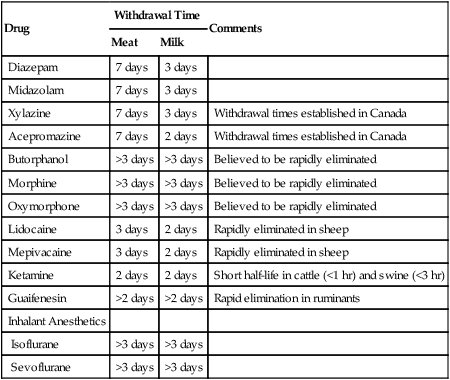
I Preparation of ruminants for anesthesia and surgery A Decrease rumen size and pressure before anesthesia 1. Withhold food for 12 to 18 hours in large ruminants 2. Withhold water for 8 to 12 hours in large ruminants, if possible 3. Withhold food for 12 to 18 hours in sheep and goats; do not withhold water 4. Withhold food for 2 to 4 hours in calves, lambs, and kids; when younger than 1 month of age, they are essentially monogastric and are less prone to regurgitation during anesthesia B Side effects of withholding food are minimal 1. Mild metabolic alkalosis is observed in healthy animals 2. Bradycardia in adult cattle results from increased vagal tone C Orotracheal and rumen tubes should be placed when appropriate to avoid bloat and aspiration of rumen contents II Most surgical techniques in cattle can be performed with local or regional anesthesia (see Chapter 5) III General anesthesia may be required when local or regional anesthetic techniques are inadequate or if dorsal recumbency is required for surgery; inadequate anesthesia predisposes the animal to stress, which may result in tachycardia and hypertension I Preanesthetic drugs are used to calm or sedate ruminants or to decrease the dose of more potent intravenous (IV) or inhalant drugs II Tranquilizers are not approved for use in food animals; drug residues in milk and meat products are problematic. Information about suggested withdrawal times is available from the Food Animal Residue Avoidance & Depletion Program’s Food Animal Residue Avoidance Databank (FARAD) at www.farad.org. (Table 23-1) TABLE 23-1 Approximate Withdrawal Times for Anesthetic Drugs in Ruminants III Preanesthetic medications include (Table 23-2): TABLE 23-2 Drug Dosages Used to Sedate and Tranquilize Ruminants (mg/kg)*
Anesthetic Procedures and Techniques in Ruminants
Overview
General Considerations
Preanesthetic Medication
Drug
Withdrawal Time
Comments
Meat
Milk
Diazepam
7 days
3 days
Midazolam
7 days
3 days
Xylazine
7 days
3 days
Withdrawal times established in Canada
Acepromazine
7 days
2 days
Withdrawal times established in Canada
Butorphanol
>3 days
>3 days
Believed to be rapidly eliminated
Morphine
>3 days
>3 days
Believed to be rapidly eliminated
Oxymorphone
>3 days
>3 days
Believed to be rapidly eliminated
Lidocaine
3 days
2 days
Rapidly eliminated in sheep
Mepivacaine
3 days
2 days
Rapidly eliminated in sheep
Ketamine
2 days
2 days
Short half-life in cattle (<1 hr) and swine (<3 hr)
Guaifenesin
>2 days
>2 days
Rapid elimination in ruminants
Inhalant Anesthetics
Isoflurane
>3 days
>3 days
Sevoflurane
>3 days
>3 days
Drug
Cattle
Calves
Sheep
Goats
IV
IM
IV
IM
IV
IM
IV
IM
Acepromazine
0.03-0.05
0.05-0.1
0.03-0.05
0.05-0.1
0.03-0.05
0.05-0.1
0.03-0.05
0.05-0.1
Diazepam
0.2-0.5
0.5-1.0
0.2-0.5
0.5-1.0
0.2-0.5
0.5-1.0
0.2-0.5
0.5-1.0
Alpha-2 Agonists
Xylazine
0.02-0.1
0.02-0.5
0.02-0.1
0.1-0.2
0.02-0.1
0.1-0.3
0.02-0.1
0.1-0.3
Detomidine
0.01-0.02
0.02-0.05
0.01-0.02
0.03-0.05
0.01-0.02
0.02-0.05
0.01-0.02
0.02-0.05
Medetomidine
0.02-0.05
0.02-0.05
0.01-0.03
0.01-0.03
Alpha-2 Antagonists†
Yohimbine
0.1-0.2
0.1-0.2
0.1-0.5
0.1-0.2
Tolazoline
1.0-2.0
1.0-2.0
1.0-2.0
1.0-2.0
Atipamezole
0.02-0.05
0.02-0.05
0.02-0.05
0.02-0.05
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


