D
2,4-D see 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid.
d symbol, deci-; 2′-deoxyribo.
Δ delta, capital; fourth letter in the Greek alphabet. A symbol for increment.
δ delta, small letter; fourth letter in the Greek alphabet.
D gene segment see diversity gene.
dacryagogue 1. an agent that induces a flow of tears. 2. a lacrimal duct.
dacry(o)- word element. [Gr.] tears or the lacrimal apparatus of the eye.
dacryoadenalgia [dak”re-o-ad” –nal’j
–nal’j ] pain in a lacrimal gland.
] pain in a lacrimal gland.
dacryoadenectomy [dak”re-o-ad” –nek’t
–nek’t –me] excision of a lacrimal gland.
–me] excision of a lacrimal gland.
dacryoadenitis [dak”re-o-ad”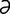 –ni’tis] inflammation of a lacrimal gland.
–ni’tis] inflammation of a lacrimal gland.
dacryoblennorrhea [dak”re-o-blen”o-re’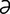 ] mucoid discharge emanating from the lacrimal apparatus.
] mucoid discharge emanating from the lacrimal apparatus.
dacryocele [dak’re-o-sēl”] see dacryocystocele.
dacryocyst [dak’re-o-sist”] see lacrimal sac.
dacryocystalgia [dak”re-o-sis-tal’j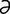 ] pain in the lacrimal sac.
] pain in the lacrimal sac.
dacryocystectomy [dak”re-o-sis-tek’t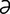 –me] excision of the lacrimal sac.
–me] excision of the lacrimal sac.
dacryocystitis, dacrocystitis [dak”re-o-sis-ti’tis] inflammation of the lacrimal sac.
dacryocystocele [dak”re-o-sis’to-sēl] hernial protrusion of the lacrimal sac; dacryocele.
dacryocystoptosis [dak”re-o-sis”top-to’sis] prolapse of the lacrimal sac.
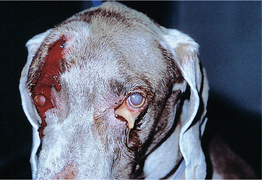
D-1: Severe dacryocystitis with multifocal cutaneous draining tracts in a Weimaraner.
Dziezyc J, Millchamp N, Color Atlas of Canine and Feline Ophthalmology. Saunders, 2005
dacryocystorhinostenosis [dak”re-o-sis”to-ri”no-st –no’sis] narrowing of the nasolacrimal duct.
–no’sis] narrowing of the nasolacrimal duct.
dacryocystostenosis [dak”re-o-sis”to-st –no’sis] narrowing of the lacrimal sac.
–no’sis] narrowing of the lacrimal sac.
dacryocystotomy [dak”re-o-sis-tot’ –me] incision of the lacrimal sac.
–me] incision of the lacrimal sac.
dacryohemorrhea [dak”re-o-hem”o-re’ ] the discharge of tears mixed with blood.
] the discharge of tears mixed with blood.
dacryolith [dak’re-o-lith”] a lacrimal calculus.
dacryolithiasis [dak”re-o-l –thi’
–thi’ –sis] the presence of dacryoliths.
–sis] the presence of dacryoliths.
dacryoma [dak”re-o’m ] a tumor-like swelling due to obstruction of the lacrimal duct.
] a tumor-like swelling due to obstruction of the lacrimal duct.
dacryon [dak’re-on] the point where the lacrimal, frontal and maxillary bones meet.
dacryops [dak’re-ops] distention of the lacrimal duct with fluid. Compare with canaliculops.
dacryopyorrhea [dak”re-o-pi”o-re’ ] the discharge of tears mixed with pus.
] the discharge of tears mixed with pus.
dacryorrhea [dak”re-o-re’ ] excessive flow of tears.
] excessive flow of tears.
dacryoscintigraphy [dak”re-o-sin-tig’r –fe] scintigraphy of the lacrimal ducts.
–fe] scintigraphy of the lacrimal ducts.
dacryosolenitis [dak”re-o”so-l –ni’tis] inflammation of a lacrimal duct.
–ni’tis] inflammation of a lacrimal duct.
dacryostenosis [dak”re-o-st –no’sis] stricture or narrowing of a lacrimal duct.
–no’sis] stricture or narrowing of a lacrimal duct.
dactylitis [dak”t –li’tis] inflammation of a digit.
–li’tis] inflammation of a digit.
dactyl(o)- word element. [Gr.] a digit.
dactylogryposis [dak”t –lo-gr
–lo-gr –po’sis] permanent flexion (contracture) of the digits.
–po’sis] permanent flexion (contracture) of the digits.
dactylomegaly [dak”t –lo-meg’
–lo-meg’ –le] abnormally large digits.
–le] abnormally large digits.
dactylus [dak’t –l
–l s] pl. dactyli [L.] a digit.
s] pl. dactyli [L.] a digit.
daddy-long-legs Pholcus phalangioides; see harvestmen.
DAF decay-accelerating factor.
daffodil [daf’ –dil] see Narcissus.
–dil] see Narcissus.
d. tree Cascabela thevetia (Thevetia peruviana).
daft lamb see cerebellar atrophy.
dags locks or staples of wool in the crutch that are heavily fouled with caked feces.
daidzein an estrogenic plant isoflavone.
d. calf calf of a mating between a bull and a cow, both of dairy breeds.
d. farmer a farmer whose major enterprise is dairy farming.
Dairy shorthorn the dairy variety of the Shorthorn breed of cattle. Called also Milking shorthorn.
dairyCOMP 305 an on-farm computer program devised to participate in dairy herd health management.
dairying 1. the occupation of being a dairy farmer. 2. the practice of running a dairy farm.
seasonal d. breeding the herd as a block so as to have the herd calve when feed supplies are good.
African d. Senecio pterophorus.
plains plover-d. Leiocarpa brevicompta.
South African d. Osteospermum.
sunflower d. Wedelia asperrima.
tufted burr d. Calotis scapigera.
wild everlasting d. Helichrysum argyrosphaerum.
woolly everlasting d. Argentipallium blandowskianum.
DALA delta-amino levulinic acid.
dalfopristin [dal-fo’pris-tin] see quinopristin/dalfopristin.
Dall sheep Ovis dalli; a medium-sized wild sheep.
Dallas grass Paspalum dilatatum.
Dalmatian insect powder see pyrethrum.
Dalmeny disease see sarcocystosis.
d. line characteristics contributed to the offspring of a cross mating by the dam.
dam-family average the average performance of the full-sib family of which the subject is a member.
dancing pigs see congenital tremor syndrome.
dandelion [dan’d –li”
–li” n] see Taraxacum officinale.
n] see Taraxacum officinale.
false d. see Hypochaeris radicata.
dandruff [dan’dr f] excessive scaling from the skin or, in humans, scalp.
f] excessive scaling from the skin or, in humans, scalp.
dandy-brush a grooming brush of stiff whisk fiber.
Danish black pied cattle Danish black and white dairy cattle, originated from Dutch Friesian.
Danish hobbles see Abildgaard method.
Danish red cattle Danish red dairy cattle.
dan’s cabbage Senecio latifolius, S. isatideus.
daphnetin [daf-ne’tin] toxic dihydroxycoumarin glycoside found in Daphne spp.
daphnin [daf’nin] a nontoxic glycoside inDaphne. Called also mezerein.
dark [dark] approaching black; reflecting little light.
d. firm, dry muscle see dark cutting beef.
Darling’s disease [dahr’ling] histoplasmosis.
darmstadtium (Ds) a chemical element, atomic number 110, atomic weight 281. See Table 4.
darnel [dahr’n l] see Lolium temulentum.
l] see Lolium temulentum.
Dartmoor pony English heavy pony, 12.2 hands high, bay, black or brown.
dartoid [dahr’toid] resembling the dartos.
dartos [dahr’tos] the contractile tissue under the skin of the scrotum; called also tunica dartos.
Dasypsyllus gallinulae a species of flea in the order Siphonaptera. It is found on wild birds.
Dasypus novemcinctus see armadillo.
data [da’t ] plural of datum. A collection of information or facts. See also information.
] plural of datum. A collection of information or facts. See also information.
continuous d. data which have an infinite number of possible values.
incidence d. data related to the occurrence of specific disease incidents.
passive d. data acquired from records collected for some other purpose.
raw d. data as they are collected and before any calculation, ordering, etc. has been done.
secondary d. the use of data for purposes other than that for which it was intended.
sentinel d. data collected from sentinel animals or other recording units.
Data source the collecting agency.
Daubentonia the plant genus Sesbania spp.
daunomycin [daw-no-mi’sin] see daunorubicin.
Davainea [da-va’ne- ] a genus of tapeworms of the family Davaineidae.
] a genus of tapeworms of the family Davaineidae.
D. proglottina causes severe enteritis in fowls and other gallinaceous birds.
day blindness see hemeralopia.
DCAD dietary cation-anion difference.
DD dichlorodiphenyldichloroethane, an insecticide; see chlorinated hydrocarbons.
DDT dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane, a powerful insect poison; see chlorinated hydrocarbons.
DDx abbreviation for differential diagnosis; used in medical records.
de- word element. [L.] down from; sometimes negative or privative, and often intensive.
dead [ded] destitute of life. The state of death.
dead man’s fingers Oenanthe crocata.
deafness [def’nis] lack or loss, complete or partial, of the sense of hearing.
cortical d. that due to disease of the cortical centers of the cerebrum.
toxic d. overdosing with aminoglycoside antibiotics causes deafness.
transmission d. conductive hearing loss.
deamidase [de-am’ –dās] an enzyme that splits amides to form a car- boxylic acid and ammonia.
–dās] an enzyme that splits amides to form a car- boxylic acid and ammonia.
deamidization [de-am’’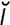 –d
–d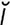 –za’sh
–za’sh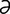 n] liberation of the ammonia from an amide.
n] liberation of the ammonia from an amide.
deamination [de-am“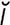 –na’sh
–na’sh n] removal of the amino group, −NH2, from a compound.
n] removal of the amino group, −NH2, from a compound.
d. agony involuntary movements of all parts of the body in the few moments before death.
d. cap a mushroom,Amanita phalloides.
clinical d. the absence of heartbeat and cessation of breathing.
DeBakey [de-ba’ke] pertaining to Michael E. DeBakey (1908–2008), American cardiovascular surgeon.
D. bulldog clamps surgical instruments designed for temporary occlusion of large blood vessels.
debilitation being in a state of debility.
debility [dd-bili-te] lack or loss of strength; weakness.
deboned carcass meat from which the bone has been removed.
débride [da-brēd’] [Fr.] to remove by débridement.
debris [d –bre’] devitalized tissue or foreign matter.
–bre’] devitalized tissue or foreign matter.
decalcify [de-kal’s –fi] to deprive of calcium or its salts.
–fi] to deprive of calcium or its salts.
decamethonium bromide a depolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent.
decannulation [de-kan“u-la’sh n] the removal of a cannula.
n] the removal of a cannula.
decanoate [dek“ –no’āt] a salt of decanoic acid.
–no’āt] a salt of decanoic acid.
decantation [de“kan-ta’sh n] the pouring of a clear supernatant liquid from a sediment.
n] the pouring of a clear supernatant liquid from a sediment.
decapeptide [dek“ –pep’tīd] a polypeptide consisting of a chain of ten amino acids.
–pep’tīd] a polypeptide consisting of a chain of ten amino acids.
decapitation [de-kap“ –ta’sh
–ta’sh n] removal of the head, as of an animal, fetus or bone.
n] removal of the head, as of an animal, fetus or bone.
decapsulation [de-kap“su-la’sh n] removal of a capsule, especially the renal capsule.
n] removal of a capsule, especially the renal capsule.
decarboxylation [de“kahr-bok“s –la’sh
–la’sh n] removal of the carboxyl group from a compound.
n] removal of the carboxyl group from a compound.
decerebration [de-ser“ –bra’sh
–bra’sh n] the act of decerebrating.
n] the act of decerebrating.
decholesterolization [de“k –les“t
–les“t r-ol-
r-ol- –za’sh
–za’sh n] reduction of cholesterol concentrations in the blood.
n] reduction of cholesterol concentrations in the blood.
basal d., decidua basalis that portion on which the implanted ovum rests.
true d. see parietal decidua (above).
d. verra see parietal decidua (above).
d. placenta, deciduate membrane endothelial and hemochorial placenta.
deciduation [d –sid“u-a’sh
–sid“u-a’sh n] the shedding of the decidua.
n] the shedding of the decidua.
deciduitis [d –sid“u-i’tis] a bacterial disease leading to changes in the decidua.
–sid“u-i’tis] a bacterial disease leading to changes in the decidua.
deciduoma [d –sid“u-o’m
–sid“u-o’m ] an intrauterine mass containing decidual cells.
] an intrauterine mass containing decidual cells.
deciduous [d –sid’u-
–sid’u- s] falling off; subject to being shed, as deciduous teeth.
s] falling off; subject to being shed, as deciduous teeth.
decimal scale in homeopathy, the scale of dilution of a remedy. Each dilution is one in ten.
decision a choice between a number of possible answers to a question.
d. theory the theoretical basis for decision analysis.
declivis [de-kli’vis] [L.] declive.
decoloration [de-kul“ r-a’sh
r-a’sh n] 1. removal of color; bleaching. 2. Lack or loss of color.
n] 1. removal of color; bleaching. 2. Lack or loss of color.
decolorizer [de-kul’ r īz“
r īz“ r] an agent that removes color, bleaches.
r] an agent that removes color, bleaches.
decompensation [de-kom“p n-sa’sh
n-sa’sh n] failure of compensation.
n] failure of compensation.
decongestive [de“k n-jes’tiv] reducing congestion.
n-jes’tiv] reducing congestion.
decrudescence [de“kroo-des’ ns] diminution or abatement of the intensity of clinical signs.
ns] diminution or abatement of the intensity of clinical signs.
ventral d. lying on the stomach.
decussate [de-kus’āt] to cross especially in the form of X.
decussatio nervorum trochlearium [de“k –sa’she-o] the decussation of the trochlear nerve.
–sa’she-o] the decussation of the trochlear nerve.
dedrobenzperidol see droperidol.
dee [de] a metal part shaped like a capital D and used in harness to make a T junction.
deer [dēr] ruminants in the Cervidae family; see also elk, reindeer, wapitii, moose and muntjac.
d. herpesvirus (DHV) the pathogenicity is unknown.
d. tick fever 1. Lyme disease. 2. tularemia.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
 –kahr’b
–kahr’b –zēn] an alkylating and antimetabolite, cell-cycle nonspecific antineoplastic agent.
–zēn] an alkylating and antimetabolite, cell-cycle nonspecific antineoplastic agent.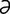 ] mucoid discharge emanating from the lacrimal sac, with constriction of the lacrimal duct.
] mucoid discharge emanating from the lacrimal sac, with constriction of the lacrimal duct. –fe] radiographic imaging of the nasolacrimal apparatus; usually performed before and after injection of an iodinated contrast agent through the lacrimal puncta.
–fe] radiographic imaging of the nasolacrimal apparatus; usually performed before and after injection of an iodinated contrast agent through the lacrimal puncta. –me] surgical creation of an opening between the lacrimal sac and nasal cavity.
–me] surgical creation of an opening between the lacrimal sac and nasal cavity. –me] passage of a probe through the lacrimal sac into the nasal cavity.
–me] passage of a probe through the lacrimal sac into the nasal cavity. –me] surgical creation of a new opening to permit drainage from the lacrimal sac.
–me] surgical creation of a new opening to permit drainage from the lacrimal sac. –no-mi’sin] an antibiotic of the actinomycin complex (actinomycin D), produced by several species of Streptomyces; used as an antineoplastic agent.
–no-mi’sin] an antibiotic of the actinomycin complex (actinomycin D), produced by several species of Streptomyces; used as an antineoplastic agent. l] a digit.
l] a digit. –lār’e-
–lār’e- ] seeOchroconis gallopavum. A thermophilic dematiaceous hyphomycete known to cause encephalitis in chicken and poults. Called also dactylariosis.
] seeOchroconis gallopavum. A thermophilic dematiaceous hyphomycete known to cause encephalitis in chicken and poults. Called also dactylariosis. –lār”e-o’sis] a fungal encephalitis of birds caused by Ochroconis (Dactylaria) gallopavum.
–lār”e-o’sis] a fungal encephalitis of birds caused by Ochroconis (Dactylaria) gallopavum. –lo-ji’r
–lo-ji’r s] a genus of monogenetic flukes of the family Dactylogyridae that infest fish.
s] a genus of monogenetic flukes of the family Dactylogyridae that infest fish. –lol’
–lol’ –sis] 1. surgical correction of syndactyly. 2. loss or amputation of a digit.
–sis] 1. surgical correction of syndactyly. 2. loss or amputation of a digit. –rin] a low molecular weight heparin used in dogs in the treatment of pulmonary thromboembolism.
–rin] a low molecular weight heparin used in dogs in the treatment of pulmonary thromboembolism. n] an arbitrary unit of mass, being one-twelfth the mass of the nuclide of carbon-12, equivalent to 1.657 × 10–24 g. Called also atomic mass unit.
n] an arbitrary unit of mass, being one-twelfth the mass of the nuclide of carbon-12, equivalent to 1.657 × 10–24 g. Called also atomic mass unit. n] the pressure exerted by a mixture of nonreacting gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the separate components.
n] the pressure exerted by a mixture of nonreacting gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of the separate components. –lin’e-
–lin’e- ] a genus of mammal lice of the superfamily Ischnocera. Called also Bovicola. Includes Damalinia bovis (cattle), D. caprae (goats), D. crassiceps (goats), D. equi syn. D. pilosus (horses), D. limbata (Angora goats) and D. ovis (sheep).
] a genus of mammal lice of the superfamily Ischnocera. Called also Bovicola. Includes Damalinia bovis (cattle), D. caprae (goats), D. crassiceps (goats), D. equi syn. D. pilosus (horses), D. limbata (Angora goats) and D. ovis (sheep). –zol] an attenuated androgen that suppresses the ovarian-pituitary axis by inhibiting the release of gonadotropins from the pituitary gland. In animals, it has been used in the treatment of immune-mediated disorders, including anemia and thrombocytopenia.
–zol] an attenuated androgen that suppresses the ovarian-pituitary axis by inhibiting the release of gonadotropins from the pituitary gland. In animals, it has been used in the treatment of immune-mediated disorders, including anemia and thrombocytopenia.
 r] small scales from the hair or feathers of animals, which may be a cause of allergy in sensitive persons.
r] small scales from the hair or feathers of animals, which may be a cause of allergy in sensitive persons. ] a water flea; one of the intermediate hosts of Echinuria uncinata, a roundworm of ducks.
] a water flea; one of the intermediate hosts of Echinuria uncinata, a roundworm of ducks. –tin al’f
–tin al’f ] a synthetic form of erythro- poietin used in humans for the treatment of non-regenerative anemia of chronic kidney disease. It is also subject to abuse as a performance enhancing drug in human athletes and in race horses.
] a synthetic form of erythro- poietin used in humans for the treatment of non-regenerative anemia of chronic kidney disease. It is also subject to abuse as a performance enhancing drug in human athletes and in race horses. m] the theory of evolution according to which higher organisms have been developed from lower ones through the influence of natural selection.
m] the theory of evolution according to which higher organisms have been developed from lower ones through the influence of natural selection.
 ] a genus of toxic plants in the family Solanaceae; contain tropane alkaloids including hyoscine (scopolamine),hyoscyamine, atropine which cause excitement, restlessness, pupillary dilation, dryness of the oral mucosa. Poisoning in animals is rare and usually results from eating crushed seeds. Includes D. candida (Brugmansia, angel’s trumpet), D. ferox (false castor oil plant, thorn apple), D. inoxia, D. leichhardtii, D. metel, D. meteloides, D. sanguinea (Brugmansia sanguinea), D. suaveolens (Brugmansia suaveolens), D. wrightii. D. stramonium is also reported to cause arthrogryposis in piglets when fed to their dams. Fortunately the plant is very unpalatable. Called also devil’s food, devil’s trumpet, false castor oil plant, Jamestown lily, Jamestown weed, jimson weed, mad apple, thorn apple.
] a genus of toxic plants in the family Solanaceae; contain tropane alkaloids including hyoscine (scopolamine),hyoscyamine, atropine which cause excitement, restlessness, pupillary dilation, dryness of the oral mucosa. Poisoning in animals is rare and usually results from eating crushed seeds. Includes D. candida (Brugmansia, angel’s trumpet), D. ferox (false castor oil plant, thorn apple), D. inoxia, D. leichhardtii, D. metel, D. meteloides, D. sanguinea (Brugmansia sanguinea), D. suaveolens (Brugmansia suaveolens), D. wrightii. D. stramonium is also reported to cause arthrogryposis in piglets when fed to their dams. Fortunately the plant is very unpalatable. Called also devil’s food, devil’s trumpet, false castor oil plant, Jamestown lily, Jamestown weed, jimson weed, mad apple, thorn apple. s] plant in the family Apiaceae; excessive consumption has caused hypervitaminosis A in a rabbit. Called also carrot, Queen Anne’s lace, wild carrot.
s] plant in the family Apiaceae; excessive consumption has caused hypervitaminosis A in a rabbit. Called also carrot, Queen Anne’s lace, wild carrot. r] 1. female offspring. 2. arising from cell division, as a daughter cell. 3. product of the decay or radioactive disintegration of a radionuclide. Usually formed as a result of successive transformations in a series. See also decay (3).
r] 1. female offspring. 2. arising from cell division, as a daughter cell. 3. product of the decay or radioactive disintegration of a radionuclide. Usually formed as a result of successive transformations in a series. See also decay (3).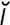 –nās] an enzyme causing deamination, or removal of an amino group from organic compounds, named according to its substrate as adenosine deaminase, cytidine deam- inase, guanine deaminase, etc.
–nās] an enzyme causing deamination, or removal of an amino group from organic compounds, named according to its substrate as adenosine deaminase, cytidine deam- inase, guanine deaminase, etc.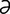 r en’zīm] an enzyme involved in the glycogenolytic process of releasing glucose from glycogen. A deficiency of the enzyme results in accumulation of glycogen in tissues. Both are characteristics of type III glycogen storage diseases.
r en’zīm] an enzyme involved in the glycogenolytic process of releasing glucose from glycogen. A deficiency of the enzyme results in accumulation of glycogen in tissues. Both are characteristics of type III glycogen storage diseases.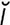 –f
–f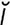 –ka’sh
–ka’sh n] 1. the process of removing calcareous matter. Used in processing of bone samples for histological sections. 2. the loss of calcium salts from bone or teeth.
n] 1. the process of removing calcareous matter. Used in processing of bone samples for histological sections. 2. the loss of calcium salts from bone or teeth. –no’ik] one of the saturated fatty acids found in the endosperm of the coconut (Cocos nucifera), in coconut oil and in other seed oils. Used in diets for patients with fat malabsorption syndromes. Called also n-capric acid.
–no’ik] one of the saturated fatty acids found in the endosperm of the coconut (Cocos nucifera), in coconut oil and in other seed oils. Used in diets for patients with fat malabsorption syndromes. Called also n-capric acid. –lās] any of the lyase class of enzymes that catalyze the removal of a carbon dioxide molecule from a compound.
–lās] any of the lyase class of enzymes that catalyze the removal of a carbon dioxide molecule from a compound. –brāt] to eliminate cerebral function by transecting the brainstem or by ligating the common carotid arteries and basilar artery at the center of the pons; an animal so prepared, or a brain-damaged animal with similar neurological signs.
–brāt] to eliminate cerebral function by transecting the brainstem or by ligating the common carotid arteries and basilar artery at the center of the pons; an animal so prepared, or a brain-damaged animal with similar neurological signs. –b
–b l] a unit used to express the relative intensity and pressure of sound; the ratio of two powers, usually electric or acoustic powers, equal to one-tenth of a bel; one decibel equals approximately the smallest difference in acoustic power the human ear can detect. See also bel.
l] a unit used to express the relative intensity and pressure of sound; the ratio of two powers, usually electric or acoustic powers, equal to one-tenth of a bel; one decibel equals approximately the smallest difference in acoustic power the human ear can detect. See also bel. –sid’u-
–sid’u- ] a name applied to the human and primate endometrium during pregnancy, all of which except for the deepest layer is shed after birth of the young. Called also the decidual, or deciduous, membrane.
] a name applied to the human and primate endometrium during pregnancy, all of which except for the deepest layer is shed after birth of the young. Called also the decidual, or deciduous, membrane. –sid’u-āt, d
–sid’u-āt, d –sid’u-
–sid’u- s, d
s, d –sid’u-
–sid’u-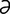 l] characterized by shedding, e.g. teeth, placenta.
l] characterized by shedding, e.g. teeth, placenta. –sid“u-o’sis] the presence of decidual tissue or of tissue resembling the endometrium of human or primate pregnancy in an ectopic site.
–sid“u-o’sis] the presence of decidual tissue or of tissue resembling the endometrium of human or primate pregnancy in an ectopic site. n] seeping of a substance, usually woody stems, barks, berries, rhizomes and root material, in water to obtain its soluble principles and use as a tea for oral administration. See also infusion (1).
n] seeping of a substance, usually woody stems, barks, berries, rhizomes and root material, in water to obtain its soluble principles and use as a tea for oral administration. See also infusion (1). –zish’
–zish’ n] 1. biologically speaking, the separation of compound bodies into their constituent principles; the natural process of biodegradation of animal and plant materials. Its occurrence in human and animal foods is a constant threat and preventing it is the prime objective of the food hygienist. 2. statistically speaking, the removal of accountable influences on a set of data so that only variation due to random error remains.
n] 1. biologically speaking, the separation of compound bodies into their constituent principles; the natural process of biodegradation of animal and plant materials. Its occurrence in human and animal foods is a constant threat and preventing it is the prime objective of the food hygienist. 2. statistically speaking, the removal of accountable influences on a set of data so that only variation due to random error remains. n] 1. the return to normal environmental pressure after exposure to greatly increased pressure. 2. the artificial lowering of barometric pressure, e.g. to simulate high altitude.
n] 1. the return to normal environmental pressure after exposure to greatly increased pressure. 2. the artificial lowering of barometric pressure, e.g. to simulate high altitude. n-dish’
n-dish’ n-ing] reversal of the training-induced adaptations, usually for physical activity; loss of fitness.
n-ing] reversal of the training-induced adaptations, usually for physical activity; loss of fitness. n-jes’t
n-jes’t nt)] 1. tending to reduce congestion or swelling. 2. an agent that reduces congestion or swelling, usually of the nasal membranes. Decongestants may be inhaled, administered as spray or nose drops, or used orally in liquid or tablet form. The medication acts by reducing swelling of the nasal membranes and thus opening up the nasal passages. Among the leading medications used as decongestants are epinephrine, ephedrine and phenylephrine. Antihistamines, alone or in combination with decongestants, may also be effective.
nt)] 1. tending to reduce congestion or swelling. 2. an agent that reduces congestion or swelling, usually of the nasal membranes. Decongestants may be inhaled, administered as spray or nose drops, or used orally in liquid or tablet form. The medication acts by reducing swelling of the nasal membranes and thus opening up the nasal passages. Among the leading medications used as decongestants are epinephrine, ephedrine and phenylephrine. Antihistamines, alone or in combination with decongestants, may also be effective. n-tam“
n-tam“ –na’sh
–na’sh n] a step in treatment for toxicosis; includes washing from the body surface, inducing emesis, and administration of activated charcoal and sometimes a cathartic.
n] a step in treatment for toxicosis; includes washing from the body surface, inducing emesis, and administration of activated charcoal and sometimes a cathartic. –rin] a small chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan found in connective tissue and bone, thought to be involved in the organization and mineralization of bone.
–rin] a small chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan found in connective tissue and bone, thought to be involved in the organization and mineralization of bone. –ka’sh
–ka’sh n] 1. removal of the outer covering from a plant, seed or root. 2. removal of portions of the cortical substance of a structure or organ.
n] 1. removal of the outer covering from a plant, seed or root. 2. removal of portions of the cortical substance of a structure or organ. –m
–m nt] the recovery after a fever; the excessive stored heat is dissipated by vasodilatation and sweating, and heat production is reduced by relaxation of muscles. Called also defervescence.
nt] the recovery after a fever; the excessive stored heat is dissipated by vasodilatation and sweating, and heat production is reduced by relaxation of muscles. Called also defervescence. –t
–t l] an ulcer due to local interference with the circulation; called also pressure sore. The ulcer usually occurs over a bony prominence such as that of the sacrum, hip, heel, shoulder or elbow. Excessive or prolonged pressure produced by the weight of the body or limb is the primary cause.
l] an ulcer due to local interference with the circulation; called also pressure sore. The ulcer usually occurs over a bony prominence such as that of the sacrum, hip, heel, shoulder or elbow. Excessive or prolonged pressure produced by the weight of the body or limb is the primary cause. –t
–t s] pl. decubitus. 1. the act of lying down; the position assumed in lying down. 2. a decubitus ulcer.
s] pl. decubitus. 1. the act of lying down; the position assumed in lying down. 2. a decubitus ulcer. –sa’sh
–sa’sh n] a crossing over; the intercrossing of fellow parts or structures especially in the form of an X.
n] a crossing over; the intercrossing of fellow parts or structures especially in the form of an X.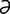 r-en“she-a’sh
r-en“she-a’sh n] regression from a more specialized or complex form to a simpler state.
n] regression from a more specialized or complex form to a simpler state.



