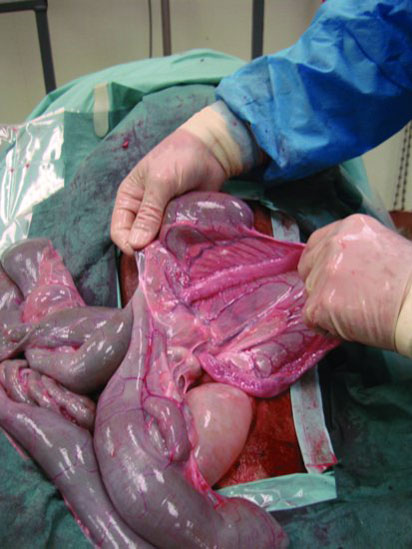
Figure 43.2 A #10 scalpel blade is used to divide the linea alba for a length of 2 cm, then manual digital pressure is applied until the peritoneum is penetrated as denoted by a sudden release of resistance.
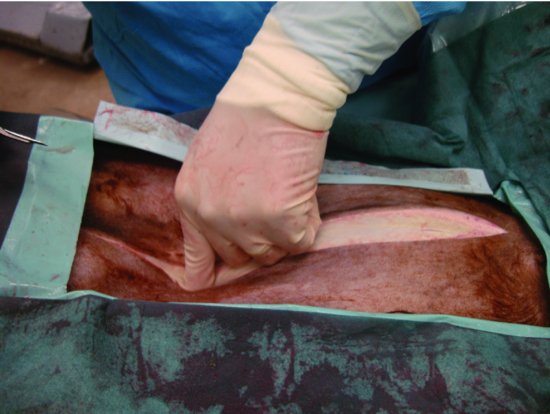
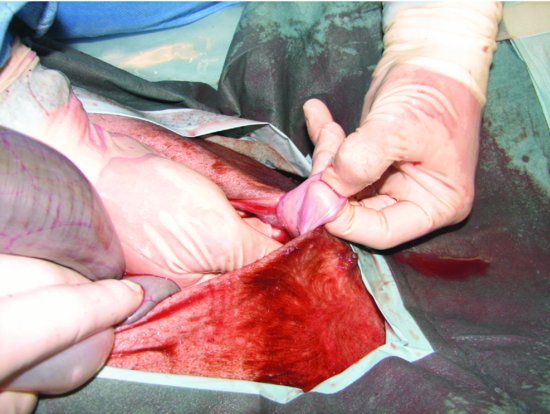
Figure 43.3 The surgeon’s index finger and middle finger are inserted into the abdomen and the ventral abdominal wall elevated to facilitate the remainder of the incision.
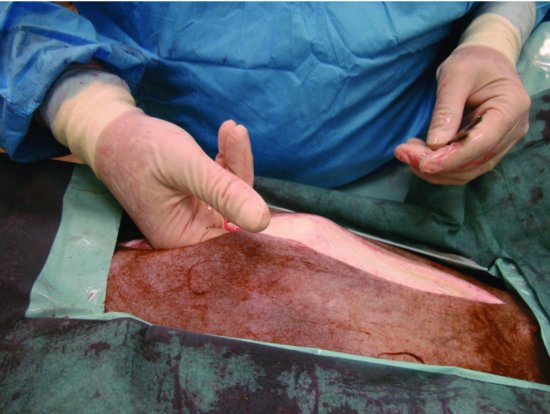
Figure 43.4 The ventral sacs of C1 are easily viewed and can be partially exteriorized via a ventral midline laparotomy incision.
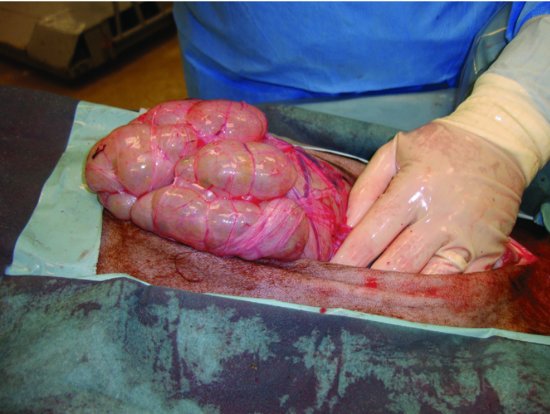
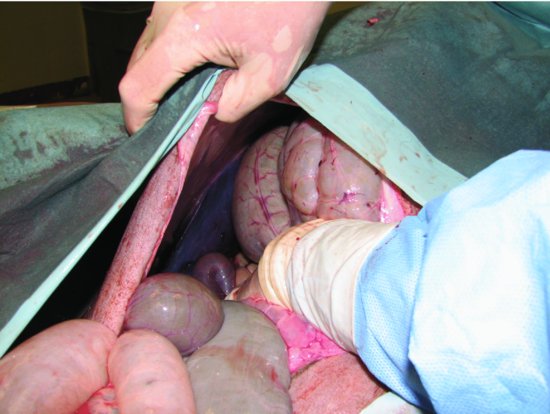
Figure 43.5 The main body (fundus) of C3 can be partially exteriorized and inspected via ventral midline.
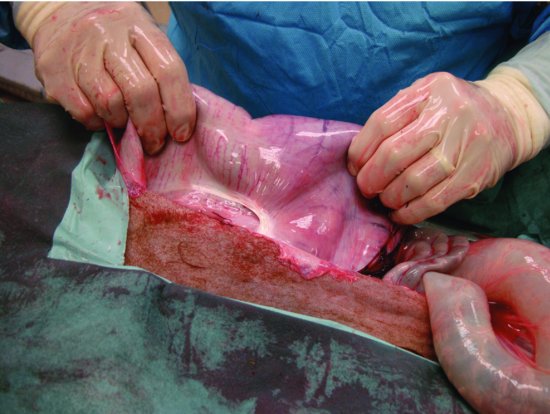
Figure 43.6 The proximal loop of the spiral colon and the spiral colon can easily be exteriorized via a ventral midline approach.
Wound Closure
The wall of the ventral abdomen is relatively thin and must be carefully reconstructed with close attention to detail. Incisions contained within the linea alba provide for good suture holding power and minimal postoperative complication. Incisions that deviate to the rectus abdominus are more prone to herniation and the external rectus sheath must be accurately reconstructed to minimize this risk. Suture size and selection should be made with consideration for tissue holding, knot security, absorption times, and bulkiness of knots (Table 43.1). Suture patterns with suture bites taken a minimum of 1.5 cm from the margin and no more than 1.5 cm apart provide for accurate reconstruction and minimize risk of dehiscence. Either simple continuous or interrupted suture patterns are acceptable. Appositional suture patterns are preferred to facilitate rapid tissue healing. When significant tension is present on the abdominal wall, tension-relieving interrupted suture patterns may be used (e.g., cruciate pattern). Absorbable suture materials should be used, and either monofilament or braided suture materials are appropriate. The subcutaneous layer is more substantial along the ventral midline and a subcutaneous suture closure is recommended. Skin can be closed using continuous or interrupted suture patterns or stainless steel skin staples. The author prefers to use a Ford Interlocking pattern (also known as forward interlocking pattern), but suture bites should not be taken more than 1 cm from the skin margin and should be spaced no more than 1 cm apart to maintain accurate alignment of the skin edges.
Table 43.1 Suture selection and suture patterns for reconstruction of the ventral midline abdominal wall of llamas and alpacas after laparotomy.
| Suture | Size | |
| Linea alba/rectus abdominus muscle | Polydioxanone Polyglactin 910 Polyglycolic acid | Adult: Alpaca: #1; Llama: #2 Weanlings: Alpaca: #0; Llama: #1 Neonates: Alpaca: #0; Llama: #0 |
| Subcutaneous tissue | Polyglecaprone Polyglactin 910 Polyglycolic acid | Adult: Alpaca: #2-0; Llama: #0 Weanlings: Alpaca: #2-0; Llama: #2-0 Neonates: Alpaca: #3-0; Llama: #2-0 |
| Skin | Nylon Polypropylene Polymerized caprolactam | Adult: Alpaca: #1; Llama: #2 Weanlings: Alpaca: #0; Llama: #1 Neonates: Alpaca: #0; Llama: #0 |
Operative Techniques for Correction of Intestinal Obstruction
Exploratory Examination for Simple Intraluminal Obstruction
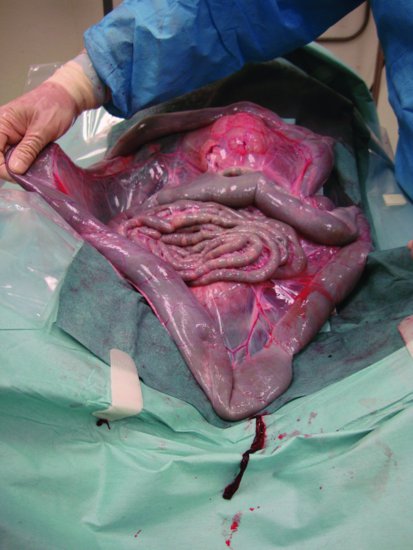
When obstruction of the duodenum, jejunum, or spiral colon is present, the site of obstruction can be found by exteriorizing a segment of normal or distended intestine and tracing this segment orad or aborad, respectively, until the obstruction is found (Video 43.1: Obstruction). The intestines of llamas and alpacas are relatively easily traumatized, and the surgeon should take precautions not to cause injury to the bowel. The author prefers to apply carboxymethylcellulose jelly to the intestine as a lubricant to prevent unintended intestinal irritation. For intraluminal obstructions, such as trochophytobezoars, the obstructed segment of intestine should be exteriorized from the abdomen, isolated using moistened surgical towels, and an enterotomy performed.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree