Chapter 144 Electrocardiography
Electrocardiography is the graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart with time displayed on the x-axis and voltage displayed on the y-axis. Electrocardiograms (ECGs) are easy to perform and readily available to practicing veterinarians. There are numerous indications for performing ECGs, and the examination provides information that is useful and often pivotal to the diagnosis and management of cardiac and systemic disturbances. Veterinarians or their technicians can perform and interpret their own ECGs or utilize readily available fax, transtelephonic, or computer consultation services.
GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY
Indications for Performing Electrocardiography
Technique for Recording an Electrocardiogram
Table 144-1 ELECTRODE PLACEMENT
| Chest Lead | Placement of the V Lead |
|---|---|
| CV5RL (rV2) | Fifth intercostal space on the right side near the sternum |
| CV6LL (V2) | Sixth intercostal space on the left side near the sternum |
| CV6LU (V4) | Sixth intercostal space on the left side at the costochondral junction |
| V10 | Over the dorsal spine of the seventh thoracic vertebra |
Normal Cardiac Conduction
The ECG records the electrical activity of the heart. Electrical impulses originate in specialized pacemaker tissue in the sinus node of the right atrium. The impulse rapidly traverses the atrium, causing atrial contraction, and then slows as it passes through the atrioventricular (AV) node located at the proximal portion of the interventricular septum. Electrical activity then rapidly passes through the bundle of His, the anterior and posterior branches of the left bundle branch, the right bundle branch, and the terminal Purkinje fibers. This causes activation of the interventricular septum and the left and right ventricular myocardium (Fig. 144-1).
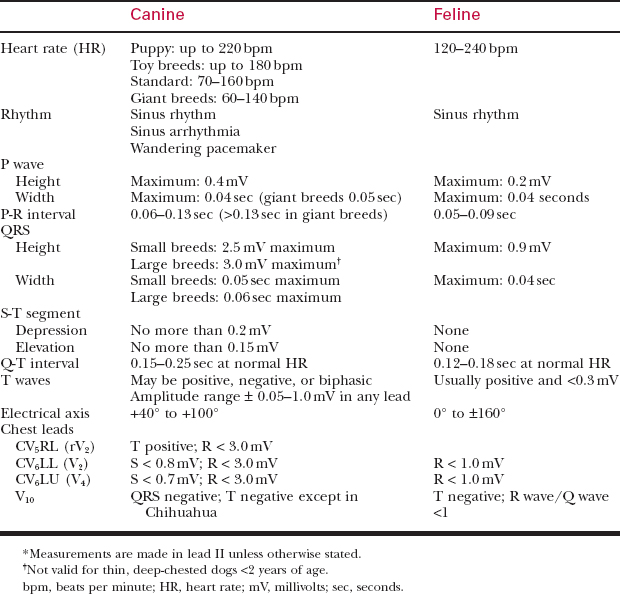
Components of the Electrocardiographic Tracing (Fig. 144-2)
How to Evaluate the Electrocardiogram
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHIC ABNORMALITIES
Electrocardiographic abnormalities can be divided into those involving heart rate and rhythm and those involving the configuration of the complexes. This chapter discusses abnormalities involving the ECG complexes. Arrhythmias are discussed in more detail in Chapter 145.