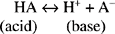24 INTRODUCTION TO ACID-BASE ABNORMALITIES
1 What four basic parameters are typically measured on a routine blood gas analysis?
c. PCO2: partial pressure (tension) of carbon dioxide, the amount of gaseous CO2 dissolved in the blood; used as a measure of the respiratory component of acid-base disturbances
9 If hydrogen ions are present in such low concentrations compared with other electrolytes, why are changes in pH so important?
11 What are the definitions of an “acid” and a “base”?
An acid is a substance that can donate a hydrogen ion, whereas a base is an H+ acceptor.
In which A− acts as a base because it can bind to free H+ ion.
12 What are the normal body defenses that serve to protect against changes in pH?
The body contains many buffers, which blunt changes in pH. A buffer is a substance that can gain or lose hydrogen ions and thus minimize changes in pH. A buffer pair consists of a weak acid (HA) and its conjugate base (A−). If a large amount of hydrogen ions are added to a system, the buffer pair binds some of the H+ ion, thus minimizing the change in pH.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree