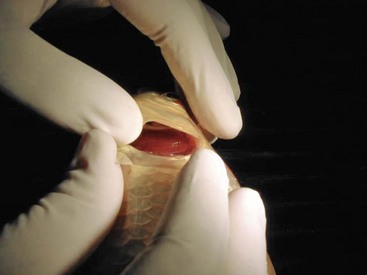
• Monogeneans typically infest the skin and gills. • Clinical signs include lethargy, decreased appetite, flashing (rubbing against objects in the pond/aquarium), and excessive production of mucus (from gills or skin). • When branchial infestations are present, respiratory signs such as increased opercular rate, piping (gasping for air at the water surface), and respiratory distress may be seen. • Dermatologic abnormalities include erythema, scale loss, white to gray irregular patches, excessive production of mucus, hemorrhages, erosions, and ulcerations. • Ophthalmic lesions such as corneal edema can be seen if the parasite affects the corneal epithelium (most commonly seen with Neobenedenia melleni). • Secondary bacterial and fungal infections may be present in areas parasitized by monogeneans. • Monogeneans of the genera Dactylogyrus and Gyrodactylus commonly affect freshwater fish. Dactylogyrus predominantly affects the gills, whereas Gyrodactylus is more commonly found on the skin. • Monogeneans affecting marine fish include the capsalids; species such as Benedenia and Neobenedenia can infest the skin and gills. • Life cycles: Monogeneans may be oviparous (egg laying) or viviparous (live bearers). Transmission of monogeneans from fish to fish occurs primarily via direct contact. Most monogeneans have direct life cycles. Oviparous monogeneans (Dactylogyridae) release eggs into the water, which hatch into a free-swimming stage (oncomiracidium) that seeks out a fish host. Viviparous monogeneans (Gyrodactylidae) release live larvae that are immediately parasitic. • Viviparous monogeneans can achieve rapid increases in population with doubling times as short as 24 hours. • The diagnostic approach to a fish with monogeneans should begin with complete history, water chemistry (temperature, salinity, pH, ammonia, nitrites, nitrates, alkalinity, dissolved oxygen), and thorough evaluation of the environment/husbandry. • Direct observation of the fish in the aquarium or pond • Complete physical examination • Definitive diagnosis can be made with wet mounts of the skin or gills.
Flukes (Monogenean Parasites)
Basic Information
![]()
Clinical Presentation
History, Chief Complaint
Physical Exam Findings
Etiology and Pathophysiology
Diagnosis
![]()
Initial Database
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Flukes (Monogenean Parasites)
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue