei blue, while eosin stains cytoplasm, connective tissue and other extracellular substances pink or red.
(a)
Hematoxylin staining: 3–6 min × 1
(b)
Rinse in running tap water: 10–20 min × 1
(c)
Eosin staining: 2–30 min × 1
(d)
Dehydrated in graded ethanol
(e)
Xylene
2.
Elastica van Gieson staining (Fig. 2b)
Elastica van Gieson staining has been used to evaluate the change of internal elastic lamina of arterial wall. This method stains elastic fibers blue–black to black, cell nuclei blue to black, collagen red, and other tissue elements yellow.




(a)
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Weigert’s Resorcin-fuchsin solution: 30 min to 12 h
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


