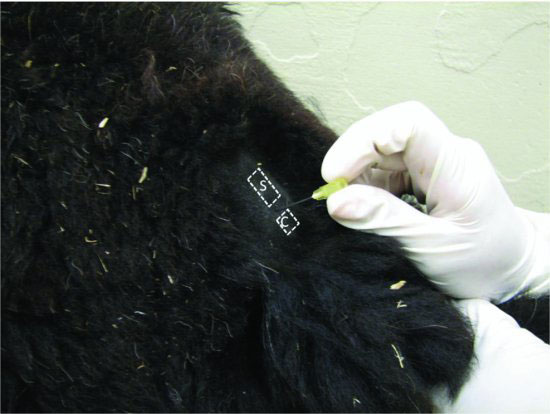
Figure 20.2 The needle is being inserted just caudal to the sacral vertebrae (S) and cranial to the first coccygeal vertebrae (C). Note that the clinician will have to decrease the angle of the needle to advance ventral to the sacral vertebrae into the epidural space.
Practice Tip to Facilitate Procedure
Retain a small air pocket in the syringe with the anesthetic. Note the compression or displacement of air during injection. Lack of resistance during injection is observed when the air pocket does not compress during injection. This indicates that the needle is most likely in the epidural space.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


