Figure 60.2 Complete extension of the penis and prepuce from the sheath in an alpaca. The glans penis and cartilaginous process (open yellow arrow), prepuce (solid orange arrow), fornix (preputial attachment to the penis; solid orange triangle), prepuce (open black arrow), preputial orifice (solid black arrow), and sheath (solid black triangle) are seen. A polyurethane catheter is in place to demonstrate the location of the urethral opening.
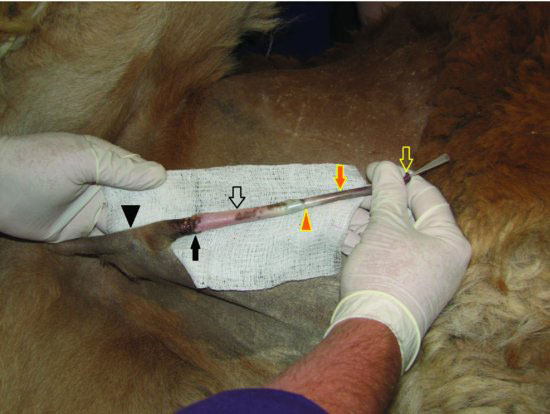
Camelids have a fibrovascular penis that is retained within the sheath by the retractor penis muscles (Figure 60.3). This is accomplished by the formation of a sigmoid flexure when the nonengorged penis is retracted. The urethra courses along the ventral margin of the penis and can be identified by careful palpation of a groove, or depression, in the fibrous sheath of the corpus spongiosum penis. The tip of the free end of the penis includes the glans penis and a cartilaginous projection (Figure 60.4). This cartilaginous projection has a spiral curve to it, and the urethral opening is found on the tip of the glans penis close to the base of this cartilage (Figure 60.5). The prepuce is attached to the penis at the fornix.
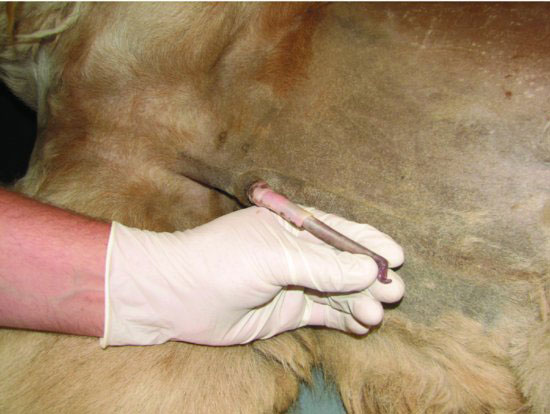
Figure 60.3 The fibrovascular penis is flaccid when not engorged and tightly erect during engorgement for breeding.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


