L
L Latin; left; length; [L.] libra (pound, balance); licentiate; light sense; [L.] limen (boundary); liter; lumbar; coefficient of induction.
λ lambda, small letter; eleventh letter in the Greek alphabet.
L genes class I MHC genes in mice.
l-region that part of the major histocompatibility complex where immune response genes are present.
La chemical symbol, lanthanum.
La Pieded Michoacan virus cause of blue eye disease of pigs; now called porcine rubulavirus.
LA test latex agglutination test.
la tremblante [Fr.] see scrapie.
label [la′b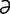 l] something that identifies; an identifying mark, tag, etc.
l] something that identifies; an identifying mark, tag, etc.
radioactive l. radioactive tracer.
labellum mouthparts of insects; carry tubes for the passage of aspirated fluids.
labia [la′be-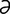 ] [L.] plural of labium.
] [L.] plural of labium.
oral l. lips of the mouth; musculomembranous folds that surround the mouth. Called also labia oris.
pudendal l. lips of the vulva. Called also labium pudendi vulvae.
labial [la′be-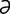 l] pertaining to a lip, or labium.
l] pertaining to a lip, or labium.
l. ulcer see eosinophilic ulcer.
lability [l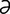 -bil′
-bil′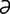 -te] the quality of being labile.
-te] the quality of being labile.
labio- word element. [L.] lip.
labioglossolaryngeal [la″be-o-glos″o-l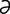 -rin′je-
-rin′je-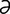 l] pertaining to the lips, tongue and larynx.
l] pertaining to the lips, tongue and larynx.
labioglossopharyngeal [la″be-o-glos″o-f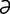 -rin′je-
-rin′je- l] pertaining to the lips, tongue and pharynx.
l] pertaining to the lips, tongue and pharynx.
labiomental [la″be-o-men′t l] pertaining to the lips and chin.
l] pertaining to the lips and chin.
labionasal [la″be-o-na′z l] pertaining to the lip and nose.
l] pertaining to the lip and nose.
labiopalatine [la″be-o-pal′ -tin] pertaining to the lips and palate.
-tin] pertaining to the lips and palate.
labioplasty [la′be-o-plas″te] plastic repair of a lip; cheiloplasty.
Labiostrongylus the largest of the common nematodes in the stomach of macropods.
labium pl. labia [L.] a fleshy border or edge; a lip.
laboratory [lab′r -tor″e] a place equipped for making tests or doing experimental work.
-tor″e] a place equipped for making tests or doing experimental work.
l. findings the results of laboratory examinations, usually with analyses and judgments.
labrum [la′br m] pl. labra [L.] an edge, rim or lip, e.g. upper lip of insects.
m] pl. labra [L.] an edge, rim or lip, e.g. upper lip of insects.
acetabular glenoidal l. see acetabular labrum (above).
laburnum Laburnum anagyroides.
osseous l. see bony labyrinth (above).
labyrinthectomy [lab“ -rin-thek′t
-rin-thek′t -me] excision of the labyrinth.
-me] excision of the labyrinth.
labyrinthine [lab“ -rin′thēn] pertaining to or emanating from a labyrinth.
-rin′thēn] pertaining to or emanating from a labyrinth.
l. responses include righting and placing reflexes and nystagmus.
labyrinthitis [lab“ -rin-thi′tis] inflammation of the labyrinth; otitis interna.
-rin-thi′tis] inflammation of the labyrinth; otitis interna.
labyrinthotomy [lab“ -rin-thot′
-rin-thot′ -me] incision of the labyrinth.
-me] incision of the labyrinth.
lac [lak] pl. lacta [L.] milk.
lac operon [lak op′ r-on] the lactose operon, a nucleotide sequence in Escherichia coli that controls the synthesis of the enzyme β-galactosidase comprising binding sequence motifs for the cap protein, which activates transcription, the repressor protein, which inhibits transcription, and a region with which RNA polymerase interacts. The first, best studied and best understood model for gene regulation.
r-on] the lactose operon, a nucleotide sequence in Escherichia coli that controls the synthesis of the enzyme β-galactosidase comprising binding sequence motifs for the cap protein, which activates transcription, the repressor protein, which inhibits transcription, and a region with which RNA polymerase interacts. The first, best studied and best understood model for gene regulation.
lac repressor see lac repressor.
Lacazia loboi a fungus that causes lobomycosis in dolphins and keloidal blastomycosis in humans.
lacertilian generally, like a lizard; specifically, a member of the suborder of lizards, Lacertilia.
laces a term describing white marking on the legs in cats.
Lachnagrostis a genus of grasses in the plant family Poaceae.
lachry- for words beginning thus see words beginning lacri-.
lacrimal [lak′r -m
-m l] pertaining to tears.
l] pertaining to tears.
l. canaliculus see lacrimal canaliculus.
l. fossa fossa in the medial wall of the orbital rim which houses the lacrimal sac.
l. gland atrophy the result of chronic dacryoadenitis in keratoconjunctivitis sicca.
imperforate l. punctum see imperforate punctum.
l. reflex tear production caused by irritation of the cornea and conjunctiva.
l. system see lacrimal apparatus (above).
lacrimation [lak″r -ma′sh
-ma′sh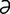 n] secretion and discharge of tears.
n] secretion and discharge of tears.
lacrimator [lak′r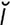 -ma″t
-ma″t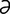 r] an agent, such as a gas, that induces the flow of tears.
r] an agent, such as a gas, that induces the flow of tears.
lacrimatory [lak′r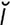 -m
-m -tor″e] causing a flow of tears.
-tor″e] causing a flow of tears.
lacrimomimetic a tear substitute; artificial tears.
lacrimotomy [lak″r -mot′
-mot′ -me] incision of the lacrimal duct or sac.
-me] incision of the lacrimal duct or sac.
lactacidemia [lak-tas“ -de′me-
-de′me- ] an excess of lactic acid in the blood; lacticemia; lactic acidemia.
] an excess of lactic acid in the blood; lacticemia; lactic acidemia.
lactacidosis see lactic acidosis.
lactaciduria [lak-tas“ -du′re-
-du′re- ] lactic acid in the urine.
] lactic acid in the urine.
lactagogue [lak′t -gog] an agent that promotes the flow of milk; galactagogue.
-gog] an agent that promotes the flow of milk; galactagogue.
lactate [lak′tāt] 1. any salt of lactic acid or the anion of lactic acid. 2. to secrete milk.
compound sodium l. see Hartmann’s solution.
l. shuttle the production of lactate in resting muscle where adequate oxygenation is available; represents a mechanism for conserving glucose absorbed from the gut by allowing it to be converted to lactate by skeletal muscle and later used for work or transferred to the liver for glycogen synthesis.
l. Tm maximal tubular concentration of lactate.
lactated potassium saline see Darrows solution.
lactating cows cows actually in milk; contrast with milking cows.
artificial l. see lactation induction (below).
current l. listing a list of all the cows in a herd which are currently being milked.
early l. drop an unexpected downturn in the lactation curve of a dairy cow in early lactation.
l. hormone lactogenic hormone, or prolactin.
inappropriate l. see galactorrhea.
l. ketosis see primary ketosis.
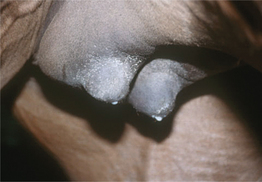
L-2 Premature lactation in a mare with ascending placentitis.
From McAuliffe SB, Slovis NM, Color Atlas of Diseases and Disorders of the Foal. Saunders, 2008.
lacteal [lak′te- l] 1. pertaining to milk. 2. any of the intestinal lymphatics that transport chyle.
l] 1. pertaining to milk. 2. any of the intestinal lymphatics that transport chyle.
lactenin [lak′t -nin] a bacteriostatic substance in milk.
-nin] a bacteriostatic substance in milk.
lactescence [lak-tes′ ns] resemblance to milk.
ns] resemblance to milk.
lactic [lak′tik] pertaining to milk.
l. a. indigestion see carbohydrate engorgement.
ruminal l. a. the concentration is high in carbohydrate engorgement.
lactic acidemia [lak″tik-as“ -de′me-
-de′me- ] lactacidemia.
] lactacidemia.
lactic acidosis [lak″tikas“ -do′sis] see lactic acidosis.
-do′sis] see lactic acidosis.
lacticemia [lak″t -se′me-
-se′me- ] lactacidemia.
] lactacidemia.
lactiferous [lak-tif′ r-
r- s] conveying milk.
s] conveying milk.
lactifuge [lak′t -fūj] checking or stopping milk secretion; an agent that so acts.
-fūj] checking or stopping milk secretion; an agent that so acts.
lactigenous [lak-tij′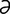 -n
-n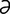 s] producing milk.
s] producing milk.
lactigerous [lak-tij′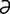 r-
r-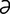 s] see lactiferous.
s] see lactiferous.
lactivorous [lak-tiv′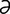 -r
-r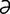 s] feeding or subsisting upon milk.
s] feeding or subsisting upon milk.
lact(o)- word element. [L.] milk.
lactobacillus pl. lactobacilli; any individual organism of the genus Lactobacillus.
lactocele [lak′to-sēl] see galactocele.
Lactococcus parviae [lak″to-kok′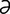 s] see Enterococcus seriolicida.
s] see Enterococcus seriolicida.
lactogen [lak′to-j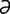 n] any substance that enhances lactation.
n] any substance that enhances lactation.
lactogenic [lak″to-jen′ik] stimulating the production of milk.
lactoglobulin [lak″to-glob′u-lin] a globulin occurring in milk.
immune l′s antibodies (immunoglobulins) occurring in the colostrum of mammals.
lactoperoxidase [lak″to-p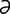 r-ok′s
r-ok′s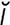 -dās] an enzyme found in milk that oxidizes thiocyanate to bacteriostatic products.
-dās] an enzyme found in milk that oxidizes thiocyanate to bacteriostatic products.
lactose [lak′tōs] a sugar derived from milk, which on hydrolysis yields glucose and galactose.
l. digestion test see lactose tolerance test (below).
lactoside [lak′to-sīd] glycoside in which the sugar constituent is lactose.
lactosuria [lak″to-su′re-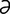 ] lactose in the urine.
] lactose in the urine.
lactotherapy treatment by milk diet.
lactotrophin, lactotropin [lak′to-tro″fin] see prolactin.
Lactuca genus in the plant family Asteraceae; includes L. sativa, L. seriola. Called also lettuce.
L. sativa toxin unidentified; large intakes reputed to cause narcosis. Called also lettuce.
cartilage l. any of the small cavities within the cartilage matrix, containing a chondrocyte.
Howship’s l. the concave cavities which are formed by osteoclasts in the process of bone resorption.
urethral l. numerous small depressions or pits in the mucous membrane of the urethra.
vascular l. a breach in any membrane or other tissue which is traversed by blood vessels.
lacunule [l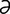 -ku′nūl] a minute lacuna.
-ku′nūl] a minute lacuna.
lacus [la′k s] pl. lacus [L.] lake.
s] pl. lacus [L.] lake.
l. lacrimalis see lacrimal lake.
Lady Campbell weed Echium plantagineum.
Laekenois see Belgian Laekenois.
Laelaptidae a family of mites, found as occasional infestations on chickens and pigeons.
laev(o)- see words commencing with levo-.
Lafora’s disease see glycoproteinosis.
l. screw a screw used in compression plating of bone fractures; it has U-shaped threads.
Lagenidium a genus of Oomycota; a parasite of mosquito larvae. Causes lagenidiosis.
lageniform [l -jen′
-jen′ -form] flask-shaped.
-form] flask-shaped.
Lagochilascaris [lag″o-k -la′k
-la′k -ris] a genus of nematodes in the family Ascarididae.
-ris] a genus of nematodes in the family Ascarididae.
L. minor found in wild felines and didelphoids (American opossums).
Lahey forceps surgical forceps of several kinds.
lahiet el tis [Ar.] see Perralderia coronopifolia.
Lahore canine fever canine ehrlichiosis.
LAK cells lymphokine-activated killer cells.
lacrimal l. see lacrimal lake.
lalobe see Balanites aegyptica.
Lama genus containing llamas, alpacas, guanacos and vicuñas.
bummer l. an American term for an orphan lamb that has to be fed artificially with milk replacer.
goat l. name for a lamb with border disease; not commonly used.
l. industry includes stud flocks which produce rams of fat lamb breeds, e.g. Dorset Down, commercial farms breeding crossbred fat lamb mothers and fattening the lambs. The latter may be undertaken in feedlots or on special pasture fattening farms. Saleyards and sale rings, lamb abattoirs and wholesale outlets comprise the marketing side of the industry.
l. marking earmarking, castration and tail docking.
l’s quarter Chenopodium album.
sucker l. a lamb still sucking the ewe and ready for slaughter. The most succulent lamb of all.
l’s tongue Scleroblitum (Chenopodium) atriplicinum, Plantago varia.
lambdoid [lam′doid] shaped like the Greek letter lambda, Λ or λ.
lambert crazyweed [lam′b rt] Oxytropis lambertii.
rt] Oxytropis lambertii.
Lambertia Australian genus of shrubs in the family Proteaceae.
L. formosa contains cyanogenic glycosides. Called also honeysuckle, honeyflower, mountain devil.
lambing parturition in the ewe.
intensive l. see shed lambing.
l. out the act of supervising and caring for the ewes in a flock during parturition.
l. paralysis see maternal obstetric paralysis.
l. rate numbers of lambs born per hundred ewes mated.
l. sickness see ovine hypocalcemia.
Lamblia [lam′ble- ] see Giardia.
] see Giardia.
lambliasis [lam-bli′ -sis] giardiasis.
-sis] giardiasis.
lambs’ tail see Anredera cordifolia.
lamella [l -mel′
-mel′ ] pl. lamellae [L.] a thin scale or plate, as of bone.
] pl. lamellae [L.] a thin scale or plate, as of bone.
circumferential l. one of the bony plates that underlie the periosteum and endosteum.
concentric l. haversian lamella (see below).
endosteal l. one of the bony plates lying deep to the endosteum.
ground l. intermediate lamella (see below).
haversian l. one of the concentric bony plates surrounding a haversian canal.
interstitial l. see intermediate lamella (above).
lamellar [l -mel′
-mel′ r] pertaining to or emanating from lamella.
r] pertaining to or emanating from lamella.
l. phagosomes common degradation product in pigment epithelium.
lameness [lām′nis] the state of being lame.
regional l. lameness in a particular part of a limb, e.g. stifle lameness.
supporting leg l. discomfort is evident when the animal is standing or bearing weight on the leg.
three-legged l. the animal does not put weight on one of its limbs.
weightbearing l. the lameness is not caused by movement of the limb but by putting weight on it.
whirlbone l. see trochanteric bursitis.
epithelial l. the layer of ependymal cells covering the choroid plexus and facing the ventricle.
l. epithelialis mucosae the layer of epithelial cells on the surface of the mucosa.
l. propria, l. propria mucosae the connective tissue layer of mucous membrane.
spiral l., l. spiralis 1. a double plate of bone winding spirally around the modiolus, dividing the spiral canal of the cochlea into the scala tympani and scali vestibuli. 2. a bony projection on the outer wall of the cochlea in the lower part of the first turn.
l. terminalis grisea thin plate forming the rostral wall of the third ventricle.
udder suspensory l. see udder suspensory apparatus.
laminagraphy [lam“ -nag′r
-nag′r -fe] see tomography.
-fe] see tomography.
laminar [lam′ -n
-n r] made up of laminae or layers; pertaining to a lamina.
r] made up of laminae or layers; pertaining to a lamina.
laminated [lam′ -nāt″ed] made up of laminae or thin layers.
-nāt″ed] made up of laminae or thin layers.
lamination a laminar structure or arrangement.
continuous l. the procedure is carried out on all cervical vertebrae for multiple lesions.
selected l. for single lesions, bone is removed from only the adjacent vertebrae.
laminin [lam′ -nin] a glycoprotein found in basement membrane (extracellular matrix).
-nin] a glycoprotein found in basement membrane (extracellular matrix).
laminography [lam“ -nog′r
-nog′r -fe] a special technique of body-section radiography. See tomography.
-fe] a special technique of body-section radiography. See tomography.
Laminosioptes [lam“ -no-se-op′tēz] a genus of mites in the family Laminosioptidae.
-no-se-op′tēz] a genus of mites in the family Laminosioptidae.
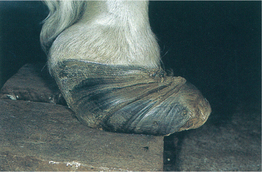
L-3 Typical rings and abnormal hoof growth of chronic laminitis in a horse.
From Pascoe R, Knottenbelt DC, Manual of Equine Dermatology. Saunders, 1999.
 l] 1. gliding; moving from point to point over the surface; unstable; fluctuating. 2. chemically unstable.
l] 1. gliding; moving from point to point over the surface; unstable; fluctuating. 2. chemically unstable. -v
-v l] a thickening of the embryonal stomodeal ectoderm eventually forming the oral vestibule.
l] a thickening of the embryonal stomodeal ectoderm eventually forming the oral vestibule. l] paired swellings flanking the developing genital tubercle and urogenital orifice prior to sex differentiation; destined to form the labia or scrotum.
l] paired swellings flanking the developing genital tubercle and urogenital orifice prior to sex differentiation; destined to form the labia or scrotum.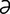 r] the function of the female organism by which the product of conception is expelled from the uterus through the vagina to the outside world. Labor may be divided into three stages. The first stage (dilatation and fetal orientation) begins with the onset of regular uterine contractions and ends when the cervical os is completely dilated and flush with the vagina, thus completing the birth canal. The second stage (expulsion) extends from the end of the first stage until the expulsion of the neonate is completed. The third stage (placental) extends from the expulsion of the neonate until the placenta and membrane are expelled and contraction of the uterus is completed. Called also parturition.
r] the function of the female organism by which the product of conception is expelled from the uterus through the vagina to the outside world. Labor may be divided into three stages. The first stage (dilatation and fetal orientation) begins with the onset of regular uterine contractions and ends when the cervical os is completely dilated and flush with the vagina, thus completing the birth canal. The second stage (expulsion) extends from the end of the first stage until the expulsion of the neonate is completed. The third stage (placental) extends from the expulsion of the neonate until the placenta and membrane are expelled and contraction of the uterus is completed. Called also parturition.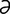 -bur′n
-bur′n m] plant member of the legume family Fabaceae; popular but very poisonous tree; the pods and seeds contain the quinolizidine alkaloid cytisine, which causes incoordination, excitement, sweating, convulsions and death. Vomiting also occurs in dogs. Called also laburnum, Cytisus laburnum, golden chain, golden rain.
m] plant member of the legume family Fabaceae; popular but very poisonous tree; the pods and seeds contain the quinolizidine alkaloid cytisine, which causes incoordination, excitement, sweating, convulsions and death. Vomiting also occurs in dogs. Called also laburnum, Cytisus laburnum, golden chain, golden rain.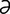 -rinth] the system of interconnecting cavities or canals of the internal ear, consisting of the vestibule, cochlea and semicircular canals. The cochlea is concerned with hearing, and the vestibule and semicircular canals with equilibrium.
-rinth] the system of interconnecting cavities or canals of the internal ear, consisting of the vestibule, cochlea and semicircular canals. The cochlea is concerned with hearing, and the vestibule and semicircular canals with equilibrium.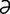 r-a′sh
r-a′sh n] 1. the act of tearing. 2. a wound produced by the tearing of body tissue, as distinguished from a cut or incision.
n] 1. the act of tearing. 2. a wound produced by the tearing of body tissue, as distinguished from a cut or incision.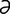 -sur′t
-sur′t s] pl. lacerti [L.] a name given to certain fibrous attachments of muscles, such as the ′lacertus fibrosus′, the fibrous insertion of the biceps brachii muscle on the medial surface of the extensor carpi radialis muscles. It is especially well-developed in horses where it forms an integral part of the stay apparatus.
s] pl. lacerti [L.] a name given to certain fibrous attachments of muscles, such as the ′lacertus fibrosus′, the fibrous insertion of the biceps brachii muscle on the medial surface of the extensor carpi radialis muscles. It is especially well-developed in horses where it forms an integral part of the stay apparatus. ] a bacterial species resident in rumens and involved in ruminant digestion.
] a bacterial species resident in rumens and involved in ruminant digestion.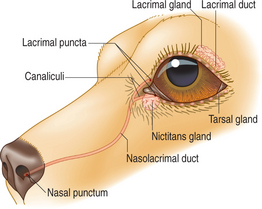
 -mo-na′z
-mo-na′z l] pertaining to the lacrimal sac and nose; more commonly called nasolacrimal.
l] pertaining to the lacrimal sac and nose; more commonly called nasolacrimal. m] a cyclic amide formed from aminocarboxylic acids by elimination of water; lactams are isomeric with lactims, which are enol forms of lactams.
m] a cyclic amide formed from aminocarboxylic acids by elimination of water; lactams are isomeric with lactims, which are enol forms of lactams. n] 1. the secretion of milk by the mammary glands. 2. the period of weeks or months during which the dam lactates.
n] 1. the secretion of milk by the mammary glands. 2. the period of weeks or months during which the dam lactates.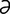 n tet′
n tet′ -ne] 1. lactation tetany of ruminants is a highly fatal disease of recently calved, lactating cows and recently lambed ewes. The disease reaches serious levels of prevalence in animals grazing grass dominated pastures and cereal crops. It is characterized by hypomagnesemia and usually an accompanying hypocalcemia. Clinical highlights include tonic and clonic muscular spasms, and convulsions and death due to respiratory failure. The disease in cattle is called also hypomagnesemic tetany, grass tetany, grass staggers. 2. lactation tetany of mares is a similar disease clinically but occurs at the foaling heat or just after the foal is weaned. It is primarily a hypocalcemia, with hypomagnesemia an uncommon finding. 3. lactation tetany of dogs and cats, see puerperal tetany.
-ne] 1. lactation tetany of ruminants is a highly fatal disease of recently calved, lactating cows and recently lambed ewes. The disease reaches serious levels of prevalence in animals grazing grass dominated pastures and cereal crops. It is characterized by hypomagnesemia and usually an accompanying hypocalcemia. Clinical highlights include tonic and clonic muscular spasms, and convulsions and death due to respiratory failure. The disease in cattle is called also hypomagnesemic tetany, grass tetany, grass staggers. 2. lactation tetany of mares is a similar disease clinically but occurs at the foaling heat or just after the foal is weaned. It is primarily a hypocalcemia, with hypomagnesemia an uncommon finding. 3. lactation tetany of dogs and cats, see puerperal tetany.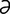 n-
n- l] may facilitate fracture of the femur, vertebrae and phalanges in lactating sows fed diets deficient in calcium and normal to high phosphorus.
l] may facilitate fracture of the femur, vertebrae and phalanges in lactating sows fed diets deficient in calcium and normal to high phosphorus.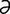 -sil′
-sil′ s] a genus of gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, all of which are generally considered to be nonpathogenic, although they have been isolated from abscesses in cats. They produce lactic acid by fermentation and play a part in the development of lactic acidosis in ruminants fed too much carbohydrate. See also yogurt.
s] a genus of gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, all of which are generally considered to be nonpathogenic, although they have been isolated from abscesses in cats. They produce lactic acid by fermentation and play a part in the development of lactic acidosis in ruminants fed too much carbohydrate. See also yogurt. -sis] the process of differentiation of cells of the mammary alveoli, as a consequence of which the alveolar cells develop the capacity to secrete milk. Called also galactopoiesis.
-sis] the process of differentiation of cells of the mammary alveoli, as a consequence of which the alveolar cells develop the capacity to secrete milk. Called also galactopoiesis.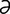 ] excessive or spontaneous milk flow; persistent secretion of milk irrespective of nursing; galactorrhea.
] excessive or spontaneous milk flow; persistent secretion of milk irrespective of nursing; galactorrhea.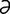 -ku′n
-ku′n ] pl. lacunae [L.] 1. a small pit or hollow cavity. 2. a defect or gap, as in the field of vision (scotoma).
] pl. lacunae [L.] 1. a small pit or hollow cavity. 2. a defect or gap, as in the field of vision (scotoma). -je′n
-je′n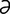 ] 1. the curved, flask-shaped organ of hearing in vertebrates more primitive than mammals, corresponding to the cochlear duct. 2. the upper extremity of the cochlear duct.
] 1. the curved, flask-shaped organ of hearing in vertebrates more primitive than mammals, corresponding to the cochlear duct. 2. the upper extremity of the cochlear duct.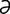 -morfs] members of the order Lagomorpha; hares, rabbits and pikas. Often mistakenly regarded as rodents, they differ in that all species are terrestrial and herbivorous with four upper incisors; in the male, the scrotum is located cranial to the penis.
-morfs] members of the order Lagomorpha; hares, rabbits and pikas. Often mistakenly regarded as rodents, they differ in that all species are terrestrial and herbivorous with four upper incisors; in the male, the scrotum is located cranial to the penis.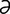 s] incomplete or defective closure of the eyelids typically due to inherited macropalpebral fissure and shallow orbits in brachycephalic animals, but also may occur due to marked ectropion, dysfunction of cranial nerve VII, proptosis, or exophthalmos. Typically leads to exposure keratitis.
s] incomplete or defective closure of the eyelids typically due to inherited macropalpebral fissure and shallow orbits in brachycephalic animals, but also may occur due to marked ectropion, dysfunction of cranial nerve VII, proptosis, or exophthalmos. Typically leads to exposure keratitis. s] a rhabdovirus found in bats that has serological similarities to, but significant differences from, the rabies virus.
s] a rhabdovirus found in bats that has serological similarities to, but significant differences from, the rabies virus. -mel“
-mel“ -po′de-
-po′de- m] pl. lamellipodia [L., Gr.] delicate sheetlike extension of cytoplasm that forms transient adhesions with the cell substrate and waves gently, enabling the cell to move along the substrate.
m] pl. lamellipodia [L., Gr.] delicate sheetlike extension of cytoplasm that forms transient adhesions with the cell substrate and waves gently, enabling the cell to move along the substrate. -n
-n ] pl. laminae [L.] a thin, flat plate or layer; a layer of a composite structure. Often used alone to mean a vertebral lamina.
] pl. laminae [L.] a thin, flat plate or layer; a layer of a composite structure. Often used alone to mean a vertebral lamina. -nek′t
-nek′t -me] surgical excision of the dorsal arch of a vertebra. The procedure is most often performed to relieve the signs caused by a ruptured intervertebral disk or a spaceoccupying lesion that is compressing the spinal cord.
-me] surgical excision of the dorsal arch of a vertebra. The procedure is most often performed to relieve the signs caused by a ruptured intervertebral disk or a spaceoccupying lesion that is compressing the spinal cord. -ni′tis] a disease of horses and housed dairy cattle, characterized by damage to the sensitive laminae of the hooves, and clinically by severe lameness, especially in the front hooves. There is heat and pain at the coronets and in bad cases protrusion of the third phalanx through the sole of the hoof. Hypoxia at the corium results in defective keratinization and the production of a laminitic ring with the occurrence of multiple rings in the hooves of animals with chronic laminitis. Most cases are caused by severe toxemia, as in engorgement on grain or metritis in the mare, and are called metabolic laminitis. Sporadic cases in heavily pregnant, overfat mares are referred to as puerperal laminitis. Some are caused by trauma, such as in pawing due to boredom or in horses transported over long distances without rest, and are called traumatic laminitis. Called also founder.
-ni′tis] a disease of horses and housed dairy cattle, characterized by damage to the sensitive laminae of the hooves, and clinically by severe lameness, especially in the front hooves. There is heat and pain at the coronets and in bad cases protrusion of the third phalanx through the sole of the hoof. Hypoxia at the corium results in defective keratinization and the production of a laminitic ring with the occurrence of multiple rings in the hooves of animals with chronic laminitis. Most cases are caused by severe toxemia, as in engorgement on grain or metritis in the mare, and are called metabolic laminitis. Sporadic cases in heavily pregnant, overfat mares are referred to as puerperal laminitis. Some are caused by trauma, such as in pawing due to boredom or in horses transported over long distances without rest, and are called traumatic laminitis. Called also founder.


