Gait Analysis
Basic Information 
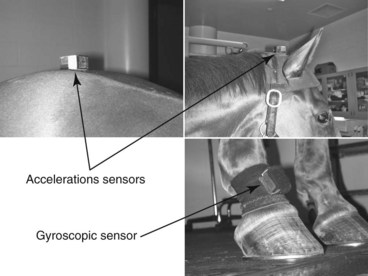
Preparation: Important Checkpoints (Figure 1)
• Attach the head sensor to the head bumper.
• Attach the pelvis sensor to a strip of 3M Dual Lock tape on the dorsal midline and tape in place.
• Place the gyroscopic sensor in the right forelimb pastern pouch on the dorsal aspect of the limb.
• Place sensor labels face up (head and pelvis sensors) or out (right forelimb sensor).
• Face the light-emitting diodes of sensors forward (head and pelvis sensors) or up (right forelimb sensor). Collect at least 25 strides.
Procedure
FORELIMB LAMENESS (Figure 2)
• Pain in first half of stance:
 By convention, HEADDIFFMIN is positive when the head falls less during right forelimb stance and negative when the head falls less during left forelimb stance.
By convention, HEADDIFFMIN is positive when the head falls less during right forelimb stance and negative when the head falls less during left forelimb stance. By convention, HEADDIFMAX is positive when the head rises more after left forelimb push-off and negative when the head rises more after right forelimb push-off.
By convention, HEADDIFMAX is positive when the head rises more after left forelimb push-off and negative when the head rises more after right forelimb push-off. Lameness closer to beginning of stance will cause greater asymmetry in HEADIFFMAX than in HEADDIFFMIN.
Lameness closer to beginning of stance will cause greater asymmetry in HEADIFFMAX than in HEADDIFFMIN. Horses with positive HEADDIFFMIN and HEADDIFFMAX have lameness in the first half of right forelimb stance.
Horses with positive HEADDIFFMIN and HEADDIFFMAX have lameness in the first half of right forelimb stance. Horses with negative HEADDIFFMIN and HEADDIFFMAX have lameness in the first half of left forelimb stance.
Horses with negative HEADDIFFMIN and HEADDIFFMAX have lameness in the first half of left forelimb stance.• Pain in second half of stance:
 Measure the difference in maximum head position (HEADDIFFMAX) after push-off between right and left limbs.
Measure the difference in maximum head position (HEADDIFFMAX) after push-off between right and left limbs. By convention, HEADDIFFMAX is negative when the head rises more after push-off of the right forelimb and negative when the head rises more after push-off of the left forelimb.
By convention, HEADDIFFMAX is negative when the head rises more after push-off of the right forelimb and negative when the head rises more after push-off of the left forelimb. Horses with negative HEADDIFFMAX and positive HEADDIFFMIN have lameness in the second half of the right forelimb stance.
Horses with negative HEADDIFFMAX and positive HEADDIFFMIN have lameness in the second half of the right forelimb stance. Horses with positive HEADDIFFMAX and negative HEADDIFFMIN have lameness in the second half of the left forelimb stance.
Horses with positive HEADDIFFMAX and negative HEADDIFFMIN have lameness in the second half of the left forelimb stance.• Forelimb lameness is displayed as a ray diagram (see Figure 2). The x-axis is HEADDIFFMAX and the y-axis is HEADDIFFMIN.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree