Atrial Fibrillation
Basic Information 
Epidemiology
Risk Factors
• Underlying cardiovascular pathology leading to:
• Frequent occurrence of atrial premature beats (eg, caused by electrolyte disturbances, structural lesions, viral disease, myocardial stretch [exercise])
• High vagal tone (leads to dispersion in refractoriness of the atrial myocardium)
Clinical Presentation
Disease Forms/Subtypes
History, Chief Complaint
• Obvious signs of performance loss in horses working at maximal speed: Pulling up during race with signs of respiratory distress, ataxia, or even collapse
• Less pronounced signs of decreased performance in jumping and dressage horses or horses working at lower levels
• May be an incidental finding in pleasure horses, breeding horses, or horses at rest
• Signs of heart failure in horses with severe underlying cardiac disease and secondary AF
Etiology and Pathophysiology
 A high trigger burden, that is, a high number of atrial premature beats: induced by stretch (eg, high atrial pressure during exercise), myocardial lesions, or electrolyte disturbances.
A high trigger burden, that is, a high number of atrial premature beats: induced by stretch (eg, high atrial pressure during exercise), myocardial lesions, or electrolyte disturbances. A suitable substrate, that is, the atrial myocardium: large atrial size, high vagal tone, short refractoriness of the myocardium and structural lesions.
A suitable substrate, that is, the atrial myocardium: large atrial size, high vagal tone, short refractoriness of the myocardium and structural lesions. At rest: no impairment of cardiac function (long diastolic time renders ventricular filling sufficient).
At rest: no impairment of cardiac function (long diastolic time renders ventricular filling sufficient). During exercise: impaired cardiac function occurs because of impaired ventricular filling as a result of (1) an absent atrial contractile function and (2) a disproportionate increase in heart rate. Some horses may present with epistaxis because of effects on pulmonary vascular pressures.
During exercise: impaired cardiac function occurs because of impaired ventricular filling as a result of (1) an absent atrial contractile function and (2) a disproportionate increase in heart rate. Some horses may present with epistaxis because of effects on pulmonary vascular pressures.Diagnosis 
Initial Database
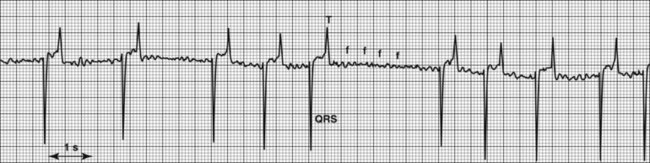
• AF may be strongly suspected on auscultation: an irregularly irregular rhythm, a loud first heart sound, and absence of the atrial sound.
• Final diagnosis is made with an electrocardiogram (ECG) by the typical characteristics (Figures 1 and 2):
• Assess for signs of underlying cardiac disease such as a cardiac murmur, ventral edema, jugular pulsations, and tachycardia.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree