Location
ICP level (mmHg)
Intraventricular
8 ± 1.6
Intraparenchymal
11 ± 1.3
Cisterna magna
6 ± 0.9
The main advantage of intraparenchymal ICP measurement with fiberoptic catheters besides its simplicity is that it is a reliable and reproducible method. It is much easier and less time-consuming than ventricular or cisterna magna cannulation and ICP monitoring. However, cortical damage was larger in intraparenchymal monitoring in some series caused by a bigger probe size than after intraventricular ICP measurement. This might be a technical limitation in studies in which cortical damage must be avoided. The main advantage of intraventricular and especially cisternal cannulation is the possibility to access CSF for additional examination. Furthermore, using a PE tube coupled to any sensitive pressure transducer is cheaper than specific intraparenchymal ICP-measurement probes.
2.2 Surgical Trauma by Probe Implantation
Insertion of ICP-probe into the brain can cause injury and bleeding that may evoke increase of ICP. Upon histological examination, localized tissue trauma at the site of probe insertion is observed. Furthermore, cortical damage was more extended after intraparenchymal monitoring caused by a bigger ICP-probe size than after intraventricular ICP measurement (18). Care has to be taken to avoid brainstem injury while cannulating the cisterna magna. Venous bleeding while puncturing the membrana atlanto-occipitalis is common. Artificious blood contamination may lead to misinterpretation of experimental results.
2.3 CSF Sampling
In rats, CSF production rates were estimated to be 2.2 μl/min with a total volume of 400–550 μl (19). Usually less than 150 μl can be collected via the cisterna magna (20). Therefore, minor artificious blood contaminations of the CSF can strongly alter CSF content profiles and lead to misinterpretations.
3 Material and Instruments
3.1 Instruments
1.
Stereotactic frame.
2.
Micromanipulator.
3.
Homeothermic blanket (Harvard Apparatus).
4.
Microscope (Zeiss).
3.2 ICP-Probe and Catheter
To implant an ICP-probe, different instruments are needed:
1.
Stereotactic frame (e.g., Small animal stereotactic frame, ASI-Instruments or David Kopf Instruments, Tujunga CA, USA).
2.
Drill (e.g., Uni-Drive N, Starnberg, Germany; Drill: Aesculap GD870, 0.8 × 5.1 mm).
3.
Micromanipulator (e.g., Kopf Instruments, USA).
4.
ICP-probes.
(a)
Parenchymal: Codman microsensor basic parenchymal probe (Codman, Germany).
(b)
Cisternal/ventricular: 22/25—gauge needle, Polyethylene (PE-50) tube and Pressure transducer (e.g., Statham P23, Viggo-Spectramed, Oxnard, CA, USA, or: Sorenson Transpac, Abbott, Laboratories).
To fixate the ICP-probe to the skull, following products are needed:
5.
Dental cement (e.g., Poly-F Plus Bondex, Dentsply DeTry, Germany).
3.3 Sampling Aids
To sample CSF after ventricular or cisternal cannulation, following products are needed:
1.
Plastic or glass sample collection vials (Fisher scientific, USA).
2.
1.5 ml micro-centrifuge tubes (Fisher scientific, USA).
4 Procedures
4.1 General Surgical Procedures
1.
Anesthetize the animal (Ketamine-Xylazine; 80mg/10mg; e.g., Sigma; or: Halothan 1.5–2% in carrier gas of O2 and N2O (1:2), e.g., Hoechst AG, Germany)
2.
Note: Body temperature should be kept at 37 ± 0.5°C. This temperature is maintained via a rectal thermistor coupled to a heating pad or a homeothermic blanket (e.g., Harvard Apparatus, USA) during experimental procedures.
3.
Place the rat on the stereotaxic table.
4.
Midline skin incision and exposure of bregma, lambda, nuchal ridge and dorsal cervical musculature.
4.2 ICP-Probe Implantation
4.2.1 Ventricular ICP Measurements
1.
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Drill a small burr hole (diameter: approximately 2 mm) at the right/left cortex; 1 mm posterior from bregma; 1.4 mm lateral from midline/sagittal suture; depth: 4 mm from skull top (Fig. 1).
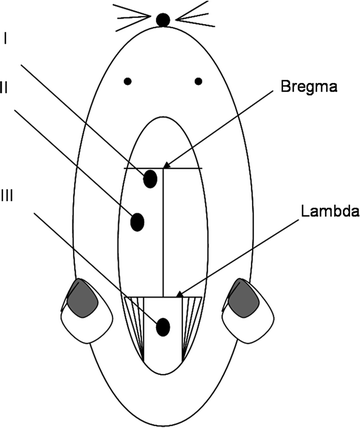





Fig. 1.
Schematic presentation of different probe locations in an experimental rat model: (I) ventricular, (II) intraparenchymal, and (III) cisternal magna cannulation.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


