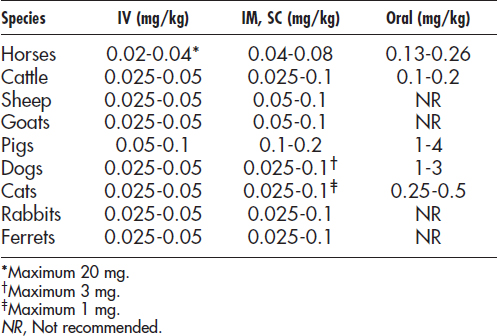
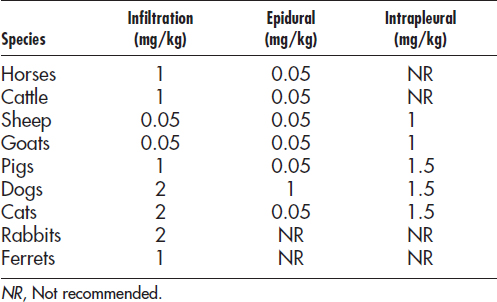
Chapter 1 Individual Drugs
ACEPROMAZINE
| PromAce | Fort Dodge Laboratories |
| Aceproject | Vetus Animal Health |
Precautions
▪ Boxers, large-breed dogs, and geriatric patients may show increased sensitivity (avoid or use low dose)
ATIPAMEZOLE
| Antisedan | Pfizer, Inc. |
Uses
▪ Drug is formulated such that the volume of atipamezole required for intramuscular (IM) injection equals the volume of medetomidine administered intravenously (IV) or IM
Doses
Doses of Atipamezole by Species
| Species | IM (mg/kg) | IV (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Horses* | — | 0.05–0.1 |
| Dogs | Use volume equal to volume of medetomidine used | Use volume equal to half of volume of medetomidine used, preferably after approximately 45 minutes |
| Rabbits | 0.25–0.5 | 0.001 IV, SC, IP† |
| Ferrets | 0.1 | 1 IV, SC, IP‡ |
* Used in horses for detomidine overdose.
† Concentration of drug is 5 mg/ml. Dose rate of 0.001 mg/kg = 0.0002 mg/kg. A 5-kg rabbit would require 0.001 ml.
ATRACURIUM
| Tracrium | GlaxoSmithKline |
Features
▪ Competes with acetylcholine (ACh) molecules released at the neuromuscular junction to bind with the ACh receptors on the postsynaptic membrane of the motor endplate without triggering a response
▪ Metabolized via ester hydrolysis and spontaneous Hofmann elimination (degradation at normal body temperature and pH)
Precautions
▪ Aminoglycoside antibiotics (e.g., gentamicin) and volatile agents may increase duration of neuromuscular blockade
Doses
Doses of Atracurium by Species
| Species | IV—Initial Dose (mg/kg) | IV—Repeat Dose (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Horses | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Cattle | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Sheep | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Goats | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Pigs | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Dogs | 0.25 | 0.1 |
| Cats | 0.22 | 0.1 |
| Rabbits | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Ferrets | 0.2 | 0.1 |
ATROPINE
| Atropine | Butler Company |
| Atroject | Vetus Animal Health |
Uses
▪ Prevention of bradycardia resulting from excessive vagal stimulation or from anticholinesterase administration during neuromuscular blockade reversal
Precautions
▪ Approximately one third of all domesticated rabbits have a naturally occurring atropinesterase enzyme that causes them to metabolize atropine more quickly than normal rabbits; may need to repeat dose frequently or use glycopyrrolate instead
BUPIVACAINE
| Marcaine | Abbott Laboratories |
Features
▪ Prevents rapid influx of sodium ions into nerve axon and production of action potential, resulting in local muscle paralysis and analgesia
Precautions
▪ Toxic effects of overdose produce either CNS effects (seizures) or cardiovascular effects (arrhythmias or cardiovascular collapse)
BUPRENORPHINE
| Buprenorphine | Abbott Laboratories |
Doses
Doses of Buprenorphine by Species
| Species | IV (mg/kg) | IM, SC (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Horses | NA | NA |
| Cattle | 0.005–0.01 | 0.005–0.01 |
| Sheep | 0.005–0.01 | 0.005–0.01 |
| Goats | 0.005–0.01 | 0.005–0.01 |
| Pigs | 0.01–0.1 | 0.01–0.1 |
| Dogs | 0.01–0.02 | 0.01–0.02 |
| Cats | 0.01–0.02 | 0.01–0.02 |
| Rabbits | 0.05–0.1 | 0.05–0.1 |
| Ferrets | 0.01–0.02 | 0.01–0.02 |
NA, Not appropriate.
BUTORPHANOL
| Torbugesic | Fort Dodge Laboratories |
| Torbutrol | Abbott Laboratories |
Uses
▪ Partial reversal of effects of pure agonists (e.g., in animals with slow recovery from anesthesia)
Precautions
▪ Caution must be exercised in patients with head trauma or conditions associated with increased cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure
Doses
Doses of Butorphanol by Species
| Species | IV (mg/kg) | IM, SC (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Horses* | 0.02–0.04 | 0.02–0.04 |
| Cattle | 0.01–0.04 | 0.01–0.04 |
| Sheep | 0.05† | 0.05–0.5 |
| Goats | NRP | 0.05–0.5 |
| Pigs | 0.1–0.5 | 0.1–0.5 |
| Dogs | 0.1–0.4 | 0.1–0.4 |
| Cats | 0.1–0.8 | 0.1–0.8 |
| Rabbits | 0.1–0.5 | 0.1–0.5 |
| Ferrets | 0.1–0.5 | 0.1–0.5 |
NRP, Not reported.
* Usually used with xylazine or acepromazine for premedication.
DETOMIDINE
| Dormosedan | Pfizer, Inc. |
Features
▪ Decreases MAC and the requirement for other anesthetic agents (MAC is the minimum alveolar concentration of an anesthetic agent that prevents response to a noxious stimulus in 50% of patients; MAC is used for comparison of agents)
▪ Initial and transient vasoconstriction and hypertension (peripheral effect), then vasodilation and hypotension (central effect)
Doses
Doses of Detomidine by Species
| Species | IV (mg/kg) | IM (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Horses | 0.02–0.04 | 0.02–0.04 |
| Cattle* | 0.03–0.06 | 0.03–0.06 |
DIAZEPAM
| Diazepam | Baxter Healthcare Corporation |
| Abbott Laboratories |
Doses
| Species | IV (mg/kg) | IM, SC (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Horses* | 0.01–0.03 | NA |
| Cattle | 0.2–0.4 | 0.55–1 |
| Sheep | 0.2–0.4 | 0.2–1 |
| Goats | 0.2–0.4 | 0.2–1 |
| Pigs | 0.4–0.8 | 0.5–1.5 |
| Dogs | 0.1–0.2 | 0.1–0.5 |
| Cats† | 0.1–0.2 | 0.1–0.4 |
| Rabbits | 0.4–0.8 | 0.5–2 |
| Ferrets | 0.4–0.8 | 0.5–2 |
NA, Not appropriate.
* Not to be used alone; best used after premedication and as part of induction technique (e.g., with ketamine).
† Excitement may occur when used alone, especially IV; best used with other agents.