Chapter 90 Diseases of the Ovaries and Uterus
DISEASES OF THE OVARIES
Disorders of the Ovarian Cycle
Etiology
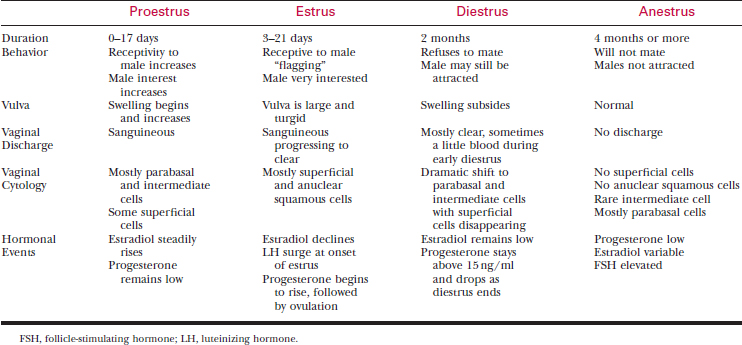
Disorders of the ovarian cycle are seen when ovarian secretion of estrogen and/or progesterone are abnormal. Hormonal abnormalities can be associated with cystic ovarian disease, ovarian dysgenesis, ovarian neoplasia, ovarian remnants, and secondary conditions that affect ovarian function. Ovarian cycle abnormalities usually manifest as abnormalities in reproductive events. The hormonal, physiologic, cytologic, and behavioral events of the normal estrus cycle are presented in Table 90-1.
Clinical Signs
Failure to Cycle or Persistent Anestrus
Short Interestrous Intervals
Prolonged Estrus
Diagnosis
Physical Examination
Examine the vulva to determine degrees of swelling and types of discharge that suggest various stages of the estrous cycle (see Table 90-1).
Vaginal Cytology Technique
Hormonal Analysis
Estradiol
Progesterone
Treatment
Failure to Cycle or Persistent Anestrus
Prolonged Estrus
Ovarian Remnant Syndrome
Etiology
Clinical Signs
Clinical signs of estrus typically reoccur between 1 and 3 years following ovariohysterectomy.
Diagnosis
Ovarian Neoplasia
Etiology
Clinical Signs
Diagnosis
DISEASES OF THE NON-PREGNANT UTERUS
Pyometra
Etiology
Risk Factors for Pyometra
Clinical Signs
Diagnosis
History and Physical Examination
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree