Chapter 150 Cardiomyopathy
OVERVIEW
Cardiomyopathies often are classified by the postmortem anatomic appearance of the left (or right) ventricle and by the correlative echocardiographic features of ventricular anatomy and function. The most important forms of cardiomyopathy can be classified as follows (see Table 150-1):
This chapter will next describe the clinical features of feline cardiomyopathies and the therapy of related complications. Following this is a consideration of canine DCM and arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy.
FELINE HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY
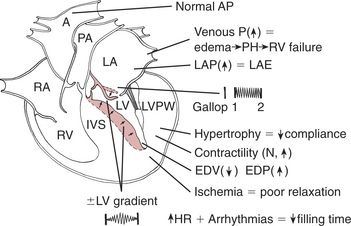
Overview and Pathophysiology of Feline HCM
Table 150-2 DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF FELINE CARDIOMYOPATHY AND HEART FAILURE*
Other Causes of Dyspnea/Tachypnea
Other Causes of Cardiac Murmurs/Gallops/Arrhythmias/Cardiomegaly
Clinical Findings in Feline HCM
The clinical presentation and examination findings in feline HCM are variable.
Diagnostic Tests in HCM
A number of routine diagnostic tests are helpful in recognizing and staging HCM.
There may be generalized involvement with greater involvement of the septal or free wall segments.
FELINE RESTRICTIVE CARDIOMYOPATHY (RCM)
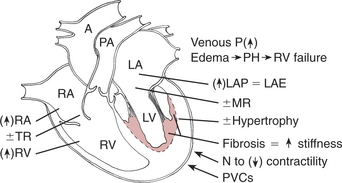
Overview and Pathophysiology of Feline RCM
Clinical Findings in Feline RCM
DILATED CARDIOMYOPATHY IN CATS
OTHER FELINE MYOCARDIAL DISEASES
A number of other diseases that affect the myocardium of the cat are briefly considered below.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree