Chapter 32 Diseases of the Parathyroid Gland and Calcium Metabolism
NORMAL CALCIUM METABOLISM
Distribution of Calcium
Regulation of Calcium
Vitamin D Metabolites
The cholecalciferol (vitamin D3 of animal origin) metabolites 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (calcidiol) and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 (calcitriol) are the most important vitamin D metabolites. These metabolites may also be derived from ergocalciferol (vitamin D2 of plant origin), and are equally bioactive. Dogs and cats inefficiently photosynthesize vitamin D in their skin and consequently are dependent on vitamin D in their diet. Hydroxylation of vitamin D occurs in the liver to produce 25-hydroxyvitamin D. This 25-hydroxyvitamin D is further hydroxylated in the proximal tubule of the kidney to form calcitriol.
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS OF CALCIUM
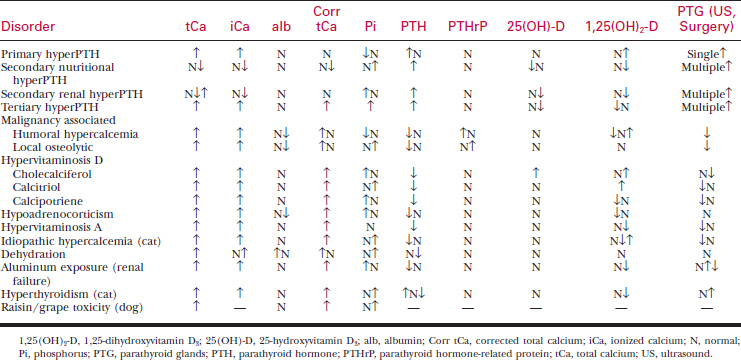
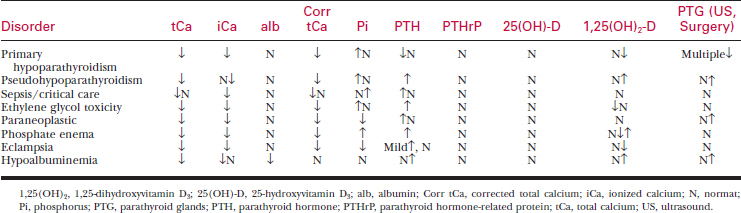
Measurement of total calcium, ionized calcium, and hormones of calcium metabolism aid in the diagnosis of calcium disorders (see Tables 32-1 and 32-2).
Ionized Calcium Concentration
Vitamin D Metabolites
HYPERCALCEMIA
Defining Criteria
Etiology
See Table 32-3 for a list of hypercalcemia-related conditions.
Table 32-3 CONDITIONS ASSOCIATED WITH HYPERCALCEMIA
Pathologic Conditions
Parathyroid-dependent hypercalcemia
Parathyroid-independent hypercalcemia
Malignancy-associated hypercalcemia
Adenocarcinoma of the apocrine glands of the anal sac
Cholecalciferol (rodenticide) toxicity
Iatrogenic due to dietary supplementation
Houseplants (Cestrum diurnum, Solanum malacoxylon, Trisetum flavescens)
Granulomatous disease (blastomycosis, schistosomiasis)
Bone lesions (sepsis, disuse osteoporosis)
Clinical Signs
Diagnosis
Radiography and Ultrasound
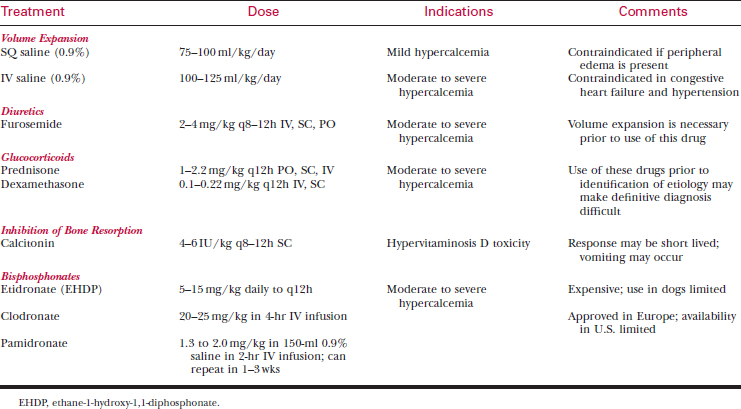
Principles of Treating Hypercalcemia
Unfortunately, the etiology may not be apparent, and supportive measures must be taken to decrease the serum calcium concentration (see Table 32-4 for specific drugs and dosage recommendations). Supportive measures may include the following.
Loop Diuretics
Glucocorticoids
Bisphosphonates (Diphosphonates)
These compounds inhibit osteoclastic bone resorption.
CONDITIONS ASSOCIATED WITH
For a complete list of conditions associated with hypercalcemia, see Table 32-3.