E
e- for words beginning thus, see also those beginning oe-.
η eta, small letter; seventh letter in the Greek alphabet.
EAE 1. experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. 2. enzootic abortion of ewes.
EAEC enteroaggregative or enteroadherent Escherichia coli.
EAN experimental allergic neuritis.
e. alopecia see pinnal alopecia.
bat e. an erect, broad-based ear in some dogs, especially the French bulldog and Welsh corgi.
bear e. one with a very rounded tip.
break in e. the fold line in the semi-dropped ear of dogs.
e. cartilage see auricular cartilage.
e. chewing a vice of confined pigs due largely to boredom and overcrowding.
e. hematoma see auricular hematoma.
e. mange see psoroptic mange, Otodectescynotis, Raillietia.
e. notch see ear mark (above).
e. points see auricular points.
e. resection see lateral ear resection, vertical ear canal resection.
e. rigid ear pricked and patient unable to move them; indicative of general skeletal muscle tetany.
spinose e. tick see Otobiusmegnini.
e. tooth see ear cyst (above).
eardrum [ēr′dr m] see tympanic membrane.
m] see tympanic membrane.
earsore [ēr′sor] dermatitis around the ear of water buffalo caused by Stephanofilaria zaheeri.
infusorial e. see diatomaceous earth (above).
siliceous e. see diatomaceous earth (above).
earth-eating most commonly associated with nutritional deficiency of sodium chloride. See also pica.
East African swine fever see African swine fever.
East Friesian, East Friesland marsh-type dairy sheep, polled, with a woolless rat-tail.
east-west front in dog conformation, front feet turned outwards.
Easter lily see Lilium longiflorum.
Eastern equine encephalitis see Eastern equine encephalomyelitis.
easy keeper an animal of any species that grows or fattens on a smaller intake than average.
eating [ēt′ing] combined prehension, mastication and swallowing.
e. disorders see anorexia, regurgitation, quidding, dysphagia, polyphagia, pica.
EBHS European brown hare syndrome.
Ebner named after Victor von Ebner (1842–1925), Australian anatomist and histologist.
E’s lines incremental lines in the dentin of normal teeth.
Ebola virus [eb′o-l ] see Filoviridae.
] see Filoviridae.
ecaudate [e-kaw′dāt] tailless.
ecbolic [ek-bol′ik] oxytocic; promotes myometrial contractions.
ecchymoma [ek- -mo’m
-mo’m ] swelling due to blood extravasation.
] swelling due to blood extravasation.
ecchymotic hemorrhage [ek-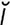 -mot’ik] see ecchymosis.
-mot’ik] see ecchymosis.
e. tumors adenomas and adenocarcinomas occur rarely.
eccritic 1. promoting excretion. 2. an agent that promotes excretion.
ECF 1. extracellular fluid. 2. early conception factor
ECF-A eosinophil chemotactic factor of anaphylaxis.
ECG electrocardiogram. Called also EKG.
echimidine one of the toxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids in Echium plantagineum.
echinatine a toxic alkaloid in Cynoglossum officinale.
echinococcosis [e-ki″no-kok-o’sis] an infection of humans and animals, usually of the liver or lungs, caused by the larval stage (hydatid cysts) of tapeworms of the genus Echinococcus, marked by the development of expanding cysts. See also hydatid disease. A disease notifiable to the OIE (see Table 22).
Echinococcus [e-ki″no-kok’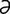 s] a genus of small tapeworms of the family Taeniidae.
s] a genus of small tapeworms of the family Taeniidae.
E. oligarthus occurs in wild cats with larval stages in rodents.
E. vogeli occurs in domestic and wild dogs with intermediate stages in rodents and humans.
Echinoparyphium a genus of the fluke family Echinostomatidae.
E. paraulum see Echinostomarevolutum.
Echinophthirius horridus sucking lice of seals; cause pruritus and self-injury.
E. iliocanum found in the intestine of dogs, rodents and humans and may cause enteritis.
Echinostomatidae [ek″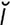 -no-sto-mat’
-no-sto-mat’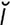 de] a family of flukes (digenetic trematodes) found in birds.
de] a family of flukes (digenetic trematodes) found in birds.
echinulate [e-kin’u-lāt] having small spikes or prickles.
echiumidine one of the hepatoxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids in Echium plantagineum.
echo [ek’o] a reflected sound; the basis for echocardiography and ultrasonography.
echocardiogram [ek″o-kahr’de-o-gram″] the record produced by echocardiography.
echocontrast agents [ek″o-kon’trast] see contrast echocardiography.
echoencephalogram [ek″o-en-sef’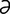 -lo-gram] the record produced by echoencephalography.
-lo-gram] the record produced by echoencephalography.
echogram [ek’o-gram] the record made by echography.
Eck’s fistula [ek] an artificial communication made between the portal vein and the vena cava.
bitch e. see puerperal tetany.
guinea pig e. see pregnancy toxemia (3) and ketosis.
mare e. see lactation tetany (2).
puerperal e. see puerperal tetany.
eclamptogenic [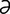 -klamp″to-jen’ik] causing eclampsia.
-klamp″to-jen’ik] causing eclampsia.
ecological emanating from or pertaining to ecology.
e. fallacy bias following misinterpretation that ecological factors affect all individuals equally.
e. interface the border between two ecosystems.
e. mosaic a pattern of interspersed ecosystems.
ecologist [e-kol’o-jist] a person skilled in ecology.
EcoR1 EcoR1 restriction endonuclease.
ecotype [e’ko-tīp] a breed or race within a species adapted to a specific environment.
ECSU extracorporeal circulatory support unit.
ECT electroconvulsive therapy.
ectasia [ek-ta’zh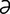 ] expansion, dilatation or distention.
] expansion, dilatation or distention.
ectasis [ek’t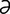 -sis] see ectasia.
-sis] see ectasia.
-ectasis suffix meaning expansion.
ectental [ek-ten’t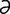 l] pertaining to the ectoderm and endoderm, and to their line of junction.
l] pertaining to the ectoderm and endoderm, and to their line of junction.
ecthyma [ek-thi’m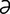 ] a shallowly eruptive form of impetigo.
] a shallowly eruptive form of impetigo.
ect(o)- word element. [Gr.] external, outside.
ectoblast [ek’to-blast] the ectoderm.
ectocardia [ek″to-kahr’de-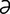 ] congenital displacement of the heart; exocardia.
] congenital displacement of the heart; exocardia.
ectocervix [ek″to-sur’viks] the vaginal part of the cervix. Called also portio vaginalis.
ectodermal [ek″to-dur’m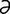 l] pertaining to the ectoderm.
l] pertaining to the ectoderm.
ectoentad [ek″to-en’tad] from without inward.
ectoenzyme [ek″to-en’zīm] an extracellular enzyme.
ectogenous [ek-toj’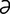 -n
-n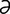 s] originating outside the organism.
s] originating outside the organism.
ectoglobular [ek″to-glob’u-l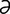 r] formed outside the blood cells.
r] formed outside the blood cells.
ectomere [ek’to-mēr] one of the blastomeres taking part in formation of the ectoderm.
-ectomy word element. [Gr.] excision, surgical removal.
ectoparasite [ek″to-par’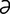 -sīt] a parasite living on the surface of the host’s body.
-sīt] a parasite living on the surface of the host’s body.
ectophyte [ek’to-fīt] a plant parasite living on the surface of the host’s body.
ectopia [ek-to’pe-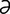 ] [L.] ectopy displacement or malposition, especially if congenital.
] [L.] ectopy displacement or malposition, especially if congenital.
e. cordis congenital displacement of the heart outside the thoracic cavity.
e. kidney usually an unascended kidney.
E-10: Ectropion of the lower eyelid (and unrelated immature cataract) in an 8-year-old Saint Bernard.
From Dziezyc J, Millchamp N, Color Atlas of Canine and Feline Ophthalmology. Saunders, 2004.
ectosteal [ek-tos’te- l] pertaining to or situated on the outside of a bone. See also periosteal.
l] pertaining to or situated on the outside of a bone. See also periosteal.
ectozoon [ek″to-zo’on] ectoparasite.
ectr(o)- word element. [Gr.] miscarriage, congenital absence.
ectrodactyly [ek″tro-dak’t -le] see ectrodactylia.
-le] see ectrodactylia.
ectrogeny [ek-troj’ -ne] congenital absence or defect of a part.
-ne] congenital absence or defect of a part.
ectromelus [ek-trom’ -l
-l s] exhibiting ectromelia.
s] exhibiting ectromelia.
ectropion [ek-tro’pe-on] eversion or turning outward, as of the margin of an eyelid.
cicatricial e. caused by contraction of scar tissue following injury or surgery to the eyelid.
miliary e. see feline miliary dermatitis.
moist e. see acute moist dermatitis.
nasal e. see solar dermatitis. Called also Collie nose.
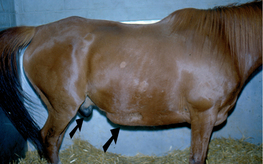
E-12: Dependant edema in the subcutaneous tissues of the ventral abdomen and in the prepuce of a horse.
summer e. see equine allergic dermatitis.
watery e. exudative epidermitis.
eczematoid [ek-zem’ -toid] resembling eczema.
-toid] resembling eczema.
eczematous [ek-zem’ -t
-t s] characterized by or of the nature of eczema.
s] characterized by or of the nature of eczema.
ED50 median effective dose; 50% effective dose.
EDB ethylene dibromide; a grain fumigant toxic to chickens.
angioneurotic e. see angioedema.
cerebral e. see cerebral edema.
dependent e. edema affecting most severely the lowermost parts of the body.
gravitational e. see dependent edema (above).
gut e. see edema disease (above).

E-13: Edema disease. Recumbent depressed pig showing edema of eyelid and forehead. Courtesy of JT Done.
laryngeal e. see laryngeal edema.
vasogenic e. see vasogenic cerebral edema.
edematogenic [ -dem″
-dem″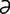 -to-jen’ik] producing or causing edema.
-to-jen’ik] producing or causing edema.
edentate [e-den’tāt] an animal without teeth, e.g. giant anteater.
edentia [e-den’sh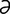 ] absence of the teeth.
] absence of the teeth.
edentulous [e-den’tu-l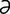 s] without teeth.
s] without teeth.
edetic acid [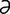 -det’ik] ethylenediamine tetra-acetic acid (EDTA).
-det’ik] ethylenediamine tetra-acetic acid (EDTA).
EDIM epizootic diarrhea of infant mice. See murine epizootic
Edles Warmblut horse German light horse.
EDRF endothelium-derived relaxing factor.
EDTA ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. See edetate.
Ca-EDTA calcium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. See edetate.
Edwards medium [ed’w rdz] agar medium selective for streptococci, which show esculin hydrolysis.
rdz] agar medium selective for streptococci, which show esculin hydrolysis.
E. ictaluri causes enteric septicemia in catfish.
EEE Eastern equine encephalomyelitis.
EENT eye–ear–nose–throat; see otolaryngology.
ef- prefix meaning away from or outward.
Coolidge e. the stimulation of sexual behavior in a male animal upon exposure to a new female.
cumulative e. cumulation action.
direct e. the effect of one variable on another without passing through a third variable.
pressure e. the sum of the changes that are due to obstruction of tissue drainage by pressure.
effective [ -fek’tiv] exerting a measurable effect.
-fek’tiv] exerting a measurable effect.
e. cell cell in the immune system that mediates an immune function.
effemination [ -fem″
-fem″ -na’sh
-na’sh n] feminization.
n] feminization.
e. arterioles see efferent arteriole.
γ e’s small nerves supplying intrafusal muscle fibers.
efficacy [ef’ -k
-k -se] intrinsic activity; is equal to the magnitude of the maximal response.
-se] intrinsic activity; is equal to the magnitude of the maximal response.
efflorescence [ef″lo-res’ ns] 1. the quality of being efflorescent. 2. a rash or eruption.
ns] 1. the quality of being efflorescent. 2. a rash or eruption.
efflorescent [ef″lo-res’ nt] becoming powdery by losing the water of crystallization.
nt] becoming powdery by losing the water of crystallization.
anagen e. see anagen defluxion.
EGD esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
egesta [e-jes’t ] undigested material discharged from the body.
] undigested material discharged from the body.
grader e. a reject from those destined for household use; used in petfood manufacture.
e. peritonitis see egg peritonitis.
e. retention see egg bound (above).
eggplant [eg’plant] Solanummelongena.
egophony [e-gof’o-ne] egobronchophony.
EHD epizootic hemorrhagic disease.
EHDV epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus.
EHEC enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli.

E-15: Ehlers-Danlos syndrome in a 5-monthold Weimaraner showing the characteristic skin elasticity.
From Medleau L, Hnilica KA, Small Animal Dermatology, 2nd Edition. Saunders, 2006.
 l] raptor bird of the family Accipitridae. Although there is variation between species, they are generally large powerful birds with very good vision, a hooked beak and powerful talons making them formidable predators. Includes the harpy eagle (Harpia harpyja), golden eagle (Aquila chrysaetos), tawny eagle (Aquila rapax) and bald eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus).
l] raptor bird of the family Accipitridae. Although there is variation between species, they are generally large powerful birds with very good vision, a hooked beak and powerful talons making them formidable predators. Includes the harpy eagle (Harpia harpyja), golden eagle (Aquila chrysaetos), tawny eagle (Aquila rapax) and bald eagle (Haliaeetus leucocephalus).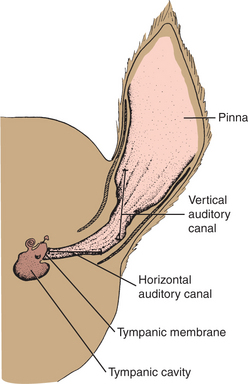


 rth] 1. soil; softer part of the land, as distinct from rock. 2. metallic oxides in the form of unchangeable powder.
rth] 1. soil; softer part of the land, as distinct from rock. 2. metallic oxides in the form of unchangeable powder. rth′ing] the safety device of connecting an electrical system in a building to the earth, especially in a milking shed. Failure of the connection causes electrification of parts of the building. This may cause poor milk letdown, restlessness, convulsions or sudden death depending on the strength of the current and the completeness of the animals’ contact with the floor. See also electrocution, free electricity.
rth′ing] the safety device of connecting an electrical system in a building to the earth, especially in a milking shed. Failure of the connection causes electrification of parts of the building. This may cause poor milk letdown, restlessness, convulsions or sudden death depending on the strength of the current and the completeness of the animals’ contact with the floor. See also electrocution, free electricity. rth’werm] the common oligochete worm of the genera Lumbricus, Allobophora, Eisenia, etc.; they act as intermediate or transport hosts for a number of internal parasites of livestock, and are reputed to bring anthrax spores to the surface and precipitate an outbreak of the disease.
rth’werm] the common oligochete worm of the genera Lumbricus, Allobophora, Eisenia, etc.; they act as intermediate or transport hosts for a number of internal parasites of livestock, and are reputed to bring anthrax spores to the surface and precipitate an outbreak of the disease.
 r-na’sh
r-na’sh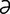 n] formation of smooth, dense bone surfaces in false joints, or joints whose articular cartilage has been destroyed.
n] formation of smooth, dense bone surfaces in false joints, or joints whose articular cartilage has been destroyed.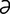 , ek″on-dro′sis] a hyperplastic growth of cartilaginous tissue on the surface of a cartilage or projecting under the periosteum of a bone.
, ek″on-dro′sis] a hyperplastic growth of cartilaginous tissue on the surface of a cartilage or projecting under the periosteum of a bone.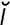 -mo’sis] pl. ecchymoses [Gr.] a hemorrhagic spot, larger than a petechia, in the skin or mucous membrane, forming a nonelevated, rounded or irregular, blue or purplish patch.
-mo’sis] pl. ecchymoses [Gr.] a hemorrhagic spot, larger than a petechia, in the skin or mucous membrane, forming a nonelevated, rounded or irregular, blue or purplish patch.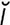 -sis] shedding of the external layers of the skin-only the epidermis participates. Is controlled by the endocrine glands. May be complete or incomplete due usually to poor nutrition. Called also exuviate. See also dysecdysis.
-sis] shedding of the external layers of the skin-only the epidermis participates. Is controlled by the endocrine glands. May be complete or incomplete due usually to poor nutrition. Called also exuviate. See also dysecdysis.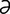 ] a small (up to 15 lb) monotreme, covered in coarse hair and sharp spines. The short-beaked echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus) is found in Australia and New Guinea and the long-beaked echidna (Zaglossus bruijni) only in New Guinea. These two species, in the Family Tachyglossidae, are the only members of their genera. They have no teeth, but use their sticky tongue for feeding on ants and termites; their pectoral girdle has two additional bones; the males have prominent hindlimb spurs and the male’s glans is divided into four heads, each with a branch of the urethra. As monotremes, the female lays her egg directly into a shallow abdominal pouch and feeds her young with milk expressed directly onto the skin of the pouch. The young are called puggles. Called also spiny anteater.
] a small (up to 15 lb) monotreme, covered in coarse hair and sharp spines. The short-beaked echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus) is found in Australia and New Guinea and the long-beaked echidna (Zaglossus bruijni) only in New Guinea. These two species, in the Family Tachyglossidae, are the only members of their genera. They have no teeth, but use their sticky tongue for feeding on ants and termites; their pectoral girdle has two additional bones; the males have prominent hindlimb spurs and the male’s glans is divided into four heads, each with a branch of the urethra. As monotremes, the female lays her egg directly into a shallow abdominal pouch and feeds her young with milk expressed directly onto the skin of the pouch. The young are called puggles. Called also spiny anteater.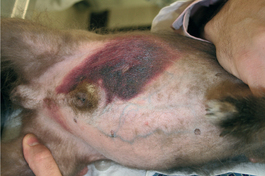

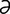 -g
-g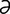 ] a genus of fleas that remain attached to the host for long periods. Includes E. myrmecobii (in rabbits) and E. perilis (in rats).
] a genus of fleas that remain attached to the host for long periods. Includes E. myrmecobii (in rabbits) and E. perilis (in rats).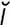 -na’sh
-na’sh ] a genus of plants in the family Astraceae; source of the popular herbal product echinacea, used mainly as a stimulant of the immune system.
] a genus of plants in the family Astraceae; source of the popular herbal product echinacea, used mainly as a stimulant of the immune system. s] a genus of flukes of the family Echinostomatidae. Includes E. perfoliatus in intestines of carnivores.
s] a genus of flukes of the family Echinostomatidae. Includes E. perfoliatus in intestines of carnivores.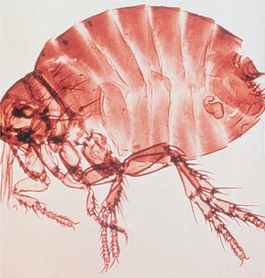
 ps] the spiny rat mite, transmitter of Hepatozoon spp., the protozoan blood parasite. A mite of the Gamasidae family. Called also laelapid mite.
ps] the spiny rat mite, transmitter of Hepatozoon spp., the protozoan blood parasite. A mite of the Gamasidae family. Called also laelapid mite. s] acanthocephalan parasite of freshwater and marine fish. Found in the intestine of salmonids.
s] acanthocephalan parasite of freshwater and marine fish. Found in the intestine of salmonids. -nos’to-m
-nos’to-m ] a genus of flukes in the family Echinostomatidae. Includes, besides those listed below, E. aphylactum, E. caproni, E. hortense, E. jassyenese, E. lindoensis and E. suinum.
] a genus of flukes in the family Echinostomatidae. Includes, besides those listed below, E. aphylactum, E. caproni, E. hortense, E. jassyenese, E. lindoensis and E. suinum. -fe] recording of the position and motion of the heart walls or internal structures of the heart and neighboring tissue by the echo obtained from beams of ultrasonic waves directed through the chest wall. Echocardiography is based on the same principle as the oceanographic technique of depth-sounding; that is, it utilizes ultrasound to delineate anatomical structures by recording on a graph the echoes from the heart structures. It is particularly useful in demonstrating, without danger to the patient, valvular and other structural deformities of the heart which formerly required cardiac catheterization or some other elaborate procedure for accurate diagnosis. See also ultrasonography.
-fe] recording of the position and motion of the heart walls or internal structures of the heart and neighboring tissue by the echo obtained from beams of ultrasonic waves directed through the chest wall. Echocardiography is based on the same principle as the oceanographic technique of depth-sounding; that is, it utilizes ultrasound to delineate anatomical structures by recording on a graph the echoes from the heart structures. It is particularly useful in demonstrating, without danger to the patient, valvular and other structural deformities of the heart which formerly required cardiac catheterization or some other elaborate procedure for accurate diagnosis. See also ultrasonography. -log’r
-log’r -fe] a diagnostic technique in which pulses of ultrasonic waves are beamed through the head from both sides, and echoes from the midline structures of the brain are recorded graphically; shifts from any midline may indicate a centrally placed mass.
-fe] a diagnostic technique in which pulses of ultrasonic waves are beamed through the head from both sides, and echoes from the midline structures of the brain are recorded graphically; shifts from any midline may indicate a centrally placed mass. -te] the characteristic ability of a tissue or substance to reflect sound waves and produce echoes. Bone and gas are most echogenic and fluids such as urine and bile the least. Organ parenchyma and soft tissues are intermediate, but each differs slightly from the other and relative characteristics are known.
-te] the characteristic ability of a tissue or substance to reflect sound waves and produce echoes. Bone and gas are most echogenic and fluids such as urine and bile the least. Organ parenchyma and soft tissues are intermediate, but each differs slightly from the other and relative characteristics are known. -kog’r
-kog’r -fe] ultrasonography; the use of ultrasound as a diagnostic aid. Ultrasound waves are directed at the tissues, and a record is made, as on an oscilloscope, of the waves reflected back through the tissues, which indicate interfaces of different acoustic densities and thus differentiate between solid and cystic structures.
-fe] ultrasonography; the use of ultrasound as a diagnostic aid. Ultrasound waves are directed at the tissues, and a record is made, as on an oscilloscope, of the waves reflected back through the tissues, which indicate interfaces of different acoustic densities and thus differentiate between solid and cystic structures. n] producing, receiving and interpreting ultra-high frequency sound waves for navigation or location of prey. Used by bats and toothed whales. Called also biosonar.
n] producing, receiving and interpreting ultra-high frequency sound waves for navigation or location of prey. Used by bats and toothed whales. Called also biosonar. nt] permitting the passage of ultrasonic waves without giving rise to echoes, the representative areas appearing black on the sonogram.
nt] permitting the passage of ultrasonic waves without giving rise to echoes, the representative areas appearing black on the sonogram. -fe] the combined use of echocardiography and phonocardiography.
-fe] the combined use of echocardiography and phonocardiography. s] some viruses, which were originally considered nonpathogenic, in the family Picornaviridae, genus Enterovirus. The name is derived from the first letters of the description ‘enteric cytopathogenic human orphan’, but similar viruses ECBO and ECPO (for bovine and porcine, respectively, and other species) are also recognized. At the time of the isolation of the viruses the diseases they caused were not known, hence the term ‘orphan’, but it is now known that some of these viruses produce many different types of human disease, especially aseptic meningitis, and diarrhea and various respiratory diseases. The members of the group are now included in the enteroviruses.
s] some viruses, which were originally considered nonpathogenic, in the family Picornaviridae, genus Enterovirus. The name is derived from the first letters of the description ‘enteric cytopathogenic human orphan’, but similar viruses ECBO and ECPO (for bovine and porcine, respectively, and other species) are also recognized. At the time of the isolation of the viruses the diseases they caused were not known, hence the term ‘orphan’, but it is now known that some of these viruses produce many different types of human disease, especially aseptic meningitis, and diarrhea and various respiratory diseases. The members of the group are now included in the enteroviruses. -klamp’se-
-klamp’se-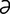 ] a syndrome including convulsions and coma occurring in animals soon after birth of the young; nonspecific because the etiology and clinical features vary depending on which species is involved.
] a syndrome including convulsions and coma occurring in animals soon after birth of the young; nonspecific because the etiology and clinical features vary depending on which species is involved.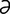 -je] the science of organisms as affected by environmental factors; the study of the environment and the life history of organisms.
-je] the science of organisms as affected by environmental factors; the study of the environment and the life history of organisms.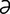 -kon’
-kon’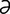 -zōl] an imidazole antifungal agent related to miconazole; used topically in the treatment of fungal infections of the skin.
-zōl] an imidazole antifungal agent related to miconazole; used topically in the treatment of fungal infections of the skin. m] the fundamental unit in ecology, comprising the living organisms and the nonliving elements interacting in a certain defined area. In more sophisticated terms, a biotic community living in its biotope.
m] the fundamental unit in ecology, comprising the living organisms and the nonliving elements interacting in a certain defined area. In more sophisticated terms, a biotic community living in its biotope. -j
-j n] 1. an antigen that seems to be loosely attached to the outside of bacteria. 2. an antigen formed in the ectoplasm (cell membrane) of a bacterium.
n] 1. an antigen that seems to be loosely attached to the outside of bacteria. 2. an antigen formed in the ectoplasm (cell membrane) of a bacterium.
 rm] the outermost of the three primitive germ layers of the embryo; from it are derived the epidermis and epidermal derivatives, such as the claws, hair and glands of the skin, the nervous system, external sense organs (eye, ear, etc.) and mucous membrane of the mouth and anus.
rm] the outermost of the three primitive germ layers of the embryo; from it are derived the epidermis and epidermal derivatives, such as the claws, hair and glands of the skin, the nervous system, external sense organs (eye, ear, etc.) and mucous membrane of the mouth and anus. r-mo’sis] a disorder based on congenital maldevelopment of organs derived from the ectoderm.
r-mo’sis] a disorder based on congenital maldevelopment of organs derived from the ectoderm. -si-tiz-
-si-tiz- m] the state in which the ectoparasite is living on the surface of the host’s body.
m] the state in which the ectoparasite is living on the surface of the host’s body. -sen’t
-sen’t l] a syncytial body formed in the murine trophoblast; an essential component of the nidation process in this species.
l] a syncytial body formed in the murine trophoblast; an essential component of the nidation process in this species. m] an old-fashioned term which referred to a peripheral band of gel-like cytoplasm, free of organelles, found in free and motile cells.
m] an old-fashioned term which referred to a peripheral band of gel-like cytoplasm, free of organelles, found in free and motile cells. -nāts] papyraceous bones in the nasal cavity which are interleaved with endoturbinates.
-nāts] papyraceous bones in the nasal cavity which are interleaved with endoturbinates. ] inherited, congenital skeletal defect in pups and kittens; there is incomplete fusion of the three rays that develop from the forelimb bud in the embryo; the paw is split up the middle as far as the metacarpals or to the carpus in some. Typically, the third metacarpal and digit are missing. Called also split-hand or lobster claw deformity.
] inherited, congenital skeletal defect in pups and kittens; there is incomplete fusion of the three rays that develop from the forelimb bud in the embryo; the paw is split up the middle as far as the metacarpals or to the carpus in some. Typically, the third metacarpal and digit are missing. Called also split-hand or lobster claw deformity. ] 1. gross hypoplasia or aplasia of one or more long bones of one or more limbs. 2. a generalized poxvirus disease of mice resembling smallpox in humans. Used in studies as a model of generalized virus infections.
] 1. gross hypoplasia or aplasia of one or more long bones of one or more limbs. 2. a generalized poxvirus disease of mice resembling smallpox in humans. Used in studies as a model of generalized virus infections. -m
-m ] 1. a general term for any superficial inflammatory process involving primarily the epidermis, marked early by redness, itching, minute papules and vesicles, weeping, oozing and crusting, and later by scaling, lichenification and often pigmentation. 2. atopic dermatitis.
] 1. a general term for any superficial inflammatory process involving primarily the epidermis, marked early by redness, itching, minute papules and vesicles, weeping, oozing and crusting, and later by scaling, lichenification and often pigmentation. 2. atopic dermatitis.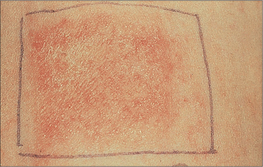
 -de’m
-de’m ] an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the cavities and intercellular spaces of the body. Edema is due to diminished capacity of small blood vessels to retain water and solutes within their lumens. This in turn is caused by three factors acting singly or in combination: (1) decreased colloid osmotic pressure within blood vessels, usually due to hypoproteinemia; (2) decreased hydrostatic pressure differential between arterial and venous ends of blood capillaries (seen in heart failure or restricted venous or lymphatic drainage); and (3) increased capillary permability caused by inflammation or other endothelial disturbance. See also anasarca, ascites, hydrothorax, hydropericardium and anatomically located edemas, e.g. brain, corneal, pulmonary edema.
] an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the cavities and intercellular spaces of the body. Edema is due to diminished capacity of small blood vessels to retain water and solutes within their lumens. This in turn is caused by three factors acting singly or in combination: (1) decreased colloid osmotic pressure within blood vessels, usually due to hypoproteinemia; (2) decreased hydrostatic pressure differential between arterial and venous ends of blood capillaries (seen in heart failure or restricted venous or lymphatic drainage); and (3) increased capillary permability caused by inflammation or other endothelial disturbance. See also anasarca, ascites, hydrothorax, hydropericardium and anatomically located edemas, e.g. brain, corneal, pulmonary edema. -de’m
-de’m -jen] an irritant that elicits edema by causing capillary damage but not the cellular response of true inflammation.
-jen] an irritant that elicits edema by causing capillary damage but not the cellular response of true inflammation. -tāt] any salt of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), including edetate disodium calcium, used in the diagnosis and treatment of lead poisoning, and edetate disodium, used in the treatment of poisoning with lead and other heavy metals, and, because of its affinity for calcium, in the treatment of hypercalcemia. Also commonly used as anticoagulants for blood samples collected for laboratory analysis, particularly hematology.
-tāt] any salt of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), including edetate disodium calcium, used in the diagnosis and treatment of lead poisoning, and edetate disodium, used in the treatment of poisoning with lead and other heavy metals, and, because of its affinity for calcium, in the treatment of hypercalcemia. Also commonly used as anticoagulants for blood samples collected for laboratory analysis, particularly hematology. m] a cholinergic used in the form of the chloride salt as a curare antagonist; used in the edrophonium challenge test to diagnose myasthenia gravis. See also Tensilon.
m] a cholinergic used in the form of the chloride salt as a curare antagonist; used in the edrophonium challenge test to diagnose myasthenia gravis. See also Tensilon.
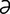 ] a genus of bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Inhabits the intestines of snakes; found also in water.
] a genus of bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Inhabits the intestines of snakes; found also in water. -fās’m
-fās’m nt] the obliteration of form or features; applied to the cervix uteri during labor when it is so changed that only the ostium uteri remains.
nt] the obliteration of form or features; applied to the cervix uteri during labor when it is so changed that only the ostium uteri remains. -fekt’] a result produced by an action. The relationship between the two can be expressed in linear form. The total association between them may be the sum of a number of effects. The effect may be direct when it is exerted without being transmitted through intervening factors, or indirect when it is. It may also be a spurious effect when the observed changes are due to causes and correlations common to both.
-fekt’] a result produced by an action. The relationship between the two can be expressed in linear form. The total association between them may be the sum of a number of effects. The effect may be direct when it is exerted without being transmitted through intervening factors, or indirect when it is. It may also be a spurious effect when the observed changes are due to causes and correlations common to both. -fek’tiv-nis] the ability to produce a specific result or to exert a specific measurable influence.
-fek’tiv-nis] the ability to produce a specific result or to exert a specific measurable influence. -fek’t
-fek’t r] 1. a muscle or gland that contracts or secretes, respectively, in direct response to nerve impulses. 2. a molecule that binds to an enzyme with an effect on its catalytic activity, i.e. either an activator or inhibitor.
r] 1. a muscle or gland that contracts or secretes, respectively, in direct response to nerve impulses. 2. a molecule that binds to an enzyme with an effect on its catalytic activity, i.e. either an activator or inhibitor. r-
r- nt] conducting or progressing away from a center or specific site of reference, as an efferent nerve.
nt] conducting or progressing away from a center or specific site of reference, as an efferent nerve. –fish’
–fish’ n-se] 1. in clinical practice equals the effect achieved in relation to the expenditure and effort expended. 2. In physiological terms, efficiency of any organ or tissue is equal to the ratio of useful energy produced to total energy expended.
n-se] 1. in clinical practice equals the effect achieved in relation to the expenditure and effort expended. 2. In physiological terms, efficiency of any organ or tissue is equal to the ratio of useful energy produced to total energy expended.
 -rahzh’] [Fr.] stroking movement in massage, intended to encourage venous and lymphatic return.
-rahzh’] [Fr.] stroking movement in massage, intended to encourage venous and lymphatic return. nt] waste from an abattoir carried away in liquid form. Disposal is a major problem because of the need to avoid pollution of waterways. See aerobic effluent treatment, anaerobic effluent treatment.
nt] waste from an abattoir carried away in liquid form. Disposal is a major problem because of the need to avoid pollution of waterways. See aerobic effluent treatment, anaerobic effluent treatment. –floo’ve-
–floo’ve- m] pl. effluvia [L.] 1. an outflowing or shedding, as of the hair. 2. an exhalation or emanation, especially one of noxious nature.
m] pl. effluvia [L.] 1. an outflowing or shedding, as of the hair. 2. an exhalation or emanation, especially one of noxious nature. -fu’zh
-fu’zh n] 1. escape of a fluid into a part; exudation or transudation. See also specific anatomic sites. 2. an exudate or transudate.
n] 1. escape of a fluid into a part; exudation or transudation. See also specific anatomic sites. 2. an exudate or transudate. -thēn″] an antiprotozoal agent, used as the hydrochloride in trypanosomiasis and Pneumocystiscarinii pneumonia.
-thēn″] an antiprotozoal agent, used as the hydrochloride in trypanosomiasis and Pneumocystiscarinii pneumonia.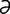 ft] the terrestrial juvenile stage of newts, following metamorphosis from tadpoles and before adulthood.
ft] the terrestrial juvenile stage of newts, following metamorphosis from tadpoles and before adulthood.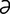 n] the casting out of undigested material, as in birds that eject from the gizzard.
n] the casting out of undigested material, as in birds that eject from the gizzard.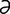 rz] slotted contact plate for orthopedic use in stainless steel or vitallium. Fitted with matching screws.
rz] slotted contact plate for orthopedic use in stainless steel or vitallium. Fitted with matching screws.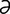 rz dahn-los’] a congenital hereditary syndrome of joint hyperextensibility, hyperelasticity and fragility of the skin, poor wound healing leaving parchment-like scars, capillary fragility and subcutaneous nodules after trauma. Called also cutis hyperelastica, cutaneous asthenia, hereditary collagen dysplasia. In humans a series of these disorders, listed as Ehlers–Danlos syndrome Type I to Type VII, represent different errors in collagen synthesis and maintenance with subsequent variations in clinical and pathological manifestations.
rz dahn-los’] a congenital hereditary syndrome of joint hyperextensibility, hyperelasticity and fragility of the skin, poor wound healing leaving parchment-like scars, capillary fragility and subcutaneous nodules after trauma. Called also cutis hyperelastica, cutaneous asthenia, hereditary collagen dysplasia. In humans a series of these disorders, listed as Ehlers–Danlos syndrome Type I to Type VII, represent different errors in collagen synthesis and maintenance with subsequent variations in clinical and pathological manifestations.


