Chapter 175 Ferrets
Clinical Techniques
RESTRAINT
DIAGNOSTICS
Blood Collection
There are several suitable sites for blood collection in ferrets:
Indications
Other Considerations
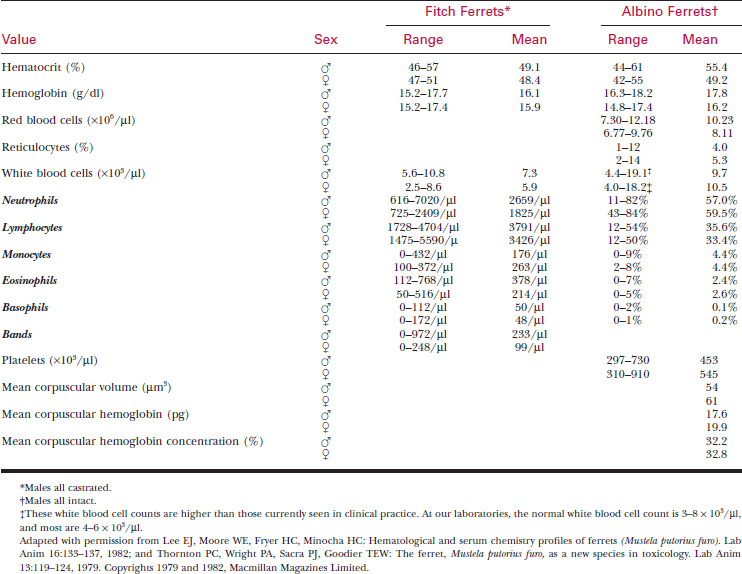
Table 175-2 REFERENCE RANGES FOR SERUM BIOCHEMISTRY VALUES IN FERRETS
| Value | Albino* | Fitch† |
|---|---|---|
| Total protein (g/dl) | 5.1–7.4 | 5.3–7.2 |
| Albumin (g/dl) | 2.6–3.8 | 3.3–4.1 |
| Glucose (mg/dl) | 94–207 | 62.5–134 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dl) | 90–125‡ | |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dl) | 10–45 | 12–43 |
| Creatinine (mg/dl) | 0.4–0.9 | 0.2–0.6 |
| Sodium (mmol/L) | 137–162 | 146–160 |
| Potassium (mmol/L) | 4.5–7.7 | 4.3–5.3 |
| Chloride (mmol/L) | 106–125 | 102–121 |
| Calcium (mg/dl) | 8.0–11.8 | 8.6–10.5 |
| Phosphorus (mg/dl) | 4.0–9.1 | 5.6–8.7 |
| Alanine aminotransferase (U/L) | 82–289 | |
| 78–149§ | ||
| Aspartate aminotransferases (U/L) | 28–120 | 57–248§ |
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/L) | 9–84 | 30–120 |
| 31–66§ | ||
| Bilirubin (mg/dl) | <1.0 | 0–0.1§ |
| Cholesterol (mg/dl) | 64–296 | 119–209§ |
| Carbon dioxide (mmol/L) | 16.5–28 | 16–28§ |
* Combined values of male (N = 40) and female (N = 24) ferrets from Thornton PC, Wright PA, Sacra PJ, Goodier TEW: The ferret, Mustela putorius furo, as a new species in toxicology. Lab Anim 13:119–124, 1979.
† Combined values of intact male, female, and castrated male ferrets (total N = 13, aged 4–8 mo) from Lee EJ, Moore WE, Fryer HC, Minocha HC: Haematological and serum chemistry profiles of ferrets (Mustela putorius furo). Lab Anim. 16:133–137, 1982, except where noted.
‡ From Brown S: Personal communication, 1995.
§ Combined values from cardiac and orbital venipuncture of male ferrets (N = 16)
from Fox JG: Normal clinical and biologic parameters. In: Fox JG (ed): Biology and Diseases of the Ferret. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger, 1988, pp 159–173.
Techniques
Cephalic Vein
Lateral Saphenous Vein
Jugular Vein
Cranial Vena Cava
Technique
Ventral Tail Artery
Technique
Diagnostic Imaging
Radiography
Bone Marrow Aspiration
Splenic Aspiration
Technique
THERAPEUTIC TECHNIQUES
Intravenous Therapy
Cephalic or Saphenous IV Catheter Placement
Technique
Jugular Catheter Placement
Intraosseous Catheter Placement
Technique
Subcutaneous and Intramuscular Injections
Fluid Therapy
Oral Therapy
Nutritional Support
Drug-Dosing Guidelines
Urinary Catheterization
Males
Females
Sedation
Doses for parenteral agents used in ferrets are listed in Table 175-3.
Table 175-3 DRUGS RECOMMENDED FOR CHEMICAL RESTRAINT AND ANALGESIA OF FERRETS
| Drug | Dosage (mg/kg) | Route |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Restraint | ||
| Acepromazine | 0.1–0.3 | IM, SC |
| Ketamine plus acepromazine* | 25–35 | IM, SC |
| 0.2–0.3 | ||
| Ketamine plus diazepam | 25–35 | IM |
| 2–3 | ||
| Ketamine plus xylazine | 10–25 | IM |
| 1–2 | ||
| Analgesics | ||
| Buprenorphene | 0.01–0.03 mg/kg q8–12h | SC, IM, IV |
| Butorphanol tartrate | 0.05–0.5 mg/kg q8–12h | SC, IM |
| Carprofen | 1 mg/kg q12–24h | PO |
| Flunixin meglumine | 0.5–2.0 mg/kg q12–24h | IM, IV |
* Use this combination for minor surgery. IM, intramuscular; SC, subcutaneous.
Anesthesia and Analgesia
Infectious Diseases of the Ferret
VIRAL DISEASES
Canine Distemper
Etiology
Clinical Signs
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prevention