Ergot-Related Toxicosis
Basic Information 
Definition
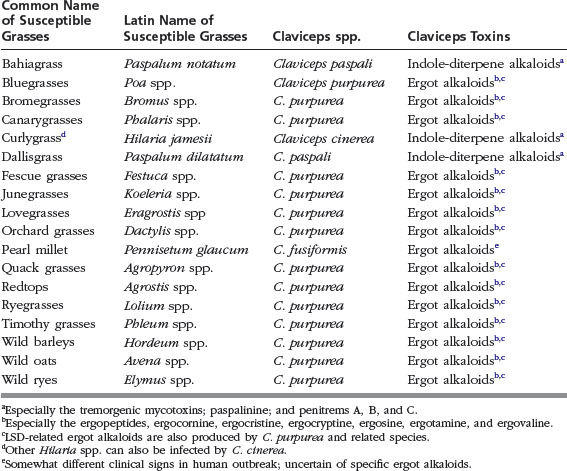
Claviceps fungi (“ergot”) produce a variety of toxins that can adversely affect the reproductive, circulatory, nervous, and musculoskeletal systems of horses. Claviceps fungi are visible as sclerotia or ergot bodies on susceptible grasses (Table 1) and small cereal grains such as wheat, barley, and oats (but not corn).
Synonyms
Epidemiology
Species, Age, Sex
• Except for agalactia and pregnancy abnormalities, horses are much less susceptible to ergotism than are cattle.
• The species and age of exposed horses may influence the amount of toxin ingested.
• Aged animals, especially mares, may have concurrent disease that is exacerbated by toxin exposure.
• Age influences the likelihood of mares cycling or becoming pregnant.
• Mares are particularly susceptible to the reproductive effects of ergopeptine alkaloids.
Risk Factors
• Claviceps ergopeptine alkaloids:
 Subacute to chronic consumption of the seed head stage of susceptible grasses or ergotized small grains or grass seed
Subacute to chronic consumption of the seed head stage of susceptible grasses or ergotized small grains or grass seed Concurrent exposure to endophyte-infected tall fescue (see “Fescue-Related Toxicosis” in this section)
Concurrent exposure to endophyte-infected tall fescue (see “Fescue-Related Toxicosis” in this section)• Claviceps indole-diterpene tremorgenic mycotoxins
 Several days’ consumption of ergotized Dallisgrass (Paspalum dilatatum) or Bahiagrass (Paspalum notatum) in pasture or hay
Several days’ consumption of ergotized Dallisgrass (Paspalum dilatatum) or Bahiagrass (Paspalum notatum) in pasture or hay Concurrent exposure to endophyte (Neotyphodium lolii)-infected perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) hay or pasture or other tremorgenic mycotoxins
Concurrent exposure to endophyte (Neotyphodium lolii)-infected perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne) hay or pasture or other tremorgenic mycotoxinsGeography and Seasonality
• Claviceps ergopeptine alkaloids
 Seen worldwide, but predisposing weather conditions are common in the northern Great Plains and Pacific Northwest regions of North America (more sporadically in Midwestern and Atlantic coastal regions of the United States)
Seen worldwide, but predisposing weather conditions are common in the northern Great Plains and Pacific Northwest regions of North America (more sporadically in Midwestern and Atlantic coastal regions of the United States)• Claviceps indole-diterpene tremorgenic mycotoxins
 Southeastern United States, Central and South America, parts of Europe, Africa, Australia, and New Zealand
Southeastern United States, Central and South America, parts of Europe, Africa, Australia, and New ZealandClinical Presentation
Disease Forms/Subtypes
• C. purpurea ergopeptine alkaloids
 Hyperthermic ergotism: Less common in horses; observed at higher toxin doses than reproductive ergotism
Hyperthermic ergotism: Less common in horses; observed at higher toxin doses than reproductive ergotism Gangrenous or cutaneous ergotism: Less common in horses; observed at higher toxin doses than reproductive ergotism
Gangrenous or cutaneous ergotism: Less common in horses; observed at higher toxin doses than reproductive ergotism• C. purpurea LSD-like ergot alkaloids, especially C. paspali indole-diterpene tremorgenic mycotoxins: Nervous or convulsive ergotism
History, Chief Complaint
• Generally, multiple animals are affected in instances of ergotism.
• Reproductive ergotism (indistinguishable from most common form of equine fescue toxicosis)
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree