J
J antigen the basis of the J blood group system in cattle.
J receptor see juxtacapillary receptor.
jaagsiektebossie Crotalaria dura, C. globifera.
jack 1. male donkey; called a stallion in Great Britain. 2. see track leg.
j. colt male donkey less than 3 years of age.
mule j. one bred to mares for the production of mules.
jack-in-the-pulpit see Arisaema.
jack sores see cutaneous habronemiasis.
jackstones see silica urolith.
jacobine [ja’ko-bin] a pyrrolizidine alkaloid found in the weed Senecio jacobea.
Jacobson’s organ [ja’k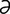 b-s
b-s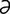 ns] vomeronasal organ.
ns] vomeronasal organ.
Jaffe reaction, Jaffe test [yah’f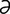 ] see alkaline picrate test
] see alkaline picrate test
Jakta slaughter see Sikh slaughter.
Jamaica Brahman cattle bred up from Ongole, Hissar and Mysore zebus.
Jamaica hope a dairy breed produced in Jamaica from Jersey and Zebu breeds.
Jamaica red a red beef breed produced in Jamaica from Zebu, Red Poll and Devon cattle.
Jamestown weed, Jamestown lily Datura stramonium; derived from Jamestown, Virginia.
janet [zhah-na’] a female mule.
janiceps [janĩ-seps] a conjoined twin with one head and two opposite faces.
Jansen retractor [Jan sen] a handheld retractor used in abdominal surgery.
januariebos Gnidia polycephala.
Japanese amberjack Seriola quinqueradiata.
Japanese encephalitis (Je) see encephalitis.
Japanese killifish see medaka.
Japanese pieris Pieris japonicum.
Japanese poll cattle polled black meat cattle formed by crossing native cattle with Angus.
Japanese river fever see scrub typhus.
Japanese Shiba inu a small, spitz-type dog with small eyes, erect ears and a dense, straight coat.
Japanese spaniel see Japanese chin.
cholestatic j. that resulting from abnormality of bile flow in the liver.
hematogenous j. hemolytic jaundice.
hepatocellular j. jaundice caused by injury to or disease of the liver cells.
nonhemolytic j. that due to an abnormality in bilirubin metabolism.
overproduction j. see hemolytic jaundice (above).
regurgitation j. obstructive jaundice (above).
toxic j. see hepatocellular jaundice (above).
j. bone the mandible or maxilla, especially the mandible.
acute j. drop syndrome see mandibular neuritis.
dropped j. see mandibular neuritis.
j. malapposition see malocclusion.
overshot j. see brachygnathism.
j. retractor a dental gag used to keep the jaws of an animal as open as possible.
rubber j. see renal secondary hyperparathyroidism.
jejunal [j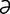 -joo’n
-joo’n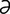 l] pertaining to the jejunum.
l] pertaining to the jejunum.
jejunectomy [j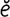 “joo-nek’t
“joo-nek’t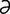 -me] excision of the jejunum.
-me] excision of the jejunum.
jejunitis [j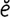 “joo-ni’tis] inflammation of the jejunum.
“joo-ni’tis] inflammation of the jejunum.
jejunocecostomy [j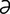 -joo“no-k
-joo“no-k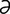 -los’t
-los’t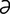 -me] anastomosis of the jejunum to the cecum.
-me] anastomosis of the jejunum to the cecum.
jejunocolostomy anastomosis of the jejunum to the colon.
jejunoileitis [j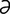 -joo“no-il”e-i’tis] inflammation of the jejunum and ileum.
-joo“no-il”e-i’tis] inflammation of the jejunum and ileum.
jejunoileum the jejunum and the ileum considered as a single organ.
jejunorrhaphy [jě“joo-nor’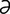 -fe] operative repair of the jejunum.
-fe] operative repair of the jejunum.
jejunoscopy inspection of the lumen of the jejunum with an endoscope.
jejunotomy [jě“joo-not’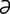 -me] incision of the jejunum.
-me] incision of the jejunum.
jejunum [j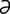 -joo’n
-joo’n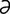 m] that part of the small intestine extending from the duodenum to the ileum.
m] that part of the small intestine extending from the duodenum to the ileum.
jelly [jel’e] a soft, coherent, resilient substance; generally, a colloidal semisolid mass.
Wharton’s j. the soft, jelly-like intracellular substance of the umbilical cord.
jennerian [jen-e’re- n] relating to Edward Jenner, who developed vaccination in England in 1796.
n] relating to Edward Jenner, who developed vaccination in England in 1796.
Jenner’s horsepox [jen’ r] see horsepox.
r] see horsepox.
jenny female donkey, called also jennet; called a mare in Great Britain.
j. filly one less than 3 years of age.
jequirity bean see Abrus precatorius.
jerk [jurk] a sudden reflex or involuntary movement.
ankle j. see gastrocnemius reflex.
biceps j. called also elbow jerk; see biceps reflex.
elbow j. see biceps jerk (above).
j. nystagmus see vestibular nystagmus.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
 ] [Af.] 1. see ovine pulmonary adenomatosis. 2. respiratory insufficiency syndrome in horses caused by bronchiolar hyperplasia induced by pyrrolizidine alkaloids from Crotalaria spp. in southern Africa; also reported from Australia; may or may not be associated with hepatic pyrrolzidine alkaloidosis. Term means ’panting sickness’ with reference to prominent lung lesions.
] [Af.] 1. see ovine pulmonary adenomatosis. 2. respiratory insufficiency syndrome in horses caused by bronchiolar hyperplasia induced by pyrrolizidine alkaloids from Crotalaria spp. in southern Africa; also reported from Australia; may or may not be associated with hepatic pyrrolzidine alkaloidosis. Term means ’panting sickness’ with reference to prominent lung lesions. n] a form of seizures marked by clonic movements that start in one muscle group and spread systematically to adjacent groups. Called also marching seizures.
n] a form of seizures marked by clonic movements that start in one muscle group and spread systematically to adjacent groups. Called also marching seizures.
 ] a genus of the plant family Euphorbiaceae; some plants contain irritant diterpenoid purgatives and cause diarrhea. Includes J. curcas (physic or purging nut), J. gossypifolia (bellyache bush), J. multifida (umbrella tree, coral bush), J. podagrica (coral plant), J. stimulosa (spurge nettle); some cause cyanide poisoning, e.g. J. multifida (umbrella tree, coral bush).
] a genus of the plant family Euphorbiaceae; some plants contain irritant diterpenoid purgatives and cause diarrhea. Includes J. curcas (physic or purging nut), J. gossypifolia (bellyache bush), J. multifida (umbrella tree, coral bush), J. podagrica (coral plant), J. stimulosa (spurge nettle); some cause cyanide poisoning, e.g. J. multifida (umbrella tree, coral bush).
 -joo“no-il”e-
-joo“no-il”e-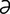 l] pertaining to the jejunum and ileum; connecting the proximal jejunum with the distal ileum.
l] pertaining to the jejunum and ileum; connecting the proximal jejunum with the distal ileum.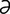 -joo“no-il”e-os’t
-joo“no-il”e-os’t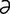 -me] surgical creation of an anastomosis between the proximal jejunum and the terminal ileum; anastomosis of the jejunum to the ileum.
-me] surgical creation of an anastomosis between the proximal jejunum and the terminal ileum; anastomosis of the jejunum to the ileum.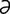 -joo“no-j
-joo“no-j “joo-nos’t
“joo-nos’t -me] surgical anastomosis between two portions of the jejunum.
-me] surgical anastomosis between two portions of the jejunum. -me] surgical creation of a permanent opening between the jejunum and the surface of the abdominal wall.
-me] surgical creation of a permanent opening between the jejunum and the surface of the abdominal wall.



