CHAPTER 1 Instruments for the Administration of Medicine
This chapter describes the instruments that are used to deliver medications or to draw blood, urine, and tissue samples from the body.
INSTRUMENT
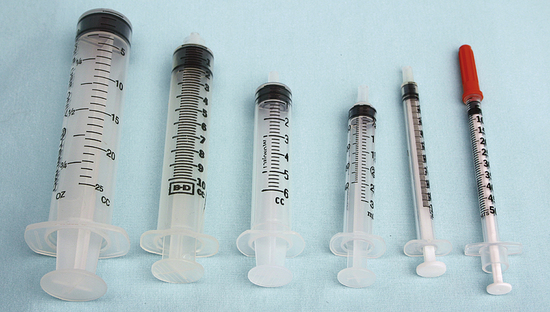
Disposable Syringe
| FUNCTION | To administer parenteral medications or to draw blood or other fluids from the body. |
| COMMON NAME | Syringe |
| CHARACTERISTICS | Plastic syringes are made of three parts. The plunger has a rubber stopper on the end of a shaft and is used to pull fluid in or push it out of the barrel of the syringe. The barrel determines the size and is marked in graduations that ensure accurate measurements of the solutions to be delivered. The tip is the part to which a needle can be attached, and it can fit into the hub of a catheter. The tip is available in three types. A slip tip can be centered, or it can be eccentric, meaning it is positioned to one side of the barrel; a Luer-Lok tip has threads onto which a needle hub can be turned and locked into place. |
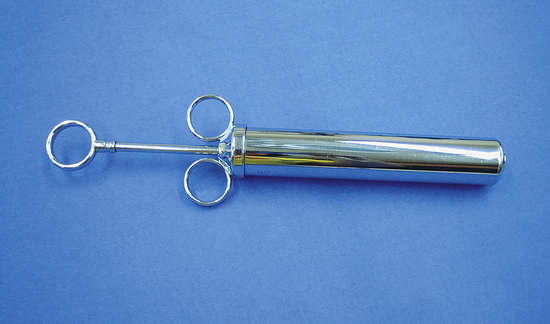
INSTRUMENT
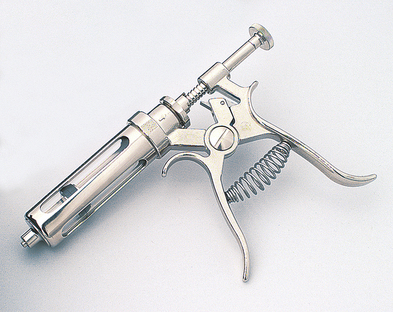
Automatic Dose Syringe
| FUNCTION | To administer intramuscular (IM) or subcutaneous (SQ) injections to multiple animals without reloading the syringe. |
| COMMON NAME | Automatic Syringe |
| CHARACTERISTICS | A syringe barrel is attached to a handle with a dial that can be set to deliver 1 to 5 ml at a time with a squeeze of the handle. Care must be taken to clean the syringe thoroughly to prevent drug interactions and to prevent the spread of disease. |
INSTRUMENT
Vetamatic Dose Syringe
| FUNCTION | To administer IM or SQ injections to multiple animals with automatic reloading of the syringe. |
| CHARACTERISTICS | This syringe has an attachment for a hose that is connected to a tankard or to a collapsible bottle. When the plunger is pushed in, the medication or vaccine is delivered; when the plunger is released, it draws in the preselected amount from the tankard or bottle. |
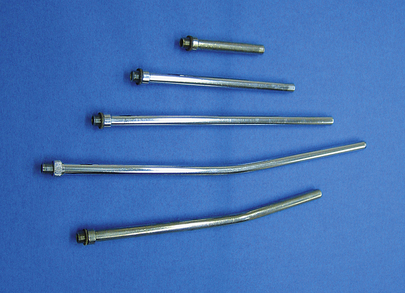
INSTRUMENT
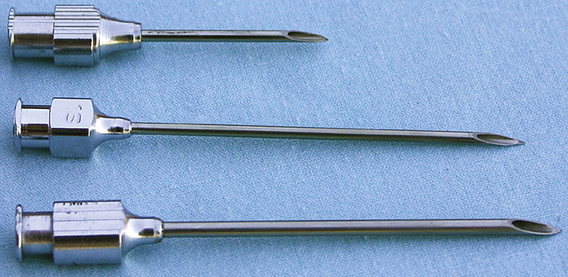
Stainless Steel Hypodermic Needle
| FUNCTION | To deliver parenteral medications. |
| COMMON NAME | Needle, Nondisposable Needle, Stainless Steel Needle, Bleeding Needle |
| CHARACTERISTICS | Stainless steel needles come in a variety of lengths and gauges. The most common sizes are 14-, 16-, and 18-gauge needles at 1½ inches to 3 inches in length. The advantage of these needles is that they can be used again after sterilization. The disadvantages are that they lose their sharp edge and must be sharpened manually and that if improperly sterilized, they may spread diseases such as malignant cattle fever, warts, and leukosis. |
INSTRUMENT
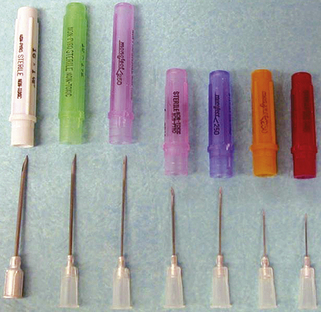
Disposable Hypodermic Needles
| FUNCTION | To inject parenteral medications. |
| COMMON NAME | Needles |
| CHARACTERISTICS | Stainless steel shafts have plastic or aluminum hubs. They come in a variety of lengths and gauges. The following is a list of gauges, from smallest lumen size to largest, and their general uses. Different name brands have different-colored covers; it is advisable to learn these colors so that identification can be made quickly in an emergency situation. |
| 27-, 26-, 25-gauge needles— | |
| Needles of these sizes are usually used on very small animals: birds, reptiles, rodents, kittens, and puppies. They can also be used for intradermal injections, for tuberculosis and allergy testing, and for the delivery of local anesthetics. The lengths of these needles are usually less than 1 inch and range from ½ inch to ⅝ inch. |
INSTRUMENT
Disposable Hypodermic Needles (continued)
| 23-, 22-, 21-gauge needles— | |
| Needles of these sizes are usually used for general injections in dogs and cats. The 22-gauge needle is the standard size found in most clinics and is used for injections and for drawing blood. The lengths of these needles usually range from ⅝ inch to 1 inch, but 1½ inch needles can also be found. | |
| 20-, 19-, 18-gauge needles— | |
| Needles of these sizes are usually used in large dogs such as Great Danes and Saint Bernards and in sheep, goats, cattle, and horses. Those used in larger animals may be as long as 1½ inches, as opposed to the standard 1 inch. |
INSTRUMENT
Disposable Hypodermic Needles (continued)
| 16-and 14-gauge needles— | |
| These two needles are not used frequently; however, they can be found in most large or mixed animal clinics. They are useful for delivering large volumes of intravenous (IV) fluids quickly. They are also useful when a very thick substance must be injected and the patient is uncooperative. |
INSTRUMENT
Dose Syringe
| FUNCTION | To administer liquid medications orally. |
| COMMON NAME | Drenching Syringe, Drencher |
| CHARACTERISTICS | A stainless steel syringe is marked in oz and ml; it can be used to give multiple animals an oral dose of medication by pushing in the plunger. |
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree