K
K 1. chemical symbol, potassium (L. kalium); symbol for kelvin. 2. equilibrium constant.
κ kappa, small letter; tenth letter in the Greek alphabet.
kaalmelkbos Euphorbia mauritanica.
Kaeshi disease Ibaraki disease.
kaffir one of the types of grain sorghum.
kakosmia [kak-oz′me– ] cacosmia.
] cacosmia.
kala-azar [kah′lah-ah-zahr′] see leishmaniasis.
marrowstem k. Brassica oleraceae var. acephala.
kalemia [k –le′me–
–le′me– ] the presence of potassium in the blood. See also hyperkalemia.
] the presence of potassium in the blood. See also hyperkalemia.
Kalicephalus a genus of hookworm of the family Diaphanoce- phalidae, found in snakes.
kaliemia [ka″le-e′me– ] kalemia.
] kalemia.
kaliopenia [ka″-o-pe′ne-d] hypokalemia.
kalium [L.] potassium (symbol K).
kaliuresis [ka″le-u-re′sis] excretion of potassium in the urine.
k. apples Solanum aviculare, S. laciniatum, S. simile, S. symonii, S. vescum, S. capsiciforme.
k. posture see kangaroo posture.
Kansas horse plague see equine viral encephalomyelitis.
Kantrowitz forceps a curved clamp with serrations at the end designed for thoracic surgery.
kappa [kap′ ] the tenth letter of the Greek alphabet, K or κ.
] the tenth letter of the Greek alphabet, K or κ.
karaka see Corynocarpus laevigatas.
karakin toxic nitrocompound in Corynocarpus laevigatus.
kary(o)- word element. [Gr.] nucleus.
karyogenesis the formation of a cell nucleus.
karyogram [kar′e-o-gram″] a graphic representation of a karyotype.
karyolymph the fluid portion of the nucleus of a cell, in which the other elements are dispersed.
karyolysis [kar″e-ol′ –sis] dissolution of the cell nucleus.
–sis] dissolution of the cell nucleus.
karyomorphism [kar″e-o-mor′fiz- m] the shape of a cell nucleus.
m] the shape of a cell nucleus.
karyon [kar’e-on] the nucleus of a cell.
karyophage [kar’e-o-faj″] a protozoan that phagocytizes the nucleus of the cell it infects.
karyoplasm [kar’e-o-plaz″ m] nucleoplasm.
m] nucleoplasm.
karyopyknosis [kar″e-o-pik-no′sis] shrinkage of a cell nucleus, with condensation of the chromatin.
karyosome any aggregation of chromatin within a cell.
karyotheca [kar″e-o-the’k ] the nuclear membrane.
] the nuclear membrane.
Kashmiri a goat; see Central Asiatic Pashmina.
kata [kah′td] see peste des petits ruminants.
kat(a)- word element. [Gr.] down, against. See also words beginning cat(a)-.
Katayama’s disease [kah-tah-yah′mah] schistosomiasis.
katipo see Latrodectus mactans.
kb kilobase; a thousand bases or nucleotides in a nucleic acid molecule. See also kbp.
kbp kilobase pair; for double-stranded nucleotides, a thousand nucleotide base pairs.
KCS keratoconjunctivitis sicca.
44-kDa phosphoprotein see osteopontin.
kebbing see enzootic abortion of ewes.
ked [ked] see Melophagus ovinus.
keep 1. to feed, e.g. long-keep steer. 2. pasturage.
Keith-Flack node [keth′ flak′] see Keith’s bundle.
KELA test kinetics-based, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
Kent Marsh [kent] see Romney Marsh.
Kenya Boran cattle an improved Kenyan version of Boran cattle.
Kenya SGPV Kenya sheep and goat poxvirus.
keraphyllocele [ker″ -fil′o-sēl] keratoma.
-fil′o-sēl] keratoma.
keratalgia [ker″d-tal′j ] corneal pain.
] corneal pain.
keratectasia [ker″d-tek-ta′zh ] corneal ectasia; protrusion of a thin, scarred cornea.
] corneal ectasia; protrusion of a thin, scarred cornea.
keratectomy excision of a portion of the cornea; kerectomy.
keratic [kd-rat′ik] 1. pertaining to keratin. 2. pertaining to the cornea.
k. tag see fibrovascular papilloma.
keratinase [ker′ –t
–t –nās] a proteolytic enzyme that hydrolyzes keratin.
–nās] a proteolytic enzyme that hydrolyzes keratin.
keratinization [ker″ –tin″
–tin″ –za’sh
–za’sh n]the development of or conversion into keratin.
n]the development of or conversion into keratin.
Keratinomyces see Trichophyton.
keratinous [k –rat′
–rat′ –n
–n s] containing or of the nature of keratin.
s] containing or of the nature of keratin.
interstitial k. inflammation of the corneal stroma, causing dense corneal opacification.
k. nigrum see corneal sequestrum.
pigmentary k. see corneal pigmentation and corneal melanosis.
k. sicca see keratoconjunctivitis sicca.
ulcerative k. see corneal ulcer.
kerat(o)- word element. [Gr.] horny tissue, cornea.
keratoacanthoma [ker″ –to-ak″an-tho′m
–to-ak″an-tho′m ] see intracutaneous cornifying epithelioma.
] see intracutaneous cornifying epithelioma.
keratocele [ker′ –to-sel″] hernial protrusion of Descemet’s membrane.
–to-sel″] hernial protrusion of Descemet’s membrane.
keratocentesis [ker″d-to-sen-te’sis] aqueocentesis.
keratoconjunctivitis [ker″d-to-kdn-junk″ti-vi′tis] inflammation of the cornea and conjunctiva.
chronic immune-mediated k. syndrome see chronic superficial keratitis.
keratoconus [ker′ –to-ko′n
–to-ko′n s] conical protrusion of the central part of the cornea.
s] conical protrusion of the central part of the cornea.
keratoderma [ker″ –to-dur′m
–to-dur′m ] hypertrophy of the horny layer of the skin.
] hypertrophy of the horny layer of the skin.
keratodermia [ker″ -to-dur′me-
-to-dur′me- ] keratoderma.
] keratoderma.
keratogenous [ker′ –toj′
–toj′ –n
–n s] giving rise to a growth of horny material.
s] giving rise to a growth of horny material.
keratoglobus [ker″ –to-glo′b
–to-glo′b s] an anomaly in which the cornea is enlarged and globular in shape.
s] an anomaly in which the cornea is enlarged and globular in shape.
keratohelcosis [ker″ –to-h
–to-h l-ko’sis] ulceration of the cornea.
l-ko’sis] ulceration of the cornea.
keratohemia [ker″ –to-he′me-
–to-he′me- ] deposition of blood in the cornea.
] deposition of blood in the cornea.
keratoid [ker′ –toid] resembling horn or corneal tissue.
–toid] resembling horn or corneal tissue.
keratoiridoscope [ker″ –to–
–to– –rid′
–rid′ –skōp] a compound microscope for examining the eye.
–skōp] a compound microscope for examining the eye.
keratoleukoma [ker″ –to-bo-ko′m
–to-bo-ko′m ] a white opacity of the cornea.
] a white opacity of the cornea.
keratolysis [ker″ –toid-sis] loosening or separation of the horny layer of the epidermis.
–toid-sis] loosening or separation of the horny layer of the epidermis.
keratoma [ker″ –to′m
–to′m ] keratosis.
] keratosis.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
 –din] kinin liberated by the action of kallikrein on a globulin of blood plasma. Kallidin I is the same as bradykinin; kal- lidin II is composed of bradykinin with a lysine added at the N-terminal.
–din] kinin liberated by the action of kallikrein on a globulin of blood plasma. Kallidin I is the same as bradykinin; kal- lidin II is composed of bradykinin with a lysine added at the N-terminal. –kre″in] any of a group of proteolytic enzymes present in various glands, lymph, urine, blood plasma, etc., or produced directly from mast cells or basophils, or indirectly from activated platelets. The major action of kallikreins is the liberation of kinins from α-2-globulins (kininogens), and they hence have vasodilator and whealing actions.
–kre″in] any of a group of proteolytic enzymes present in various glands, lymph, urine, blood plasma, etc., or produced directly from mast cells or basophils, or indirectly from activated platelets. The major action of kallikreins is the liberation of kinins from α-2-globulins (kininogens), and they hence have vasodilator and whealing actions. ] genus of North American trees in the family Ericaceae; contains the poisonous tetracyclic polyol, grayanotoxin (andromedotoxin); causes vomiting, incoordination, paralysis and hyperexcitability. Includes K. angustifolia (dwarf laurel), K. latifolia (mountain laurel), K. polifolia var. microphylla (hog laurel).
] genus of North American trees in the family Ericaceae; contains the poisonous tetracyclic polyol, grayanotoxin (andromedotoxin); causes vomiting, incoordination, paralysis and hyperexcitability. Includes K. angustifolia (dwarf laurel), K. latifolia (mountain laurel), K. polifolia var. microphylla (hog laurel). –l
–l ] derived from the plant Mallotus philippinensis; previously used as an anticestodal agent, but now replaced by better and safer compounds. Used in herbal medicine as a purgative and externally to treat ringworm and scabies.
] derived from the plant Mallotus philippinensis; previously used as an anticestodal agent, but now replaced by better and safer compounds. Used in herbal medicine as a purgative and externally to treat ringworm and scabies. –mi′sin] an aminoglycoside antibiotic active against many gram-negative and acid-fast bacteria; a high potential for nephrotoxicity. Similar to amikacin.
–mi′sin] an aminoglycoside antibiotic active against many gram-negative and acid-fast bacteria; a high potential for nephrotoxicity. Similar to amikacin.
 –n
–n r] a hereditary syndrome of humans consisting of dextrocardia, bronchiectasis and sinusitis. Cases of a similar disease are reported in dogs. The disease is primarily a defect in cilia motility. See primary ciliary dyskinesia.
r] a hereditary syndrome of humans consisting of dextrocardia, bronchiectasis and sinusitis. Cases of a similar disease are reported in dogs. The disease is primarily a defect in cilia motility. See primary ciliary dyskinesia. ] North American plant in the family Rhamnaceae; contains an unidentified toxin; causes degeneration of skeletal muscles and axonal dystrophy in the cerebellum and spinal cord. The clinical picture includes hypersensitivity, tremor, ataxia, recumbency and absence of tendon reflexes. Called also coyotillo, buckthorn, tullidora.
] North American plant in the family Rhamnaceae; contains an unidentified toxin; causes degeneration of skeletal muscles and axonal dystrophy in the cerebellum and spinal cord. The clinical picture includes hypersensitivity, tremor, ataxia, recumbency and absence of tendon reflexes. Called also coyotillo, buckthorn, tullidora. l] the SI unit of measurement to express activities of all catalysts, including enzymes, being that amount of a catalyst that catalyzes a reaction rate of 1 mole of substrate per second. katathermometer [kat”
l] the SI unit of measurement to express activities of all catalysts, including enzymes, being that amount of a catalyst that catalyzes a reaction rate of 1 mole of substrate per second. katathermometer [kat” –thdr-mom′
–thdr-mom′ –t
–t r] a thermometer with a wet bulb and a dry bulb, for detecting cooling rates.
r] a thermometer with a wet bulb and a dry bulb, for detecting cooling rates. ] Piper methysticum a plant of the western Pacific region and beverage prepared from it; sometimes marketed as a herbal supplement. Leaves and stems are ssociated with liver toxicity in dogs
] Piper methysticum a plant of the western Pacific region and beverage prepared from it; sometimes marketed as a herbal supplement. Leaves and stems are ssociated with liver toxicity in dogs r] an obstetrical spatula; a long-handled (3 ft) rod with a blunt spatulate tip, introduced into the uterus and manipulated from outside the cow or mare. Used to remove the skin of the fetus by blunt dissection.
r] an obstetrical spatula; a long-handled (3 ft) rod with a blunt spatulate tip, introduced into the uterus and manipulated from outside the cow or mare. Used to remove the skin of the fetus by blunt dissection.
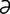 –tin] a scleroprotein (fibrous structural protein) which is the principal constituent of epidermis, hair, nails, horny tissues, and the organic matrix of the enamel of the teeth. Its solution is sometimes used in coating pills when the latter are desired to pass through the stomach unchanged.
–tin] a scleroprotein (fibrous structural protein) which is the principal constituent of epidermis, hair, nails, horny tissues, and the organic matrix of the enamel of the teeth. Its solution is sometimes used in coating pills when the latter are desired to pass through the stomach unchanged. –ti′tis] inflammation of the cornea. Keratitis may be deep (stromal) or superficial (epithelial); ulcerative or non-ulcerative, and due to trauma, bacterial, fungal, or viral infection, immune-mediated infiltration, etc.; or seen in association with a number of other ocular diseases such as blepharitis, entropion, ectropion, lagophthalmos, reduced tear quantity or quality, uve- itis, or glaucoma. Typical clinical signs include blepharospasm, serous to mucoid ocular discharge, corneal opacity and conjuncti- val or episcleral hyperemia.
–ti′tis] inflammation of the cornea. Keratitis may be deep (stromal) or superficial (epithelial); ulcerative or non-ulcerative, and due to trauma, bacterial, fungal, or viral infection, immune-mediated infiltration, etc.; or seen in association with a number of other ocular diseases such as blepharitis, entropion, ectropion, lagophthalmos, reduced tear quantity or quality, uve- itis, or glaucoma. Typical clinical signs include blepharospasm, serous to mucoid ocular discharge, corneal opacity and conjuncti- val or episcleral hyperemia.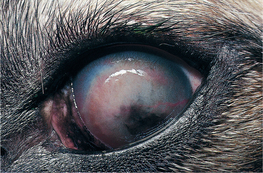
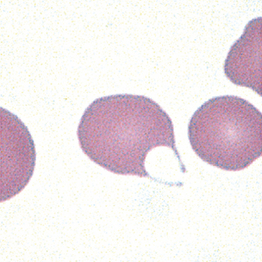
 –to-sit″] 1. a flattened cell lying between the collagenous corneal lamellae which constitute the corneal stroma. The keratocyte has branching processes that communicate with those of other keratocytes and is considered to be a resting fibroblast, which can be stimulated during wound healing to synthesize collagen. 2. a red blood cell with notches that results in projections that look like horns. Keratocytes occur when fibrin is being deposited within blood vessels as in disseminated intravascular coagulation.
–to-sit″] 1. a flattened cell lying between the collagenous corneal lamellae which constitute the corneal stroma. The keratocyte has branching processes that communicate with those of other keratocytes and is considered to be a resting fibroblast, which can be stimulated during wound healing to synthesize collagen. 2. a red blood cell with notches that results in projections that look like horns. Keratocytes occur when fibrin is being deposited within blood vessels as in disseminated intravascular coagulation. –to-jen′
–to-jen′ –sis] the production of keratin; a function of keratinocytes in the epidermis.
–sis] the production of keratin; a function of keratinocytes in the epidermis. –to-hi′
–to-hi′ –lin] the substance in the granules in the stratum granulosum of the epidermis.
–lin] the substance in the granules in the stratum granulosum of the epidermis. –to-i-ri′tis] inflammation of the cornea and iris. More commonly called keratouveitis because of the almost inevitable but often unobserved coincident inflammation of the ciliary body.
–to-i-ri′tis] inflammation of the cornea and iris. More commonly called keratouveitis because of the almost inevitable but often unobserved coincident inflammation of the ciliary body. –to-lep-tin’sis] removal of the anterior portion of the cornea and replacement with bulbar conjunctiva.
–to-lep-tin’sis] removal of the anterior portion of the cornea and replacement with bulbar conjunctiva. –to-lit′ik] 1. pertaining to or promoting keratolysis. 2. an agent that promotes keratolysis.
–to-lit′ik] 1. pertaining to or promoting keratolysis. 2. an agent that promotes keratolysis. –to-m
–to-m –b’sh
–b’sh ] softening or ′melting′ of the cornea associated with collagenase production by host corneal or white blood cells and microbial pathogens, especially gramnegative bacteria.
] softening or ′melting′ of the cornea associated with collagenase production by host corneal or white blood cells and microbial pathogens, especially gramnegative bacteria.