LEPTOSPIROSIS
Leptospirosis is considered one of the most common zoonotic diseases in the world. In humans, it is also known as Weil’s disease, swineherd’s disease, rice-field disease, swamp fever, and mud fever. In horses, it can cause a condition known as periodic ophthalmia, or moon blindness. In dogs it is known as canicola disease.
HOSTS
Over 160 mammalian species, including humans, have been identified as susceptible to leptospirosis.
TRANSMISSION
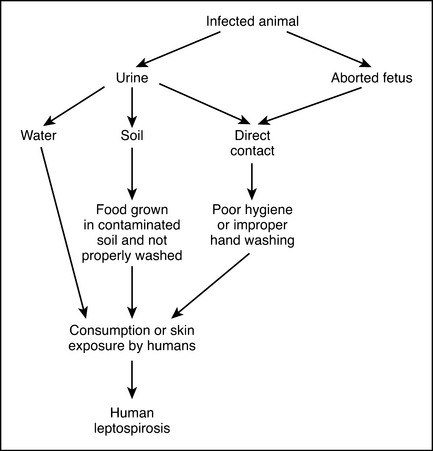
Leptospira organisms are passed in the urine of an infected host and are transmitted to another host through mucous membranes and skin lesions. Transmission may occur through exposure to water, soil, or food that has been contaminated with infected urine. The most common mode of transmission is by drinking contaminated water. Catching and eating infected rodents and eating grass and food contaminated with urine are other common modes of transmission among animals. Animals and humans can become infected by touching placentas, aborted fetuses, and related tissues (Figure 23).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree