EHRLICHIOSIS
Ehrlichiosis is a group of tick-borne diseases that attack white blood cells. It is a seasonal disease that corresponds to the months when ticks are active. In dogs the disease is also known as tracker dog disease, canine hemorrhagic fever, or canine typhus.
TRANSMISSION
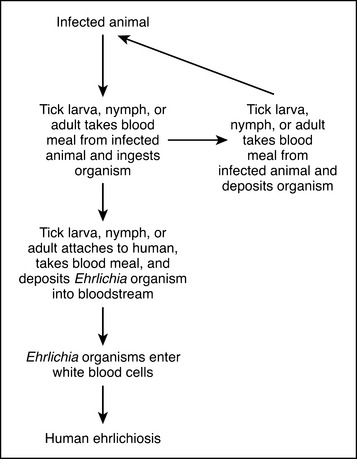
Ixodid (hard) ticks are vectors for ehrlichiosis. The Lone Star tick is the primary vector for E. chaffeensis and E. ewingii. A. phagocytophilum is transmitted by black-legged ticks. The vector for N. sennetsu is unknown. The organisms are transmitted from host to host by tick feedings. Ticks at all stages of the tick life cycle (Appendix 1) can become infected when they feed on an infected host (Figure 15).