G
G symbol for giga; gingival; glucose; gonidial; guanine.
γ gamma, small letter; third letter in the Greek alphabet.
G banding the technique of demonstrating g bands.
G-CSF granulocyte-colony stimulating factor.
G1 phase, G1 period see cell cycle.
G2 phase, G2 period see cell cycle.
G6PD glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
gadolinium (Gd) [gad″o-lin′e- m] a chemical element, atomic number 64, atomic weight 157.25. See Table 4.
m] a chemical element, atomic number 64, atomic weight 157.25. See Table 4.
Gaertner’s canal see Gartner’s ducts.
mouth g. (1) see Drinkwater mouth gag, Haussman gag, spring gag (below), Varnell gag, probang.
gagging [gag′ing] the swallowing–vomiting activity of the gag reflex.
gaggle collective noun for a group of geese.
Gaigeria [ga-je′re- ] a genus of hookworms in the family Ancylostomatidae.
] a genus of hookworms in the family Ancylostomatidae.
gain [gān] increase in body weight. See also growth rate, gain ratio.
feed cost of g. total feed cost divided by total pounds of gain.
asymmetric g. refers to right-left symmetry of leg movements; in the horse, canter and gallop.
ataxic g. an unsteady, uncoordinated walk, employing a wide base.
base-wide g. feet are wider apart than normal, suggesting instability. Seen with cerebellar ataxia.
diagonal g. one in which a forelimb is moved in unison with its opposite hindlimb, e.g. trot.

G-1: Spring gag.
From Sonsthagen TF, Veterinary Instruments and Equipment: A Pocket Guide. 2nd Edition. Mosby, 2011.
spastic g. a walk in which the legs move in a stiff manner, the toes seeming to drag and catch.
gaited [gāt’ d] see five-gaited.
d] see five-gaited.
GAL virus Gallus adeno-like virus; the Aviadenovirus genus.
galactans [g -lak’t
-lak’t ns] an ingredient of the toxins of some Mycoplasma spp.
ns] an ingredient of the toxins of some Mycoplasma spp.
galactemia [gal″ak-te′me-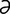 ] the presence of milk in the blood.
] the presence of milk in the blood.
galactic [g -lak′tik] 1. pertaining to milk. 2. galactagogue.
-lak′tik] 1. pertaining to milk. 2. galactagogue.
galactischia [gal″ak-tis′ke- ] suppression of milk secretion.
] suppression of milk secretion.
galact(o)- word element. [Gr.] milk.
galactoblast [g -lak′to-blast] a colostrum corpuscle in the acini of the mammary gland.
-lak′to-blast] a colostrum corpuscle in the acini of the mammary gland.
galactocerebrosidosis see globoid cell leukodystrophy.
g. deficiency see galactosemia.
galactolipid, galactolipin [g -lak″to-lip′id, g
-lak″to-lip′id, g -lak″to-lip′in] see galactocerebroside.
-lak″to-lip′in] see galactocerebroside.
galactoma [g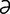 -lak″to’m
-lak″to’m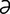 ] galactocele (1).
] galactocele (1).
galactophore [g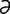 -lak′to-for] 1. galactophorous. 2. a milk duct.
-lak′to-for] 1. galactophorous. 2. a milk duct.
galactophoritis [g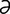 -lak″to-for-i′tis] inflammation of the milk ducts.
-lak″to-for-i′tis] inflammation of the milk ducts.
galactophorous [gal″ak-tof′o-r s] conveying milk.
s] conveying milk.
galactophygous [gal″ak-tof’ -g
-g s] arresting the flow of milk.
s] arresting the flow of milk.
galactoplania secretion of milk in some abnormal part.
galactopoiesis [g -lak″to-poi-e′sis] the production of milk by the mammary glands.
-lak″to-poi-e′sis] the production of milk by the mammary glands.
galactosamine [gal″ak-to’s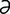 -mēn] an amino derivative of galactose.
-mēn] an amino derivative of galactose.
galactoside [g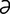 -lak′to-sīd] a glycoside containing galactose.
-lak′to-sīd] a glycoside containing galactose.
galactosis [gal″ak-to′sis] the formation of milk by the lacteal glands.
galactosuria [g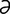 -lak″to-su′re-
-lak″to-su′re-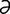 ] the presence of galactose in the urine.
] the presence of galactose in the urine.
galactosylceramidase [g -lak′to-s
-lak′to-s l“s
l“s -ram’
-ram’ -dās] see galactocerebrosidase.
-dās] see galactocerebrosidase.
galactosylceramide [g -lak′to-s
-lak′to-s l″ser’
l″ser’ -mīd] see galactocerebroside.
-mīd] see galactocerebroside.
galactosyl transferase [g -lak′to-s
-lak′to-s l″trans’f
l″trans’f r-ās] an enzyme which contributes to glycolization.
r-ās] an enzyme which contributes to glycolization.
galactotherapy [g -lak′to-ther’
-lak′to-ther’ -pe] treatment of sucking neonates by medication given to the dam.
-pe] treatment of sucking neonates by medication given to the dam.
galacturia [g -lak″to-u′re-
-lak″to-u′re- ] chyluria; the discharge of urine with a milky appearance.
] chyluria; the discharge of urine with a milky appearance.
Galba the host snail genus for the intermediate stages of Fasciola hepatica in North America.
galea [ga′le- ] pl. galeae [L.] a helmet-shaped structure.
] pl. galeae [L.] a helmet-shaped structure.
g. capitis the cap over the head of the spermatozoon. Called also acrosomal vesicle.
g. glandis the diminutive caplike glans of the ruminant penis.
galena a mineral containing lead.
galeta grass Hilaria jamesii, commonly infested with Claviceps cinerea, which causes poisoning.
Galiceno small, solid-colored (any color) pleasure horse of Mexican origin.
Galician Blond cattle Spanish cream to red-brown meat cattle.
Galician sheep prolific Spanish meat and medium-wool sheep, mostly polled.
g. edema a gross lesion in many cases of infectious canine hepatitis.
g. inflammation cholecystitis.
porcelain g. intramural mineralization of the gallbladder.
g. radiography see cholecystography.
Gallibacterium genus of gram-negative bacteria associated with disease in birds.
G. trehalosiformentans bacterial species isolated from a case of septicemia in a budgerigar.
gallinaceous, galliform belonging to the genus Gallus, hence domestic and wild fowl.
gallium (Ga) [gal′e- m] a chemical element, atomic number 31, atomic weight 69.72. See Table 4.
m] a chemical element, atomic number 31, atomic weight 69.72. See Table 4.
g. nitrate used in the treatment of hypercalcemia.
diastolic g. see gallop rhythm.
gallotannic acid [gal″o-tan′ik] tannic acid.
gallstone [gawl′stōn] a stonelike mass that forms in the gallbladder. See cholelithiasis.
G. domesticus see Gallus gallus (below).
GALT gut-associated lymphoid tissue.
Galtonia clavata see Pseudogaltonia clavata.
Galumna oribatid mites which act as intermediate hosts for Moniezia spp. (tapeworms).
galvanic current [gal-van′ik] a steady direct electric current.
galvanometer [gal“v -nom’
-nom’ -t
-t r] an instrument for measuring current by electromagnetic action.
r] an instrument for measuring current by electromagnetic action.
galvanopalpation [gal“v -no-pal-pa′sh
-no-pal-pa′sh n] testing of nerves of the skin by means of galvanic current.
n] testing of nerves of the skin by means of galvanic current.
Galway sheep polled, Irish meat and longwool sheep.
Gambian sleeping sickness [gam′be- n] see Trypanosoma gambiense.
n] see Trypanosoma gambiense.
g. fish fish hunted for sport.
g. meat meat from slaughtered game animals.
g. ranch see game farm (above).
gamefowl [gām′foul] see game cock.
gametocyte [g -me′to-sīt] an oocyte or spermatocyte; a cell that produces gametes.
-me′to-sīt] an oocyte or spermatocyte; a cell that produces gametes.
gametogenesis [g -me″to-jen’
-me″to-jen’ -sis] the development of the male and female sex cells (gametes).
-sis] the development of the male and female sex cells (gametes).
g. benzene hexachloride see chlorinated hydrocarbons.
g. delta T lymphocyte see T lymphocyte.
gamma camera see scintillation camera.
gammaglobulinopathy [gam″ -glob“u-lin-op’
-glob“u-lin-op’ -the] see gammopathy.
-the] see gammopathy.
Gammarus water crustaceans; intermediate hosts for Tetrameres spp. nematodes.
gamogenesis [gam″o-jen’ -sis] sexual reproduction.
-sis] sexual reproduction.
ganado bravo [Span.] see fighting bull.
ganglial [gang′gle- l] pertaining to a ganglion.
l] pertaining to a ganglion.
gangliated [gang′gle-āt″ d] provided with ganglia; ganglionated.
d] provided with ganglia; ganglionated.
gangliectomy [gang″gle-ek’t -me] excision of a ganglion; ganglionectomy.
-me] excision of a ganglion; ganglionectomy.
gangliform [gang′gl -form] having the form of a ganglion.
-form] having the form of a ganglion.
gangliitis [gang″gle-i′tis] see ganglionitis.
gangli(o)- word element. [Gr.] ganglion.
ganglioblast [gang′gle-o-blast″] an embryonic cell of the cerebrospinal ganglia.
gangliocyte [gang′gle-o-sīt″] a ganglion cell.
gangliocytoma [gang″gle-o-si-to’m ] see ganglioneuroma.
] see ganglioneuroma.
ganglioform [gang′gle-o-form″] gangliform.
ganglioglioma [gang″gle-o-gli-o’m ] a glioma rich in mature neurons or ganglion cells.
] a glioma rich in mature neurons or ganglion cells.
ganglioglioneuroma [gang″gle-o-gli″o-n
 -ro’m
-ro’m ] see ganglioneuroma.
] see ganglioneuroma.
ganglioma [gang″gle-o’m ] see ganglioneuroma.
] see ganglioneuroma.
aorticorenal g. small sympathetic ganglia supplying nerve fibers to the kidneys.
Arnold’s g. see otic ganglion (below).
cardiac g. ganglia of the superficial cardiac plexus found close to the aortic arch.
cerebrospinal g. those associated with the cranial and spinal nerves.
dorsal root g. spinal ganglion.
false g. an enlargement on a nerve that does not have a true ganglionic structure.
gasserian g. trigeminal ganglion.
geniculate g. the sensory ganglion of the facial nerve, on the geniculum of the facial nerve.
lumbar g. the ganglia on the lumbar part of the sympathetic trunk.
petrous g. the distal ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
sacral g. those of the sacral part of the sympathetic trunk.
semilunar g. trigeminal ganglion.
simple g. a cystic tumor in a tendon sheath.
sphenopalatine g. pterygopalatine ganglion.
spinal g. ganglia on the dorsal root of each spinal nerve.
stellate g. cervicothoracic ganglion.
thoracic g. the ganglia on the thoracic portion of the sympathetic trunk.
tympanic g. an enlargement on the tympanic branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve.
Wrisberg’s g. cardiac ganglia.
ganglion blocking [gang′gle-on] blocking of transmission through the autonomic ganglia.
ganglionated [gang′gle- -nāt″
-nāt″ d] provided with ganglia; gangliated.
d] provided with ganglia; gangliated.
ganglionectomy [gang″gle- -nek’t
-nek’t -me] excision of a ganglion; gangliectomy.
-me] excision of a ganglion; gangliectomy.
ganglioneuritis [gang″gle-o-n
 -ri′tis] see ganglionitis.
-ri′tis] see ganglionitis.
ganglionic [gang″gle-on′ik] pertaining to a ganglion.
g. blockade inhibition by drugs of nerve impulse transmission at autonomic ganglionic synapses.
g. blocking agent see ganglion blocking.
ganglionitis [gang″gle- -ni′tis] inflammation of a ganglion; gangliitis.
-ni′tis] inflammation of a ganglion; gangliitis.
myoenteric g. causes chronic intestinal pseudoobstruction in horses.
gangrenous [gang’r -n
-n s] pertaining to, marked by, or of the nature of gangrene.
s] pertaining to, marked by, or of the nature of gangrene.
g. coryza see malignant catarrhal fever.
g. dermatitis see gangrenous cellulitis (above).
ganskweek see Lasiospermum bipinnatum.
gantho metho Senecio raphanifolius.
gantho metho ajang Senecio biligulatus.
gapes [gāps] see Syngamus trachea.
gapeworm [gāp’w rm] see Syngamus trachea.
rm] see Syngamus trachea.
garbancillo Astragalus wootoni.
garbanzo [gahr-bahn′zo] see chickpea.
gargaloo Parsonsia eucalyptophylla.
garget [gahr’g t] 1. mastitis. 2. Phytolacca americana.
t] 1. mastitis. 2. Phytolacca americana.
gargoylism [gahr′goil-iz- m] mucopolysaccharidosis I; Hurler’s syndrome.
m] mucopolysaccharidosis I; Hurler’s syndrome.
garland flower [gahr’l nd] see Daphne.
nd] see Daphne.
garlic [gahr′lik] Allium sativum.
three-cornered g. Allium triquetrum.
wild g. Allium ursinum, A. vineale.
cystic G. d. cystlike structures in the floor of the vagina.
blood g. see blood gas analysis.
g. edema disease see blue wing disease.
gasoline poisoning see oil products.
gasping disease [gas′ping] see avian infectious bronchitis.
gasserian ganglion [g -se′re-
-se′re- n] see trigeminal ganglion.
n] see trigeminal ganglion.
gaster [gas’t r] [Gr.] see stomach.
r] [Gr.] see stomach.
gasterophiliasis gasterophilosis.
G. equi see G. intestinalis (below).
G. nigricornis an uncommon horse bot fly.
G. veterinus see G. nasalis (above).
gastradenitis inflammation of the gastric glands.
gastralgia [gas-tral’j ] pain in the stomach; gastric colic.
] pain in the stomach; gastric colic.
gastrectasis distention of the stomach.
gastric [gas′trik] pertaining to, affecting, or originating in the stomach.
g. acid see gastric juice (below).
g. dilatation see gastric dilatation colic.
g. dilatation–displacement see gastric dilatation–volvulus (below).
g. distention in pigs commonly results in vomiting.
g. fluid see gastric juice (below).
g. habronemiasis see habronemiasis.
g. hormones see gastrointestinal hormones.
g. impaction in horses fed a diet of coarse indigestible roughage; a cause of subacute colic.
g. mucosa secretes pepsin (as pepsinogen), hydrochloric acid.
g. outlet obstruction see pyloric obstruction, pyloric outflow failure, gastric retention syndrome.
g. waves peristaltic waves, the pacemakers for antral peristalsis.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
 -pen′tin] anticonvulsant and analgesic. Originally designed to be a structural analog of gamma-aminobutyric acid, although its anticonvulsant properties are now known to be unrelated to this property. When used as an analgesic, gabapentin seems to be particularly useful in the treatment of pain of neurogenic origin.
-pen′tin] anticonvulsant and analgesic. Originally designed to be a structural analog of gamma-aminobutyric acid, although its anticonvulsant properties are now known to be unrelated to this property. When used as an analgesic, gabapentin seems to be particularly useful in the treatment of pain of neurogenic origin. -lak’t
-lak’t -gog] 1. promoting the flow of milk. 2. An agent that promotes the flow of milk.
-gog] 1. promoting the flow of milk. 2. An agent that promotes the flow of milk. -lak″to-bol′ik] of or relating to the action of neurohypophyseal peptides which contract the mammary myoepithelium and cause ejection of milk.
-lak″to-bol′ik] of or relating to the action of neurohypophyseal peptides which contract the mammary myoepithelium and cause ejection of milk. -lak′to-sēl] 1. a milk-containing, cystic enlargement of the mammary gland. 2. hydrocele filled with milky fluid.
-lak′to-sēl] 1. a milk-containing, cystic enlargement of the mammary gland. 2. hydrocele filled with milky fluid. -lak″to-s
-lak″to-s -re′bro-sīd″] a glycosphingolipid with a galactose unit. Called also galactolipid. See globoid cell leukodystrophy.
-re′bro-sīd″] a glycosphingolipid with a galactose unit. Called also galactolipid. See globoid cell leukodystrophy. -fe] radiography of the mammary ducts after injection of a radiopaque substance into the duct system.
-fe] radiography of the mammary ducts after injection of a radiopaque substance into the duct system. -lak″to-ki’nās] an enzyme that catalyzes the first step in the metabolism of galactose, the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to galactose, producing galactose-1-phosphate.
-lak″to-ki’nās] an enzyme that catalyzes the first step in the metabolism of galactose, the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to galactose, producing galactose-1-phosphate. -lak″to-poi-et′ik] 1. pertaining to, marked by, or promoting milk production. 2. an agent that promotes milk flow.
-lak″to-poi-et′ik] 1. pertaining to, marked by, or promoting milk production. 2. an agent that promotes milk flow. -lak″to-re’
-lak″to-re’ ] excessive or spontaneous milk flow; persistent secretion of milk irrespective of nursing; lactorrhea. May occur in dogs with severe hypothyroidism due to hyperprolactinemia, pseudocyesis, or trauma to the mammary gland.
] excessive or spontaneous milk flow; persistent secretion of milk irrespective of nursing; lactorrhea. May occur in dogs with severe hypothyroidism due to hyperprolactinemia, pseudocyesis, or trauma to the mammary gland. -lak’tōs] a monosaccharide epimer of glucose. D-galactose is found in lactose, cerebrosides of the brain, raffinose of the sugar beet, and in many gums and seaweeds; L-galactose is found in flaxseed mucilage.
-lak’tōs] a monosaccharide epimer of glucose. D-galactose is found in lactose, cerebrosides of the brain, raffinose of the sugar beet, and in many gums and seaweeds; L-galactose is found in flaxseed mucilage. -lak″to-se′me-
-lak″to-se′me- ] a biochemical disorder in which there is a deficiency of enzymes necessary for proper metabolism of galactose. The condition is inherited in humans in two forms, due to deficiency of either galactokinase or galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase. Adult macropods are normally deficient in these enzymes. Normally the sugar derived from lactose in milk is changed by enzymatic action into glucose. When the conversion of galactose to glucose does not take place, the galactose accumulates in the tissues and blood, typically causing cataract formation; commonly seen in young macropods reared on cow’s milk.
] a biochemical disorder in which there is a deficiency of enzymes necessary for proper metabolism of galactose. The condition is inherited in humans in two forms, due to deficiency of either galactokinase or galactose-1-phosphate uridyltransferase. Adult macropods are normally deficient in these enzymes. Normally the sugar derived from lactose in milk is changed by enzymatic action into glucose. When the conversion of galactose to glucose does not take place, the galactose accumulates in the tissues and blood, typically causing cataract formation; commonly seen in young macropods reared on cow’s milk.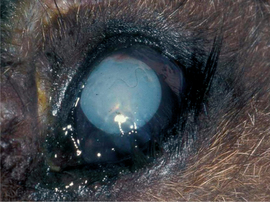
 -lak″to-si’dās] an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of galactoside to galactose; it occurs in two forms: α-galactosidase (melibiase) and β-galactosidase (lactase). In deficiency states gangliosides (galactose-containing cerebrosides) accumulate in tissues. See also GM1 gangliosidosis.
-lak″to-si’dās] an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of galactoside to galactose; it occurs in two forms: α-galactosidase (melibiase) and β-galactosidase (lactase). In deficiency states gangliosides (galactose-containing cerebrosides) accumulate in tissues. See also GM1 gangliosidosis. -lak″to-si’dās] a lysosome hydrolase catalyzing the β-gangliosides into monosaccharides.
-lak″to-si’dās] a lysosome hydrolase catalyzing the β-gangliosides into monosaccharides. -sis] 1. cessation of milk secretion. 2. abnormal collection of milk in the mammary glands.
-sis] 1. cessation of milk secretion. 2. abnormal collection of milk in the mammary glands. -len’
-len’ -k
-k lz] medicines prepared according to the formulae of Galen. The term is now used to denote standard preparations containing one or several organic ingredients, as contrasted with pure chemical substances.
lz] medicines prepared according to the formulae of Galen. The term is now used to denote standard preparations containing one or several organic ingredients, as contrasted with pure chemical substances. -mēn] a competitive neuromuscular blocking agent used as a muscle relaxant. Used as the triethiodide. It competes with acetylcholine for the cholinergic receptors at the postsynaptic membrane.
-mēn] a competitive neuromuscular blocking agent used as a muscle relaxant. Used as the triethiodide. It competes with acetylcholine for the cholinergic receptors at the postsynaptic membrane. r] the pear-shaped reservoir for bile attached to the visceral surface of the liver or in a hollow between the quadrate and right medial lobes of the liver in all domestic animals except the horse. It serves as a storage place for bile. The gallbladder may be subject to such disorders as inflammation and the formation of gallstone.
r] the pear-shaped reservoir for bile attached to the visceral surface of the liver or in a hollow between the quadrate and right medial lobes of the liver in all domestic animals except the horse. It serves as a storage place for bile. The gallbladder may be subject to such disorders as inflammation and the formation of gallstone.
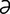 -no-kon″trak-til’
-no-kon″trak-til’ -te] contractility in response to stimulation by galvanic current.
-te] contractility in response to stimulation by galvanic current. r-dis’k
r-dis’k s] marine dinoflagellate; the main source of toxins responsible for ciguatera.
s] marine dinoflagellate; the main source of toxins responsible for ciguatera. ] small, 1 inch long, pale fish which eat mosquito larvae and are used in their control. Called also topminnows or mosquitofish.
] small, 1 inch long, pale fish which eat mosquito larvae and are used in their control. Called also topminnows or mosquitofish. -tog’
-tog’ -ne] 1. the development of merozoites into male and female gametes, which later fuse to form a zygote. 2. reproduction by means of gametes.
-ne] 1. the development of merozoites into male and female gametes, which later fuse to form a zygote. 2. reproduction by means of gametes. ] 1. the third letter of the Greek alphabet, Γ or γ. 2. used in names of chemical compounds to distinguish one of three or more isomers or to indicate the position of substituting atoms or groups.
] 1. the third letter of the Greek alphabet, Γ or γ. 2. used in names of chemical compounds to distinguish one of three or more isomers or to indicate the position of substituting atoms or groups.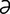 -hur“pēz-vir-i′ne] one of three subfamilies within the family Herpesviridae, comprising the following genera: Lymphocryptovirus, Macavirus, Percavirus, Rhadinovirus, and many unassigned viruses.
-hur“pēz-vir-i′ne] one of three subfamilies within the family Herpesviridae, comprising the following genera: Lymphocryptovirus, Macavirus, Percavirus, Rhadinovirus, and many unassigned viruses. -ret′ro-vi“r
-ret′ro-vi“r s] a genus of the family Retroviridae. Many species contain oncogenes and cause sarcomas and leukemias. Examples are murine leukemia virus, feline leukemia virus, feline sarcoma virus, and avian reticuloendotheliosis viruses. Many endogenous retroviruses, closely related to exogenous gammaretroviruses, are present in the DNA of mammals (including humans), birds, reptiles and amphibians.
s] a genus of the family Retroviridae. Many species contain oncogenes and cause sarcomas and leukemias. Examples are murine leukemia virus, feline leukemia virus, feline sarcoma virus, and avian reticuloendotheliosis viruses. Many endogenous retroviruses, closely related to exogenous gammaretroviruses, are present in the DNA of mammals (including humans), birds, reptiles and amphibians. -the] abnormal proliferation of the B lymphocytes resulting in abnormal concentrations of immunoglobulin production; the gammopathies include multiple myeloma, macroglobulinemia and Hodgkin’s disease. Called also gammaglobulinopathy.
-the] abnormal proliferation of the B lymphocytes resulting in abnormal concentrations of immunoglobulin production; the gammopathies include multiple myeloma, macroglobulinemia and Hodgkin’s disease. Called also gammaglobulinopathy. r] a male goose.
r] a male goose.
 -ro’m
-ro’m ] a rare benign neoplasm composed of nerve fibers and ganglion and Schwann cells. Generally, these occur in dogs, intracranially in the brain or cranial nerve ganglia, or rarely in the adrenal medulla or autonomic ganglia. See also neuroblastoma.
] a rare benign neoplasm composed of nerve fibers and ganglion and Schwann cells. Generally, these occur in dogs, intracranially in the brain or cranial nerve ganglia, or rarely in the adrenal medulla or autonomic ganglia. See also neuroblastoma. -nos’t
-nos’t -me] surgical creation of an opening into a cystic tumor on a tendon sheath or aponeurosis.
-me] surgical creation of an opening into a cystic tumor on a tendon sheath or aponeurosis. -r
-r -dik“u-li′tis] inflammation of spinal ganglia and nerve roots. Clinical signs in affected dogs include sensory deficits, ataxia, hypermetria, megaesophagus, dysphonia and Horner’s syndrome. Siberian huskies are predisposed.
-dik“u-li′tis] inflammation of spinal ganglia and nerve roots. Clinical signs in affected dogs include sensory deficits, ataxia, hypermetria, megaesophagus, dysphonia and Horner’s syndrome. Siberian huskies are predisposed.
 r] remnants of the embryonic mesonephric ducts, sometimes found on the floor of the vagina, which often open into the vestibule.
r] remnants of the embryonic mesonephric ducts, sometimes found on the floor of the vagina, which often open into the vestibule. r-of’
r-of’ -l
-l s] a genus of flies, the horse bot flies, the larvae of which develop in the gastrointestinal tract of horses and may sometimes infect humans. A member of the family Gasterophilidae.
s] a genus of flies, the horse bot flies, the larvae of which develop in the gastrointestinal tract of horses and may sometimes infect humans. A member of the family Gasterophilidae. -me] excision of the stomach (total gastrectomy) or a portion of it (partial or subtotal gastrectomy).
-me] excision of the stomach (total gastrectomy) or a portion of it (partial or subtotal gastrectomy).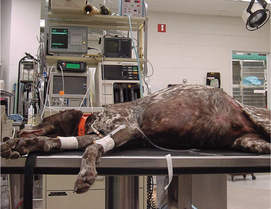
 -no’m
-no’m ] a gastrin-secreting, non-beta islet cell tumor of the pancreas, seen mainly in aged dogs and cats, associated with Zollinger–Ellison syndrome.
] a gastrin-secreting, non-beta islet cell tumor of the pancreas, seen mainly in aged dogs and cats, associated with Zollinger–Ellison syndrome.