I
I chemical symbol, iodine (L. iodum).
I band the lighter colored cross-striation of muscle fibers; composed of filaments of actin.
I-cell disease see mucolipidosis II.
-ia word element, state; condition.
-iasis word element. [Gr.] condition, state.
iatr(o)- word element. [Gr.] medicine, physician.
IACuC Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee.
Ibaraki disease see Ibaraki virus.
IBD 1. infectious bursal disease of chickens. 2. inflammatory bowel disease.
IBK see infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis.
ibotenic acid [i″bo-ten″ik] the insecticidal agent in the mushroom Amanita muscaria.
IBR see infectious bovine rhinotracheitis.
IBR/IPV see infectious bovine rhinotracheitis/infectious pustular vulvovaginitis.
i.c. medical record abbreviation for intracardiac.
-ic suffix meaning pertaining to.
-ical suffix meaning pertaining to.
ICAMs intercellular adhesion molecules.
ice plant [īs] see Mesembryanthemum.
Icelandic cattle usually polled, mostly red or red and white dairy cattle.
Icelandic pneumonia see maedi.
ICH infectious canine hepatitis.
Ich [ik] see Ichthyophthirius multifiliis and Cryptocaryon irritans.
ichor a watery discharge from wounds or sores.
ichorrhea copious discharge of ichor.
Ictadenovirus a genus in the family Adenoviridae that contains a virus isolated from sturgeon.
ichthyoid [ik′the-oid] fishlike.
ichthyology [ik″the-ol′ -je] the study of fishes.
-je] the study of fishes.
ichthyophagous [ik′the-of -g
-g s] eating or subsisting on fish.
s] eating or subsisting on fish.
ichthyophoniasis see Ichthyophonus.
Ichthyophthirius [ik″the-o-thi′re- s] a genus of protozoan parasites in the phylum Ciliophora.
s] a genus of protozoan parasites in the phylum Ciliophora.
ichthyosarcotoxin [ik″the-o-sahr′ko-tok″sin] a toxin found in the flesh of poisonous fish.
Ichthyospofidium obligate, intracellular protozoan parasites in the class Microsporea.
ichthyotoxin [ik′the-o-tok″sin] any toxic substance derived from fish. See also ichthyosarcotoxin.
ichthyotoxism [ik″the-o-tok′siz-  m] any intoxication due to an ichthyotoxin.
m] any intoxication due to an ichthyotoxin.
ICSH interstitial cell-stimulating hormone. See luteinizing hormone.
ictal [ik′t l] pertaining to or characterized by a seizure.
l] pertaining to or characterized by a seizure.
icteric [ik-ter′ik] pertaining to or affected with jaundice.
icterogenic [ik″t r-o-jen′ik] causing jaundice, e.g. icterogenic hepato- pathy.
r-o-jen′ik] causing jaundice, e.g. icterogenic hepato- pathy.
icterohepatitis [ik″t r-o-hep″
r-o-hep″ -ti′tis] inflammation of the liver with marked jaundice.
-ti′tis] inflammation of the liver with marked jaundice.
icteroid [ik′t r-oid] resembling jaundice.
r-oid] resembling jaundice.
icterus [ik′t r-
r- s] see jaundice.
s] see jaundice.
ictus [ik′t s] a seizure, stroke, blow, or sudden attack.
s] a seizure, stroke, blow, or sudden attack.
ID 1. infective dose. 2. L-iditol dehydrogenase.
ID50 median infective dose; the dose that will infect 50% of the experimental group.
-id [Gr.] a suffix meaning having the shape of, or resembling.
idazoxan an α2-adrenoceptor antagonist used to reverse xylazine.
IDDM insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
-ide suffix indicating a binary compound.
identical twins see monozygotic twins.
identity [i-den′t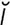 -te] the aggregate of characteristics by which an individual is recognized.
-te] the aggregate of characteristics by which an individual is recognized.
idio- word element. [Gr.] self, peculiar to a substance or organism.
juvenile amaurotic familial i. see amaurotic familial idiocy.
Idiogenes a genus of tapeworms of bustards belonging to the family Paruterinidae.
idiogram [id′e-o-gram″] a drawing or photograph of the chromosomes of a particular cell.
idiopathic [id″e-o-path′ik] self-originated; occurring without known cause.
idiopathy [id″e-op′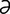 -the] an undiagnosed morbid state arising without known cause.
-the] an undiagnosed morbid state arising without known cause.
idiot fruit see Idiospermum australiense.
idiotope [id′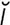 -o-tōp″] an antigenic determinant on the variable region of an antibody.
-o-tōp″] an antigenic determinant on the variable region of an antibody.
idiotrophic [id″e-o-tro′fik] capable of selecting its own nourishment.
idioventricular pertaining to the cardiac ventricle alone.
L-iditol dehydrogenase see L-iditol dehydrogenase.
idopsin a visual pigment in the cone membranous lamellae of the eye.
IDR insect development inhibitor; idiosyncratic drug reaction.
iduronidase deficiency [i″du-ron′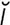 -dās] see mucopolysaccharidosis I.
-dās] see mucopolysaccharidosis I.
IDV intermittent demand ventilation.
IEWG International Elbow Working Group.
IFA test indirect fluorescent antibody test.
IFLUTD idiopathic feline lower urinary tract disease
iforrestine heterocyclic nephrotoxin in Isotropis spp.
Ig immunoglobulin of any of the five classes: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG and IgM.
IgA immunoglobulin A. See immunoglobulin.
IgD immunoglobulin D. See immunoglobulin.
IgE immunoglobulin E. See immunoglobulin.
IGF-I insulin-like growth factor I. See somatomedin C.
IgG immunoglobulin G. See immunoglobulin.
IgM immunoglobulin M. See immunoglobulin.
ignipuncture [ig′n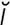 -punk″ch
-punk″ch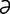 r] therapeutic puncture with hot needles.
r] therapeutic puncture with hot needles.
Ignis sacer [ig′nis] see rye ergot1.
IgY immunoglobulin Y, the avian equivalent of IgG; found in chicken yolk.
IHA isoimmune hemolytic anemia. See alloimmune hemolytic anemia of the newborn.
IHA indirect hemagglutination.
ileac [il′e-ak] 1. of the nature of ileus. 2. pertaining to the ileum.
transmissible i. hypertrophy see wet tail.
granulomatous i. see granulomatous enteritis.
proliferative i. 1. see porcine proliferative enteropathy. 2. see wet tail of hamsters.
regional i. see terminal ileitis (below).
ile(o)- word element. [L.] ileum.
ileocecal [il″e-o-se′k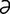 l] pertaining to the ileum and cecum.
l] pertaining to the ileum and cecum.
ileocecocolic, ileocaecocolic pertaining to the combined ileum, cecum and colon.
ileocecostomy [il″e-o-se-kos′t -me] surgical anastomosis of the ileum to the cecum.
-me] surgical anastomosis of the ileum to the cecum.
ileocolitis [il″e-o-ko-li′tis] inflammation of the ileum and colon.
ileocolostomy [il″e-o-k -los′t
-los′t -me] surgical anastomosis of the ileum to the colon.
-me] surgical anastomosis of the ileum to the colon.
ileocolotomy [il″e-o-ko-lot′ -me] incision of the ileum and colon.
-me] incision of the ileum and colon.
ileoileostomy [il″e-o-il″e-os′t -me] surgical anastomosis between two parts of the ileum.
-me] surgical anastomosis between two parts of the ileum.
ileorectal [il″e-o-rek′t l] pertaining to or communicating with the ileum and rectum.
l] pertaining to or communicating with the ileum and rectum.
ileorrhaphy [il″e-or′ -fe] suture of the ileum.
-fe] suture of the ileum.
ileoscope inspection of the lumen of the ileum, usually with a flexible endoscope.
ileoscopy inspection of the lumen of the ileum with an endoscope.
ileotomy [il″e-ot′ -me] incision of the ileum.
-me] incision of the ileum.
duplex i. congenital duplication of the ileum.
i.-umbilicus fistula a persistent and patent Meckel′s diver- ticulum.
functional i. paralytic ileus.
mechanical i. obstructive ileus.
obstructive i. a physical lesion accounts for the intestinal distention.
spastic i. persistent contraction of a segment of ileum, effectively causing an obstruction.
iliac [il′e-ak] pertaining to the ilium.
iliadelphus [il″e- -del′f
-del′f s] iliopagus.
s] iliopagus.
ili(o)- word element. [L.] ilium.
iliofemoral [il″e-o-fem′or- l] pertaining to the ilium and femur.
l] pertaining to the ilium and femur.
ilioinguinal [il″e-o-in′gw -n
-n l] pertaining to the iliac and inguinal regions.
l] pertaining to the iliac and inguinal regions.
iliolumbar [il″e-o-lum′b r] pertaining to the iliac and lumbar regions.
r] pertaining to the iliac and lumbar regions.
iliopagus [il″e-op′ -g
-g s] symmetrical conjoined twins united in the iliac region.
s] symmetrical conjoined twins united in the iliac region.
iliopectineal [il″e-o-pek-tin′e-al] pertaining to the ilium and pubes.
iliotrochanteric [il″e-o-tro-kan-ter′ik] pertaining to the ilium and femoral trochanters.
ilium [il′e-dm] pl. ilia [L.] the cranial portion of the hip bone. See also Table 10.
illacrimation [hlak″rima′sh n] see epiphora.
n] see epiphora.
illumination [ -loo″m
-loo″m -na′sh
-na′sh n] the lighting up of a part, cavity, organ or object for inspection.
n] the lighting up of a part, cavity, organ or object for inspection.
ILT infectious laryngotracheitis.
im- a prefix, replacing in- before words beginning b, m and p.
i. amplifier system includes amplifer and viewer or television camera and tape player.
i. display modes see ultrasonography, A-mode, B-mode and M- mode.
digital i. a computer graphic file made up of a matrix of picture elements (pixels).
gray-scale i. see gray scale ultrasonography.
imago [i-ma′go] pl. imagoes, imagines [L.] the adult or definitive form of an insect.
vasomotor i. autonomic imbalance.
imbecile an animal in a continuous state of imbecility.
imbibition [im″b -bish′
-bish′ n] absorption of a liquid.
n] absorption of a liquid.
imbricated [im′br -kāt″
-kāt″ d] overlapping like shingles or roof slates or tiles.
d] overlapping like shingles or roof slates or tiles.
IMHA immune mediated hemolytic anemia.
imidazothiazoles a group of broad-spectrum anthelmintics including butamisole and levamisole.
imide [im′id] any compound containing the bivalent group -CONHCO-.
immature [ m″
m″ -ch r′] unripe or not fully developed.
-ch r′] unripe or not fully developed.
i. syndrome vagal reflex, induced by contact with very cold water, causes cardiac arrest and death.
immiscible [ -mis′hb
-mis′hb l] not susceptible to being mixed.
l] not susceptible to being mixed.
immobilization [ -mo″bil-
-mo″bil- -za′sh
-za′sh n] the rendering of a part incapable of being moved.
n] the rendering of a part incapable of being moved.
immobilize [ -mo′bil-īz] to render incapable of being moved, as by a cast.
-mo′bil-īz] to render incapable of being moved, as by a cast.
immobilizing drugs see muscle relaxant.
i. competent an individual with a fully functional immune system.
i. complex see antibody-antigen complex.
i. complex reaction type III hypersensitivity (1).
i. hemolysis see immune-mediated hemolytic anemia.
i. modulator see immunomodulation.
i. reaction fever aseptic fever occurring in anaphylaxis, angioedema.
i. response (Ir) genes see immune response genes.
secondary i. response see anamnestic response.
i. tolerance see immunological tolerance.
immune-mediated caused by an unspecified immune reaction.
i.-m. contact hypersensitivity see allergic contact dermatitis.
functional i. see immunity (above).
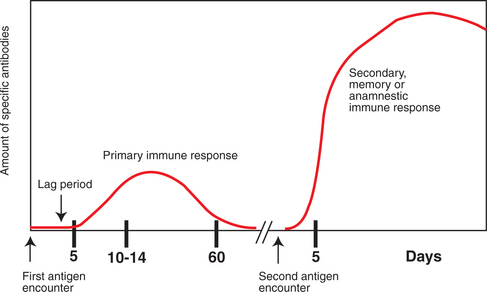
I-2: General dynamics and characteristics of the primary and secondary antibody responses.
From Cunningham JG, Klein BG. Textbook of Veterinary Physiology, 4th Edition. Saunders, 2007.
natural i. see innate immunity (above).
protective i. see immunity (above).
transplacental i. see passive immunity (above).
immunize [im′u-nīz] to render immune.
immunoadjuvant [im″u-no-aj′ -v
-v nt] see adjuvant.
nt] see adjuvant.
i. agents include BCG, mixed bacterial vaccine (MBV), and Cory- nebacterium parvum.
immunoblast [im″u-no-blast′] lymphoblast. See also B immunoblasts.
immunoblot [im′u-no-blot″] see Western blot.
immunochemotherapy [im″u-no-ke″mo-ther′ -pe] a combination of immunotherapy and chemotherapy.
-pe] a combination of immunotherapy and chemotherapy.
immunocomplex [im″u-no-kom′pl ks] immune complex.
ks] immune complex.
immunocytochemical staining [im″u-no-si″to kem′ -k
-k l] see immuno- histochemical.
l] see immuno- histochemical.
immunocytochemistry [im″u-no-si″to-kem′is-tre] see immunohisto- chemical.
acquired i. see immune deficiency disease.
combined i. see combined immune deficiency syndrome (disease).
congenital i. see immune deficiency disease.
i. disease see immune deficiency disease, combined immune deficiency syndrome (disease).
iatrogenic i. see secondary immune deficiency disease.
severe combined i. see combined immune deficiency syndrome (disease).
immunodiagnostic [im″u-no- di″ g-nos′tik] pertaining to diagnosis by immune reactions.
g-nos′tik] pertaining to diagnosis by immune reactions.
i. testing see fluorescence microscopy.
immunofluorescent see immunofluorescence.
i. antibody test see fluorescence microscopy.
i. microscopy see fluorescence microscopy.
immunogen [im′u-no-j n] substance that elicits an immune response.
n] substance that elicits an immune response.
immunogenic [im″u-no-jen′ik] producing immunity; evoking an immune response.
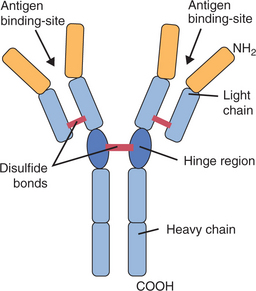
I-3: Structure of an immunoglobulin molecule.
From Tizard IR, Veterinary Immunology. An Introduction, 6th Edition. Saunders, 2001.
 n] a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent that possesses analgesic and antipyretic activities; used for symptomatic relief of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis in humans, but its use in dogs is limited by the occurrence of severe side- effects such as gastrointestinal hemorrhage.
n] a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent that possesses analgesic and antipyretic activities; used for symptomatic relief of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis in humans, but its use in dogs is limited by the occurrence of severe side- effects such as gastrointestinal hemorrhage. m-ol] an ammoniated coal tar product, used as an ointment in the treatment of acute, septic lesions such as cellu- litis and abscesses, and for a variety of skin conditions.
m-ol] an ammoniated coal tar product, used as an ointment in the treatment of acute, septic lesions such as cellu- litis and abscesses, and for a variety of skin conditions. m] poisoning due to ingestion of poisonous fish, marked by various gastrointestinal and neurological disturbances.
m] poisoning due to ingestion of poisonous fish, marked by various gastrointestinal and neurological disturbances.
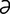 -he′dr
-he′dr l] a regular polyhedron with 20 triangular faces, 12 corners and 30 sides, having cubic symmetry with 5:3:2- fold axes. A common structural form for the capsid of many viruses including herpesviruses, adenoviruses, parvoviruses, reoviruses, picornaviruses and retroviruses.
l] a regular polyhedron with 20 triangular faces, 12 corners and 30 sides, having cubic symmetry with 5:3:2- fold axes. A common structural form for the capsid of many viruses including herpesviruses, adenoviruses, parvoviruses, reoviruses, picornaviruses and retroviruses.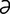 r-o-
r-o- -ne′me-
-ne′me- ] jaundice with mucosal pallor as in hemolytic anemia; see also eperythrozoonosis.
] jaundice with mucosal pallor as in hemolytic anemia; see also eperythrozoonosis. -roo′b
-roo′b -sin] an anthracycline antibiotic used as an antineoplastic agent; similar to doxorubicin.
-sin] an anthracycline antibiotic used as an antineoplastic agent; similar to doxorubicin. -f
-f -ka′sh
-ka′sh n] a description of an animal sufficient to distinguish it from others. The means of identification include a written description, earmark, paint brand or paper or fabric applied by special adhesive, freeze branding and fire branding (see brand), tattooing, neckbands, ankle bands, ear tagging, tail tagging and tail painting, and electronic identification systems including activated responders or transponders carried on the animal, often subcutaneously. See also microchip.
n] a description of an animal sufficient to distinguish it from others. The means of identification include a written description, earmark, paint brand or paper or fabric applied by special adhesive, freeze branding and fire branding (see brand), tattooing, neckbands, ankle bands, ear tagging, tail tagging and tail painting, and electronic identification systems including activated responders or transponders carried on the animal, often subcutaneously. See also microchip. -se] 1. a habit or quality of body or behavior peculiar to any individual animal. 2. an abnormal susceptibility to an agent (e.g. a drug) that is peculiar to the individual animal.
-se] 1. a habit or quality of body or behavior peculiar to any individual animal. 2. an abnormal susceptibility to an agent (e.g. a drug) that is peculiar to the individual animal. -dēn] a pyrimidine analog that prevents replication of DNA viruses; used topically in infection by herpes- viruses.
-dēn] a pyrimidine analog that prevents replication of DNA viruses; used topically in infection by herpes- viruses. -mīd] a nitrogen mustard alkylating agent used in cancer chemotherapy. It is given combination with the thiol drug mesna to avoid the development of sterile hemorrhagic cystitis. Used in dogs and cats for the treatment of sarcomas, including feline vaccine-associated sarcoma.
-mīd] a nitrogen mustard alkylating agent used in cancer chemotherapy. It is given combination with the thiol drug mesna to avoid the development of sterile hemorrhagic cystitis. Used in dogs and cats for the treatment of sarcomas, including feline vaccine-associated sarcoma. l] pertaining to the ileum. i. atresia see inherited alimentary tract segmental atresia. i. conduit use of a segment of the ileum for the diversion of urinary flow from the ureters.
l] pertaining to the ileum. i. atresia see inherited alimentary tract segmental atresia. i. conduit use of a segment of the ileum for the diversion of urinary flow from the ureters. -me] use of an isolated segment of ileum to create a passage from the urinary bladder to an opening in the abdominal wall.
-me] use of an isolated segment of ileum to create a passage from the urinary bladder to an opening in the abdominal wall. -me] an artificial opening (stoma) created in the small intestine (ileum) and brought to the surface of the abdomen for the purpose of evacuating feces.
-me] an artificial opening (stoma) created in the small intestine (ileum) and brought to the surface of the abdomen for the purpose of evacuating feces. m] the distal portion of the small intestine, extending from the jejunum to the cecum. See also ileal.
m] the distal portion of the small intestine, extending from the jejunum to the cecum. See also ileal. l mus′
l mus′ l] the more cranial of the two of the levator ani muscles; it originates on the medial surface of the body of the ilium and inserts on the ventral aspect of the tail.
l] the more cranial of the two of the levator ani muscles; it originates on the medial surface of the body of the ilium and inserts on the ventral aspect of the tail. days. Called also Illinois Variable Temperature Semen Diluent.
days. Called also Illinois Variable Temperature Semen Diluent. -loo″m
-loo″m -na′t
-na′t r] the source of light for viewing an object; the light source used to aid visualization through an endoscope, usually using a Xenon or Halogen lamp.
r] the source of light for viewing an object; the light source used to aid visualization through an endoscope, usually using a Xenon or Halogen lamp. j] the picture reproduced on the X-ray film or by other radioimaging methods such as ultrasonography.
j] the picture reproduced on the X-ray film or by other radioimaging methods such as ultrasonography. -jing] the production of diagnostic images, e.g. radiography, ultrasonography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging or scintigraphy.
-jing] the production of diagnostic images, e.g. radiography, ultrasonography, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging or scintigraphy. ns] lack of balance; especially lack of balance between muscles, as in insufficiency of ocular muscles.
ns] lack of balance; especially lack of balance between muscles, as in insufficiency of ocular muscles. -ka′sh
-ka′sh n] surgical pleating and folding of tissue to realign organs and provide extra support, e.g. chronically stretched joint capsule.
n] surgical pleating and folding of tissue to realign organs and provide extra support, e.g. chronically stretched joint capsule. -no] proline or hydroxyproline, the two amino acids in which the amino group is part of a closed ring.
-no] proline or hydroxyproline, the two amino acids in which the amino group is part of a closed ring. -pen′
-pen′ m] one of the carbapenem class of antibiotics which are β-lactamase resistant. It has a very wide spectrum, but is inactivated by renal tubular enzymes and is given in association with cilastatin, which inhibits renal metabolism.
m] one of the carbapenem class of antibiotics which are β-lactamase resistant. It has a very wide spectrum, but is inactivated by renal tubular enzymes and is given in association with cilastatin, which inhibits renal metabolism. -mip′r
-mip′r -mēn] a tricyclic antidepressant used in the treatment of behavior disorders and urinary incontinence in dogs.
-mēn] a tricyclic antidepressant used in the treatment of behavior disorders and urinary incontinence in dogs. -kwim′od] a topical immune response modifier with antiviral and antineoplasia effects. Used in veterinary medicine to treat squamous cell carcinomas, viral papillomas, feline cutaneous herpesvirus infection, and sarcoid and aural plaques in horses.
-kwim′od] a topical immune response modifier with antiviral and antineoplasia effects. Used in veterinary medicine to treat squamous cell carcinomas, viral papillomas, feline cutaneous herpesvirus infection, and sarcoid and aural plaques in horses. -me′de-
-me′de- t] direct, precipitating or primary; having no intermediate stage or mechanism, e.g. direct cause, immediate variant.
t] direct, precipitating or primary; having no intermediate stage or mechanism, e.g. direct cause, immediate variant. -mur′zh
-mur′zh n] 1. the plunging of a body into a liquid. 2. the use of the microscope with the air between specimen and front objective lens replaced by a liquid, either immersion oil or water.
n] 1. the plunging of a body into a liquid. 2. the use of the microscope with the air between specimen and front objective lens replaced by a liquid, either immersion oil or water. -″mo-bil′
-″mo-bil′ -te] standing still and disinclined to move, as in an animal suddenly blinded; responds to other stimuli unless immobility is part of a dummy syndrome when all stimuli are ignored.
-te] standing still and disinclined to move, as in an animal suddenly blinded; responds to other stimuli unless immobility is part of a dummy syndrome when all stimuli are ignored. -mūn′] 1. being highly resistant to a disease because of the formation of humoral antibodies or the development of immunologically competent cells, or both, or as a result of some innate immune mechanism, such as interferon activities in viral infections. 2. characterized by the development of antibodies or cellular immunity, or both, following exposure to antigen.
-mūn′] 1. being highly resistant to a disease because of the formation of humoral antibodies or the development of immunologically competent cells, or both, or as a result of some innate immune mechanism, such as interferon activities in viral infections. 2. characterized by the development of antibodies or cellular immunity, or both, following exposure to antigen.  . produced in response to antigen, such as immune serum globulin. The essential feature of antibody and cell-mediated immunity is that they are highly antigen specific.
. produced in response to antigen, such as immune serum globulin. The essential feature of antibody and cell-mediated immunity is that they are highly antigen specific. -mu′n
-mu′n -te] 1. the condition of being immune; security against a particular disease; nonsusceptibility to the invasive or pathogenic effects of microorganisms or helminth parasites or to the toxic effect of antigenic substances. Called also functional or protective immunity. 2. responsiveness to antigen that leads to more rapid binding or elimination of antigen than in the nonimmune state; it includes both humoral and cell-mediated immunity (below). 3. the capacity to distinguish foreign material from self, and to neutralize, eliminate or metabolize that which is foreign (non-self) by the physiological mechanisms of the immune response. The mechanisms of immunity are essentially concerned with the body’s ability to recognize and dispose of substances which it interprets as foreign and sometimes harmful to its well- being. When such a substance enters the body, complex chemical and mechanical activities are set into motion to defend and protect the body’s cells and tissues. The foreign substance, usually a protein, is called an antigen, that is, one which generates the production of an antagonist. The most readily recognized response to the antigen is the production of antibody. The antigen-antibody reaction is an essential component of the overall immune response. Of equal or greater importance to antibody, particularly for some antigens, is the development of so-called cell-mediated immune response, which involves clonal expansion of specifically reactive T lymphocytes including cytotoxic T lymphocytes (Tc lymphocytes) which play a major role in eliminating the foreign antigens that are cell associated. Immunological responses in animals can be divided into two broad categories: humoral immunity, which refers to the production of antibody which becomes part of the body fluids (humors), especially serum, and cell-mediated or cellular immunity, which involves a variety of activities designed to destroy or at least contain cells that are recognized by the body as expressing foreign antigens on their cell surface, e.g. viral antigens. Both types of response are mediated by lymphocytes that originate in the bone marrow as stem cells and later are converted into mature cells having specific properties and functions.
-te] 1. the condition of being immune; security against a particular disease; nonsusceptibility to the invasive or pathogenic effects of microorganisms or helminth parasites or to the toxic effect of antigenic substances. Called also functional or protective immunity. 2. responsiveness to antigen that leads to more rapid binding or elimination of antigen than in the nonimmune state; it includes both humoral and cell-mediated immunity (below). 3. the capacity to distinguish foreign material from self, and to neutralize, eliminate or metabolize that which is foreign (non-self) by the physiological mechanisms of the immune response. The mechanisms of immunity are essentially concerned with the body’s ability to recognize and dispose of substances which it interprets as foreign and sometimes harmful to its well- being. When such a substance enters the body, complex chemical and mechanical activities are set into motion to defend and protect the body’s cells and tissues. The foreign substance, usually a protein, is called an antigen, that is, one which generates the production of an antagonist. The most readily recognized response to the antigen is the production of antibody. The antigen-antibody reaction is an essential component of the overall immune response. Of equal or greater importance to antibody, particularly for some antigens, is the development of so-called cell-mediated immune response, which involves clonal expansion of specifically reactive T lymphocytes including cytotoxic T lymphocytes (Tc lymphocytes) which play a major role in eliminating the foreign antigens that are cell associated. Immunological responses in animals can be divided into two broad categories: humoral immunity, which refers to the production of antibody which becomes part of the body fluids (humors), especially serum, and cell-mediated or cellular immunity, which involves a variety of activities designed to destroy or at least contain cells that are recognized by the body as expressing foreign antigens on their cell surface, e.g. viral antigens. Both types of response are mediated by lymphocytes that originate in the bone marrow as stem cells and later are converted into mature cells having specific properties and functions. -za′sh
-za′sh n] the process of rendering a subject immune, or of becoming immune. See also vaccination.
n] the process of rendering a subject immune, or of becoming immune. See also vaccination. nt] a preparation of antigen attached to a solid support or antigen in an insoluble form, which absorbs homologous antibodies from a mixture of immunoglo- bulins. See immunosorbent, ELISA.
nt] a preparation of antigen attached to a solid support or antigen in an insoluble form, which absorbs homologous antibodies from a mixture of immunoglo- bulins. See immunosorbent, ELISA.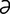 -je] that branch of biology dealing with immunological effects on such phenomena as infectious disease, growth and development, recognition phenomena, hyper- sensitivity, heredity, aging, cancer and transplantation.
-je] that branch of biology dealing with immunological effects on such phenomena as infectious disease, growth and development, recognition phenomena, hyper- sensitivity, heredity, aging, cancer and transplantation.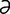 -t
-t ns] the capacity to develop an immune response following exposure to antigen.
ns] the capacity to develop an immune response following exposure to antigen. -mīzd] having reduced immune responsiveness as a result of inherited defects or infection, particularly by retroviruses and herpesviruses or by administration of immunosuppressive drugs, including antilymphocyte serum, by irradiation, by malnutrition, and by certain disease processes, e.g. cancer.
-mīzd] having reduced immune responsiveness as a result of inherited defects or infection, particularly by retroviruses and herpesviruses or by administration of immunosuppressive drugs, including antilymphocyte serum, by irradiation, by malnutrition, and by certain disease processes, e.g. cancer. n-gloo′t
n-gloo′t -nin] antibody formed against complement components that are part of an antibody-antigen complex, especially C3.
-nin] antibody formed against complement components that are part of an antibody-antigen complex, especially C3. ns] the aggregation of red cells to form rosettes around lymphocytes with surface immunoglobulins.
ns] the aggregation of red cells to form rosettes around lymphocytes with surface immunoglobulins. -fish′
-fish′ n-se] a deficiency in the immune system, either that mediated by antibody or T lymphocytes, or both. See also agammaglobulinemia, hypogammaglobulinemia, feline immunodeficiency virus, bovine immunodeficiency virus.
n-se] a deficiency in the immune system, either that mediated by antibody or T lymphocytes, or both. See also agammaglobulinemia, hypogammaglobulinemia, feline immunodeficiency virus, bovine immunodeficiency virus. -presh′
-presh′ n] see agammaglobulinemia, hypogammagIobuIinemia, immunodeficiency.
n] see agammaglobulinemia, hypogammagIobuIinemia, immunodeficiency. -tol′
-tol′ -je] the study of immuno- logical phenomena as they affect skin disorders and their treatment or prophylaxis.
-je] the study of immuno- logical phenomena as they affect skin disorders and their treatment or prophylaxis. -fu′zh
-fu′zh n] in vitro assays that involve the diffusion of antigen and antibody through a gel matrix such as agarose. For example, double immunodiffusion assays where antigen and antibody are placed in separate wells, cut in agar, such that precipitation lines form in the agar between the wells.
n] in vitro assays that involve the diffusion of antigen and antibody through a gel matrix such as agarose. For example, double immunodiffusion assays where antigen and antibody are placed in separate wells, cut in agar, such that precipitation lines form in the agar between the wells. -n
-n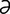 ns] the property of an anti- genic determinant that causes it to be responsible for the major immune response in a host.
ns] the property of an anti- genic determinant that causes it to be responsible for the major immune response in a host.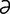 -re′sis] electrophoretic separation, usually in an agar gel, of complex mixtures of antigens which, following immunodiffusion, combine with antibody to forming precipitation lines for each separated antigen.
-re′sis] electrophoretic separation, usually in an agar gel, of complex mixtures of antigens which, following immunodiffusion, combine with antibody to forming precipitation lines for each separated antigen. ns] a method of determining the location of antigen (or antibody) in a tissue section or smear using a specific antibody (or antigen) labeled with a fluoro- chrome. In the direct methods, the fluorochome is chemically linked to the specific antibody. In indirect methods, a labeled anti-immunoglobulin that binds to the specific antibody is used. See also fluorescence microscopy.
ns] a method of determining the location of antigen (or antibody) in a tissue section or smear using a specific antibody (or antigen) labeled with a fluoro- chrome. In the direct methods, the fluorochome is chemically linked to the specific antibody. In indirect methods, a labeled anti-immunoglobulin that binds to the specific antibody is used. See also fluorescence microscopy. -net′iks] the study of the genetic factors controlling the animal’s immune response and the transmission of those factors from generation to generation.
-net′iks] the study of the genetic factors controlling the animal’s immune response and the transmission of those factors from generation to generation. -nis′ĩ-te] the ability of a substance to provoke an immune response or the degree to which it provokes a response.
-nis′ĩ-te] the ability of a substance to provoke an immune response or the degree to which it provokes a response.


