F
F1 first filial generation, a term used in genetics. See also first cross.
F2 second filial generation, the progeny produced by the mating of F1 generations.
F and R force and rhythm (of pulse).
FA fluorescent antibody. See immunofluorescence.
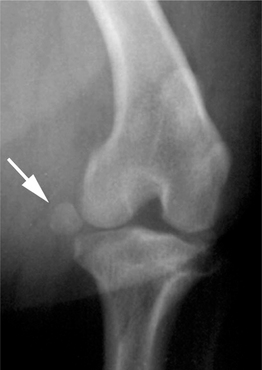
fabella [f -bel′
-bel′ ] pl. fabellae [L.] a sesamoid bone in the origin of the gastrocnemius muscle. Present in carnivores; most species have two that articulate just proximal to the femoral condyles. See Table 10.
] pl. fabellae [L.] a sesamoid bone in the origin of the gastrocnemius muscle. Present in carnivores; most species have two that articulate just proximal to the femoral condyles. See Table 10.
fabrication [fab″r -ka′sh
-ka′sh n] breaking down of a carcass of meat into consumer cuts or boned meat.
n] breaking down of a carcass of meat into consumer cuts or boned meat.
Fabricius [f -bris′e-
-bris′e- s] an Italian anatomist and surgeon. See bursa of Fabricius.
s] an Italian anatomist and surgeon. See bursa of Fabricius.
facet [fas′ t, f
t, f -set′] a small, plane surface on a hard body such as a bone.
-set′] a small, plane surface on a hard body such as a bone.
facetectomy [fas“ -tek′t
-tek′t -me] excision of the articular facet of a vertebra.
-me] excision of the articular facet of a vertebra.
facial [fa′sh l] of or pertaining to the face.
l] of or pertaining to the face.
f. fold dermatitis see fold dermatitis.
f. hyperostosis see hyperparathyroidism.
f. nerve the seventh cranial nerve; its motor fibers supply the muscles of facial expression. These are a complex group of cutaneous muscles that move the eyebrows, eyelids, ears, corners of the mouth, and other parts of the face. The sensory fibers of the facial nerve provide a sense of taste in the forward two-thirds of the tongue, and parasympathetic fibers also supply the submaxillary, sublingual and lacrimal glands for secretion. The facial and vestibulocochlear nerves arise close together at the lateral border of the trapezoid body and leave the cranium via the internal acoustic meatus. The facial nerve runs within the facial canal and leaves the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. Called also intermediofacial nerve. See also Table 14.
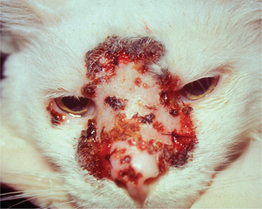
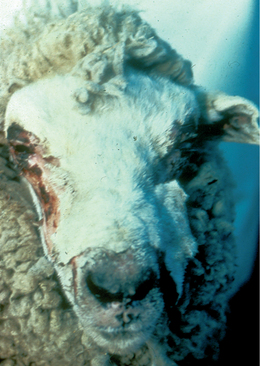
F-2: Severe ulcerative facial dermatitis.
From August JR, Consultations in Feline Internal Medicine, Volume 5. Saunders, 2005.
f. tumor disease see Tasmanian devil facial tumor disease.
facies [fa′she-ēz] facial expression.

F-4: Facial paralysis in a horse.
From Knottenbelt DC, Pascoe RR, Diseases and Disorders of the Horse. Saunders, 2003.
faci(o)- word element. [L.] face.
faciobrachial [fa″she-o-bra′ke- l] pertaining to the face and upper front limbs.
l] pertaining to the face and upper front limbs.
faciocervical [fa″she-o-sur′v -k
-k l] pertaining to the face and neck.
l] pertaining to the face and neck.
faciolingual [fa″she-o-ling′w l] pertaining to the face and tongue.
l] pertaining to the face and tongue.
facioplasty [fa′she-o-plas″te] restorative or plastic surgery of the face.
facioplegia [fa″she-o-ple′j ] see facial paralysis.
] see facial paralysis.
facteur thymique sérique (FTS) a peptide secreted by thymic epithelial cells.
factitial [fak-tish′ l] artificially produced; produced unintentionally.
l] artificially produced; produced unintentionally.
factitious [fak-tish′ s] artificial; not natural.
s] artificial; not natural.
f’s I to XIII see clotting factors and names of individual factors.
f. VIII-related antigen von Willebrand antigen.
f. IX complex a sterile, freeze-dried powder containing coagulation factors II, VII, IX and X.
f. IX deficiency plasma thromboplastin component (PTC). See also hemophilia B.
f. X deficiency see Stuart factor.
f. XI deficiency see plasma thromboplastin antecedent (PTA).
f. XII deficiency see Hageman trait.
f. analysis a statistical method for analyzing the correlations between several variables.
antinuclear f. antinuclear antibody.
f. B a complement component (C3 proactivator) that participates in the alternate complement pathway.
f. D a factor that, when activated, serves as a serine esterase in the alternate complement pathway.
extrinsic f. see extrinsic factor.
f. H see complement regulatory proteins.
intrinsic f. see intrinsic factor.
labile f. proaccelerin; one of the clotting factors.
osteoclast activating f. substance produced by lymphocytes which facilitates bone resorption.
release f. a protein that binds directly to any stop codon that reaches the A site on the ribosome.
fadge a horse gait. See foxtrot.
FADH2 reduced form of flavin adenine dinucleotide.
f. horse syndrome (1) see Arabian fading syndrome (above).
f. pig syndrome (2) see neonatal hypoglycemia.
fagopyrism [f g-op′
g-op′ -riz-
-riz- m] see Fagopyrum esculentum.
m] see Fagopyrum esculentum.
Fahrenheit [far′ n-hīt] pertaining to Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, German physicist (1686–1736).
n-hīt] pertaining to Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit, German physicist (1686–1736).
F. scale a temperature scale with the ice point at 32 degrees (32°F) and the normal boiling point of water at 212 degrees (212°F). For equivalents of Fahrenheit and Celsius temperatures, see Table 3.
FAIDS feline acquired immune deficiency syndrome. See feline leukemia virus.
failure inability to perform or to function properly.
f. of passive transfer see maternal immunity.
fairy clubs Ramaria macrofungi.
fairy grass Lachnagrostis filiformis.
falcial [fal′sh l] pertaining to a falx.
l] pertaining to a falx.
falciform [fal′s -form] sickle-shaped.
-form] sickle-shaped.
falcon a bird of prey. See Falco.
falconry the sport of hunting with trained raptors.
falcular [fal′ku-l r] see falciform.
r] see falciform.
Falculifer a genus of the family of mites Dermoglyphidae.
F. clornutus, F. rostratus feather mite of pigeons.
fall [fawl] in dog conformation, hair that hangs over the face.
fall fever [fawl] see leptospirosis.
f. to one side involuntary falling down, always to one side.
fallopian tube [f -lo′pe-
-lo′pe- n] see uterine tube. Called also oviduct.
n] see uterine tube. Called also oviduct.
Fallot’s tetralogy [f -lōz′ ] see tetralogy of Fallot.
-lōz′ ] see tetralogy of Fallot.
fallow a pale cream, light fawn, or pale yellow coat color in dogs.
f. blusher see Amanita pantherina—a mushroom.
falsification [fawl″s -f
-f -ka′sh
-ka′sh n] a deliberate misstatement or misrepresentation.
n] a deliberate misstatement or misrepresentation.
falx [falks] pl. falces [L.] a sickle-shaped structure.
f. cerebelli the fold of dura mater separating the cerebellar hemispheres.
f. cluster see familial aggregations (above).
famotidine [fam-o′t -dīn] a histamine H2-receptor antagonist, similar to cimetidine.
-dīn] a histamine H2-receptor antagonist, similar to cimetidine.
famphur an organophosphorus insecticide used in cattle, sheep and goats. Called also famophos.
fang [fang] 1. a sharp or pointed tooth. See also fighting teeth. 2. a root of a tooth.
Fannia [fan′e- ] a genus of flies in the family Muscidae that pupate in feces.
] a genus of flies in the family Muscidae that pupate in feces.
F. australis may cause tertiary blowfly strike.
F. benjamini cause insect worry.
F. canicularis, F. scalaris may cause urogenital myiasis.
fanweed [fan′wēd] see Thlaspi arvense.
FAO Food and Agriculture Organization.
FARAD Farm Animal Residue Avoidance Database.
farad (F) the unit of electric capacity; capacity to hold 1 coulomb with a potential of 1 volt.
faradic currents [f -rad′ik] see faradism.
-rad′ik] see faradism.
farcin-de-boeuf see bovine farcy.
farcy [fahr′se] the skin form of glanders. Called also glanders.
f. buds cutaneous nodules seen in equine glanders.
f. cords see farcy pipes (below).
Japanese f. epizootic lymphangitis.
Neapolitan f. see epizootic lymphangitis.
FARM Farm Animal Reform Movement.
farm [fahrm] agricultural enterprise based on land use.
dry f. a farm dependent on rainfall as its water resource—no irrigation is available.
irrigation f. a farm with a significant part of its area under irrigation.
pasture f. a farm whose principal resource is pasture for grazing animals.
f. visits see veterinary farm visits.
farriery the techniques used by a farrier. Part of the occupation of blacksmith.
f. fever see mastitis–metritis–agalactia.
f. house a specialist accommodation unit devoted to the care of sows at farrowing.
induced f. hormonal initiation of parturition before full term, usually with a prostaglandin.
f. rate the number of sows that farrow divided by the number mated.
aponeurotic f. any broad, sheet-like tendon; see aponeurosis.
crural f. the investing fascia of the leg.
iliac f. covers the iliopsoas muscle below the wing of the ilium.
thyrolaryngeal f. the fascia covering the thyroid gland and attached to the cricoid cartilage.
transverse f. that between the transversalis muscle and the peritoneum.
fascial sling [fash′e- l] see colposuspension.
l] see colposuspension.
fascicle [fas′ -k
-k l] a small bundle or cluster, especially of nerve, muscle, or tendon fibers.
l] a small bundle or cluster, especially of nerve, muscle, or tendon fibers.
fasciculated [f -sik′u-lāt-
-sik′u-lāt- d] clustered together or occurring in bundles, or fasciculi.
d] clustered together or occurring in bundles, or fasciculi.
fasciculus [f -sik′u-l
-sik′u-l s] pl. fasciculi [L.] fascicle.
s] pl. fasciculi [L.] fascicle.
f. atrioventricularis see atrioventricular bundle of His.
f. lenticularis a nerve bundle that connects the pallidum with the cerebrum and the brainstem.
fasciectomy [fas″e-ek′t -me] excision of fascia.
-me] excision of fascia.
fasciitis [fas″e-i′tis] inflammation of a fascia.
nodular f., proliferative f. see nodular granulomatous episcleritis.
pseudosarcomatous f. see nodular granulomatous episcleritis.
fasciodesis [fas″e-od′ -sis] suture of a fascia to skeletal attachment.
-sis] suture of a fascia to skeletal attachment.
Fasciola [f -si′o-l
-si′o-l ] a genus of flukes (digenetic trematode) in the family Fasciolidae.
] a genus of flukes (digenetic trematode) in the family Fasciolidae.
F. jacksoni found in elephants. Causes a disease similar to ovine fascioliasis.
fasciola [f -si′o-l
-si′o-l ] pl. fasciolae [L.] 1. a small band or striplike structure. 2. a small bandage.
] pl. fasciolae [L.] 1. a small band or striplike structure. 2. a small bandage.
fasciolicidal [fas″e-o-l -sī′d
-sī′d l] lethal for Fasciola spp.
l] lethal for Fasciola spp.
fasciolicide [fas″e-o′l -sīd] fasciolicidal.
-sīd] fasciolicidal.
Fascioloides [fas″e-o-loi′dēz] a genus of flukes (digenetic trematode) of the family Fasciolidae.
Fasciolopsis [fas″e-o-lop′sis] a genus of trematodes of the family Fasciolidae.
fascioplasty [fash′e-o-plas″te] plastic repair of a fascia.
fasciorrhaphy [fash″e-or′ -fe] repair of a lacerated fascia.
-fe] repair of a lacerated fascia.
fasciotomy [fash″e-ot′ -me] incision of a fascia.
-me] incision of a fascia.
boiling (burning) f. see acrolein poisoning.
f. embolism lesion created by a fat embolus.
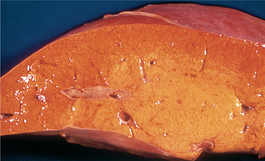
F-10: Fatty liver in fat cow syndrome.
From Blowey RW, Weaver AD, Diseases and Disorders of Cattle. Mosby, 1997.
leaf f. the best edible fat from a pig carcass, from under the peritoneum.
orbital f. fat located between the eye and the orbit; provides shock-absorbent surroundings.
soft f. unpleasant soft fat occurs in pigs fed for too long on kitchen swill.
toxic f. syndrome see chicken edema disease.
fat-granule cell see gitter cells.
fatal [fa′t l] causing death; deadly; mortal; lethal.
l] causing death; deadly; mortal; lethal.
fatality rate see case fatality rate.
fatigability [fat“ -g
-g -bil′
-bil′ -te] easy susceptibility to fatigue.
-te] easy susceptibility to fatigue.
fatty [fat′e] pertaining to or characterized by fat. See also adipose.
f. change deposition of greater than normal amounts of fat in a tissue.
f. tissue connective tissue made of fat cells in a meshwork of areolar tissue.
free f. a’s. see non-esterfied fatty acids (below).
fauces [faw′sēz] the passage from the mouth to the pharynx, the throat.
faucitis [faw-si′tis] inflammation of the fauces.
faveira plant poisoning caused by Dimorphandra mollis.
faveolate [fa-ve′o-lāt] honeycombed; alveolate.
faveolus [fa-ve′o-l s] see foveola.
s] see foveola.
FAWC Farm Animal Welfare Council.
fawn [fawn] young of the small deer species. See also Table 16.
fawn Irish setter syndrome see color dilution alopecia.
FAZD Center National Center for Foreign Animal and Zoonotic Disease Defense.
FCA Freund’s complete adjuvant.
FCI Fédération Cynologique Internationale (World Canine Organisation).
FD fatal (lethal) dose; focal distance.
FDA Food and Drug Administration.
FDP fibrin(ogen) degradation products.
FECa fractional excretion of calcium.
FEK fractional excretion of potassium.
FENa fractional excretion of sodium.
FEP fractional excretion of phosphorus.
FEurea fractional excretion of urea.
Fe chemical symbol, iron (L. ferrum).
f. clipping clipping the flight feathers will prevent flight for several months.
f. coat the total feather covering of a bird. Called also ptilosis.
f. cushion the plumage from the pelvic tract of the hen, forming the back cover.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
 -sil“
-sil“ -ta′sh
-ta′sh n] hastening or assistance of a natural process; the increased excitability of a neuron after stimulation by a subthreshold presynaptic impulse. The resistance is diminished so that second application of the stimulus evokes the reaction more easily.
n] hastening or assistance of a natural process; the increased excitability of a neuron after stimulation by a subthreshold presynaptic impulse. The resistance is diminished so that second application of the stimulus evokes the reaction more easily. -sil′
-sil′ -ta″tiv] in pharmacology, denoting a reaction arising as an indirect result of drug action, such as development of an infection after the normal microflora has been altered by an antibiotic.
-ta″tiv] in pharmacology, denoting a reaction arising as an indirect result of drug action, such as development of an infection after the normal microflora has been altered by an antibiotic. r] 1. an agent or element that contributes to the production of a result. In epidemiology and statistics called also a variable because the factor may have a number of values. In an experiment a factor is a type of treatment and in the experiment the factor will be represented in different groups by different values. Such a factor may originate spontaneously or be introduced by an investigator. 2. see clotting factors.
r] 1. an agent or element that contributes to the production of a result. In epidemiology and statistics called also a variable because the factor may have a number of values. In an experiment a factor is a type of treatment and in the experiment the factor will be represented in different groups by different values. Such a factor may originate spontaneously or be introduced by an investigator. 2. see clotting factors. l-ta″tiv] not obligatory; pertaining to or characterized by the ability to adjust to particular circumstances or to assume a particular role. See also accumulator plants.
l-ta″tiv] not obligatory; pertaining to or characterized by the ability to adjust to particular circumstances or to assume a particular role. See also accumulator plants. l-te] 1. a normal power or function, especially of the human mind. 2. the teaching staff and the facilities of an institute of learning, especially a university department.
l-te] 1. a normal power or function, especially of the human mind. 2. the teaching staff and the facilities of an institute of learning, especially a university department.
 m] a plant of the Polygonaceae family; contains fagopyrin which causes primary photosensitization. Called also F. sagittatum, F. syggitum, Polygonum sagittatum, buckwheat.
m] a plant of the Polygonaceae family; contains fagopyrin which causes primary photosensitization. Called also F. sagittatum, F. syggitum, Polygonum sagittatum, buckwheat.
 -tiv] when the result of a test in a patient is negative when the disease or condition which is the subject of the search is present.
-tiv] when the result of a test in a patient is negative when the disease or condition which is the subject of the search is present. -tiv] 1. denoting a test result that wrongly assigns a patient to a diagnostic or other category. 2. a patient so categorized. 3. an instance of a false-positive result.
-tiv] 1. denoting a test result that wrongly assigns a patient to a diagnostic or other category. 2. a patient so categorized. 3. an instance of a false-positive result. -mil′e-
-mil′e- l] occurring in or affecting members of a closely related group of animals more than would be expected by chance.
l] occurring in or affecting members of a closely related group of animals more than would be expected by chance. -le] 1. a group of animals related by blood or their inheritance. 2. a taxonomic category below an order and above a genus.
-le] 1. a group of animals related by blood or their inheritance. 2. a taxonomic category below an order and above a genus. -boof′] a hand- and finger-held surgical instrument with flat blades, one each end, designed for holding back tissues in deep cavities.
-boof′] a hand- and finger-held surgical instrument with flat blades, one each end, designed for holding back tissues in deep cavities. -diz-
-diz- m] a method of passive exercise which can be applied locally to stimulate nerves and muscles. The faradic current applied can be varied as to pulse, wave form, voltage and location.
m] a method of passive exercise which can be applied locally to stimulate nerves and muscles. The faradic current applied can be varied as to pulse, wave form, voltage and location. ] pl. fasciae [L.] a sheet or band of fibrous tissue such as lies deep to the skin or invests muscles and various body organs.
] pl. fasciae [L.] a sheet or band of fibrous tissue such as lies deep to the skin or invests muscles and various body organs.
 -sik′u-l
-sik′u-l r] clustered together; pertaining to or arranged in bundles or clusters; pertaining to a fascicle.
r] clustered together; pertaining to or arranged in bundles or clusters; pertaining to a fascicle. -sik″u-la′sh
-sik″u-la′sh n] 1. the formation of fascicles. 2. a small local involuntary muscular contraction visible under the skin, representing spontaneous discharge of a number of fibers innervated by a single motor nerve filament.
n] 1. the formation of fascicles. 2. a small local involuntary muscular contraction visible under the skin, representing spontaneous discharge of a number of fibers innervated by a single motor nerve filament.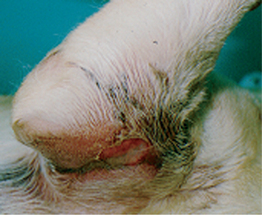
 -sis] the disease caused by infestation with fasciola. Called also distomatosis, distomiasis.
-sis] the disease caused by infestation with fasciola. Called also distomatosis, distomiasis. -sis] infection with Fasciolopsis spp. Principally a disease of humans manifested by intestinal inflammation and ulceration.
-sis] infection with Fasciolopsis spp. Principally a disease of humans manifested by intestinal inflammation and ulceration.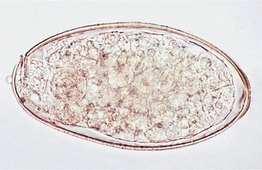
 m] [L.] 1. the highest point in the roof of the fourth ventricle of the brain. 2. the acme, or highest point. For example in fever: the high point of constant temperature between the increment and the decrement.
m] [L.] 1. the highest point in the roof of the fourth ventricle of the brain. 2. the acme, or highest point. For example in fever: the high point of constant temperature between the increment and the decrement. -tēg′] a state of increased discomfort and decreased efficiency resulting from prolonged exertion; a generalized feeling of tiredness or exhaustion; loss of power or capacity to respond to stimulation. Fatigue is a normal reaction to intense physical exertion, emotional strain or lack of rest. Fatigue that is not relieved by rest may have a more serious origin. It may be a sign of generally poor physical condition or of specific disease.
-tēg′] a state of increased discomfort and decreased efficiency resulting from prolonged exertion; a generalized feeling of tiredness or exhaustion; loss of power or capacity to respond to stimulation. Fatigue is a normal reaction to intense physical exertion, emotional strain or lack of rest. Fatigue that is not relieved by rest may have a more serious origin. It may be a sign of generally poor physical condition or of specific disease. s] a disease of fowls caused by Microsporumgallinae. Small white patches appear on the comb, then coalesce and thicken. If lesions spread to feathered parts typical favus shield-like scabs are formed. In long-standing cases scabs on the skin of the neck may be packed close together and, with their depressed centers, give a honeycomb appearance, hence the name honeycomb ringworm.
s] a disease of fowls caused by Microsporumgallinae. Small white patches appear on the comb, then coalesce and thicken. If lesions spread to feathered parts typical favus shield-like scabs are formed. In long-standing cases scabs on the skin of the neck may be packed close together and, with their depressed centers, give a honeycomb appearance, hence the name honeycomb ringworm.