Figure 18.2 A bone biopsy and aspiration needle is grasped firmly and readied for percutaneous insertion into the intramedullary canal of the femur.
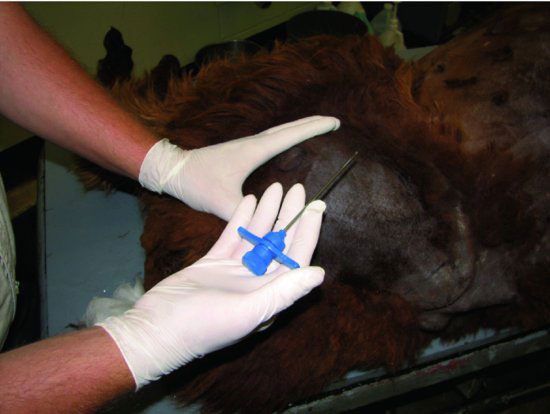
Figure 18.3 The greater trochanter is palpated and the muscle mass overlying the trochanteric fossae identified.
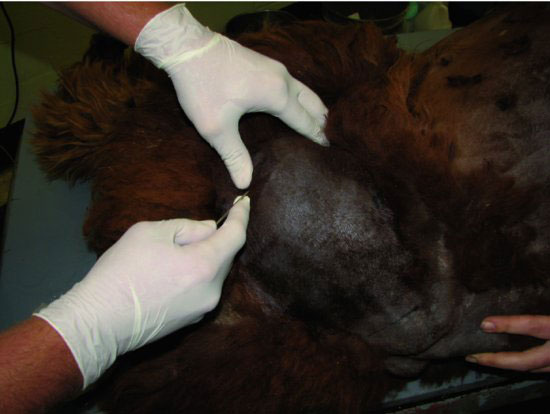
Figure 18.4 The needle is inserted through the skin and inserted into the trochanteric fossae. This may require “walking” the needle off of the medial aspect of the greater trochanter.
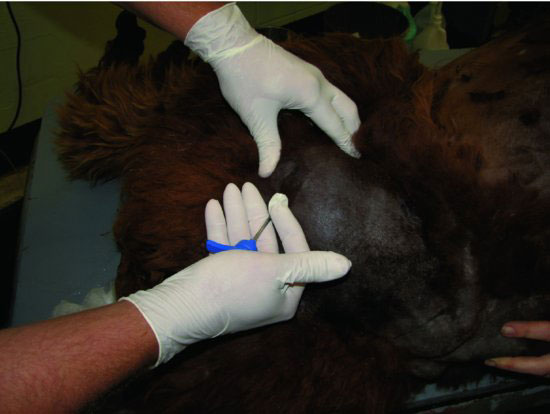
Figure 18.5 The position of the diaphysis of the femur should be assessed during insertion to ensure that the needle is threaded into the medullary canal and not placed transcortically.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


