Fig. 4.1
RT1 genomics
Using serological and histogenetic typing, several haplotypes (combination of alleles in RT1-A and RT1-B/D regions) were defined. The haplotype is marked with upper case letters (a, b, c, d, f, g, h, k, l, m, n, q, s, u or e, i, j, o, or p). Each haplotype is defined with combination of alleles in standard RT1-A regions (a, b, c, d, f, g, h, k, l, m, n, q, s, u) and standard RT1-B/D (a, b, c, d, f, h, k, l, m, n, u). The Nomenclature is explained in Fig. 4.2.
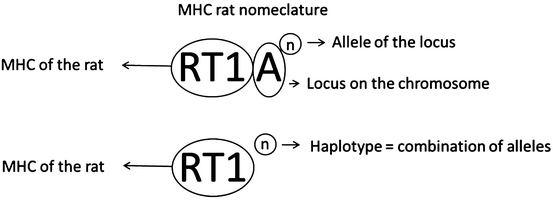

Fig. 4.2
Nomenclature of RT1
RT1-A regions contains class Ia genes, usually 1–3 genes depending on the haplotype. For example, haplotypes RT1 a,k,u contains only one class Ia gene in the RT1-A region, while haplotype c carries 2 genes and haplotype n contains 3 genes in the RT1-a region. Class Ia genes encode the highly polymorphic part of MHC I molecule that are responsible for presentation of antigens to αβ part of T-cell receptor.
RT1-C/E/M region contains several class Ib genes depending on the haplotype. Most of them are responsible for coding of non-polymorphic or monomorphic peptides of MHC antigens .
MHC class II molecules are coded by class II genes in the RT1B/D region. RT1-H genes are orthologous to HLA-DQ genes, RT1-B genes are orthologous to HLA-DP genes and RT1-D genes are orthologous to HLA-DR genes [2].
Class III region includes the heat shock protein gene family, the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family and genes of the complement system. Class III genes present in human HLA class III system are the same as those present in rat class III region.
4.1 Impact of RT1 Haplotypes on Rejection
Allografts fully mismatched in RT1 antigens are usually rejected in an acute manner. However, in some RT1 mismatched rat strains (particularly liver) can be accepted spontaneously for longer time. For example, liver from the DA rat strain can survive spontaneously in PVG rats . Similarly, kidneys from F344 rats transplanted into LEW recipients survive for longer time and this model is often used for studying chronic reject ion changes. F344 differs from LEW in the RT1C region [1]. Histoincompatibility in the RT1C region usually results in long-term acceptance of most of the organ allografts with the exception of skin grafts and pancreas grafts. When strains are different selectively in the RT1A region, transplanted organs are clearly rejected in very short time. Class II molecules are strong histoincompatible antigens and organs transplanted between RT1B/D incompatible RT1A compatible strains survive for short time due to acute rejection . Furthermore, the rejecting response depends on the presentation of donor alloantigens by recipients RT1 molecules. Generally, RT1c strains are considered as low responders with lower production of antibodies and RT1u are considered as high responders to RT1a strains [3].
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


